What Is A Warranty On A Car
Alright, let's dive deep into the often-misunderstood world of car warranties. Think of this as understanding the fine print before you need to use it. As someone who gets his hands dirty under the hood, knowing your warranty inside and out can save you a fortune and a whole lot of headaches.
Purpose: Protecting Your Investment (and Your Sanity)
A car warranty is essentially a contract between you and the manufacturer (or a third-party provider) promising to cover specific repairs or replacements for a defined period or mileage. It's not just about repairs; it's about peace of mind. Understanding your warranty helps you:
- Minimize Unexpected Repair Costs: Knowing what's covered allows you to budget appropriately and avoid nasty surprises.
- Make Informed Decisions: When deciding on repairs, you'll know whether to go to a dealer (for warranty work) or an independent mechanic.
- Understand Your Rights: Warranties are legal documents. Knowing your rights empowers you if disputes arise.
- Preserve Resale Value: A car with a transferable warranty can be more appealing to potential buyers.
The purpose of this guide is to provide you with a clear understanding of car warranties, empowering you to navigate the complexities and make informed decisions regarding vehicle maintenance and repairs.
Key Specs and Main Parts of a Warranty
Every warranty is different, but they all share some common elements. Here's a breakdown of the crucial specs and parts you need to understand:
Types of Warranties
- Factory Warranty (aka Bumper-to-Bumper or Comprehensive Warranty): This is the gold standard, covering most mechanical and electrical components of the vehicle for a specified period. It's the most inclusive type of warranty, but always check the exclusions.
- Powertrain Warranty: This covers the powertrain, the core components that make the car move: the engine, transmission, and drivetrain (differential, axles, etc.). It typically lasts longer than the bumper-to-bumper warranty.
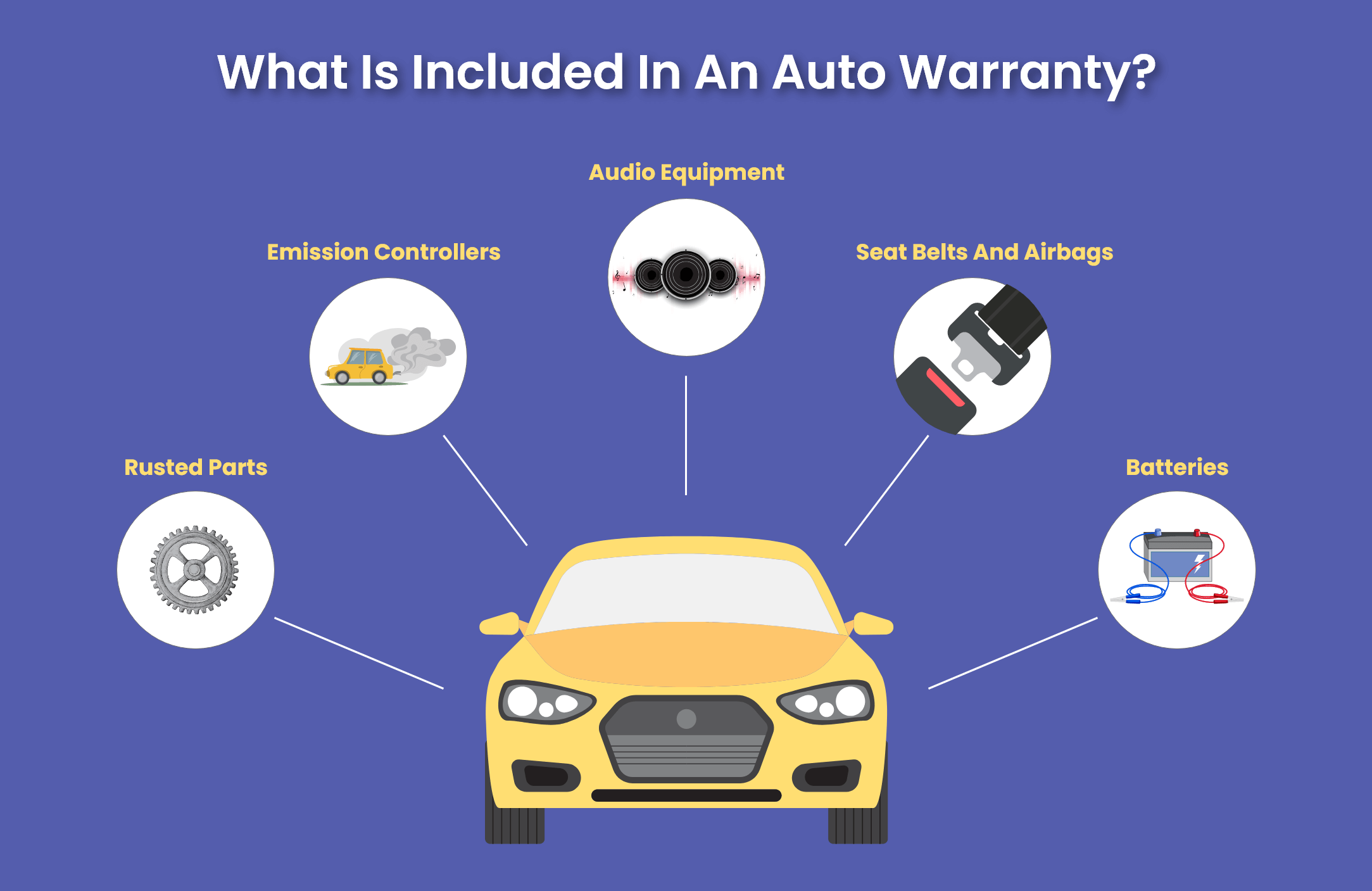
- Corrosion Warranty: Protects against rust and corrosion damage to the body panels. Pay close attention to the specifics – some only cover perforation (rust that goes all the way through the metal).
