What Is Aeb On A Car