- Emissions Warranty: Required by law in many areas, this covers components related to emissions control systems. This often includes the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, and the engine control unit (ECU).
- Hybrid/Electric Vehicle (EV) Component Warranty: Covers specific components like the battery pack, electric motors, and related electronic control systems in hybrid and electric vehicles. These often have extended terms.
- Extended Warranty (aka Service Contract): This is an optional warranty you can purchase to extend the coverage beyond the factory warranty period. These are offered by manufacturers and third-party providers. Read these contracts very carefully, as coverage and claim processes can vary widely.
Key Specifications
- Term Length: The duration of the warranty, expressed in years or mileage (e.g., 3 years/36,000 miles). The warranty expires when either the time or mileage limit is reached, whichever comes first.
- Deductible: The amount you pay out-of-pocket for each covered repair. Some warranties have no deductible.
- Coverage: The specific components and repairs covered by the warranty. This is crucial. Always read the fine print!
- Exclusions: The parts and repairs *not* covered by the warranty. Common exclusions include wear-and-tear items (brakes, tires, filters), damage from misuse or neglect, and modifications.
- Transferability: Whether the warranty can be transferred to a new owner if you sell the vehicle. This can significantly increase resale value.
Symbols: Decoding Warranty Language
Warranty documents use specific language that can be confusing. Here's a basic guide to deciphering some common terms:
- "Covered Parts": This section will list the specific components that are protected under the warranty. Look for detailed descriptions of the parts, not just general categories.
- "Exclusions": This is the most important section to review! Pay close attention to what's not covered. Look for phrases like "normal wear and tear," "abuse," "neglect," "modifications," and "environmental damage."
- "Consequential Damage": This refers to damage caused by a covered component's failure to other parts of the vehicle. Some warranties cover consequential damage, while others specifically exclude it.
- "Prior Authorization": Some extended warranties require you to obtain approval from the warranty company before authorizing any repairs.
- "Maintenance Requirements": Many warranties require you to follow the manufacturer's recommended maintenance schedule to keep the warranty valid. Keep detailed records of all maintenance performed.
How It Works: The Warranty Claim Process
Understanding the claim process is essential. Here's a general overview:
- Problem Identification: You experience a mechanical issue with your vehicle.
- Diagnosis: Take your vehicle to a qualified mechanic (often a dealer for factory warranty repairs) for diagnosis. Be sure to authorize only diagnostic work initially.
- Claim Submission (if applicable): If the issue is potentially covered by the warranty, the mechanic will typically submit a claim to the warranty company. For extended warranties, you might need to contact the warranty company yourself.
- Claim Approval/Denial: The warranty company reviews the claim and determines whether the repair is covered under the terms of the warranty. They may send an inspector to verify the damage.
- Repair Authorization: If the claim is approved, the warranty company authorizes the repair.
- Repair Completion: The mechanic performs the repair.
- Payment: The warranty company pays the mechanic for the covered portion of the repair, less any deductible. You are responsible for paying the deductible and any costs not covered by the warranty (e.g., non-covered repairs, shop supplies).
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some troubleshooting tips to help you navigate warranty issues:
- Keep Detailed Records: Maintain meticulous records of all maintenance, repairs, and inspections performed on your vehicle. This is crucial for proving that you've followed the manufacturer's recommendations and haven't neglected the vehicle.
- Know Your Warranty Terms: Before authorizing any repairs, carefully review your warranty documents to understand what's covered and what's not.
- Communicate Clearly: When dealing with mechanics or warranty companies, clearly explain the issue you're experiencing and ask specific questions about coverage.
- Get a Second Opinion: If you're unsure whether a repair is covered or if you disagree with the warranty company's decision, get a second opinion from another qualified mechanic.
- Document Everything: Keep copies of all repair orders, invoices, communications with the warranty company, and any other relevant documentation.
- "Lemon Laws": Be aware of "lemon laws" in your state. These laws provide legal recourse if your vehicle has repeated, unrepairable defects within a certain timeframe.
Safety: Modifications and the Warranty
This is critical for DIY mechanics and modders. Modifying your vehicle can void your warranty, especially if the modification directly causes a component failure. For example:
- Engine Tuning: Installing a performance chip or modifying the engine's software can void the engine warranty.
- Suspension Modifications: Installing a lift kit or lowering springs can void the suspension warranty.
- Exhaust Modifications: Replacing the exhaust system with an aftermarket system can void the emissions warranty and potentially the engine warranty.
The Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act provides some protection, stating that a manufacturer cannot void your warranty simply because you've used aftermarket parts. However, they can deny a claim if they can prove that the aftermarket part or modification caused the failure. It's a legal minefield. If you plan on modifying your car, research the potential impact on your warranty beforehand.
Risky Components to Consider: Any modification affecting the engine, transmission, or drivetrain is high-risk. Exercise extreme caution when modifying these components.
In addition, anything that alters the factory safety components like brake, air bag, or stability control systems should be carefully considered since these modifications have a high potential for causing harm.
Understanding your car's warranty is crucial for protecting your investment and avoiding costly repairs. By understanding the different types of warranties, the key specifications, and the claim process, you can navigate the complexities of warranty coverage with confidence.
We have a detailed warranty diagram that visually represents the information discussed here. You can download the file to further enhance your understanding of car warranties and how they apply to your vehicle. This diagram can be a valuable tool for troubleshooting warranty-related issues and making informed decisions about vehicle maintenance and repairs.
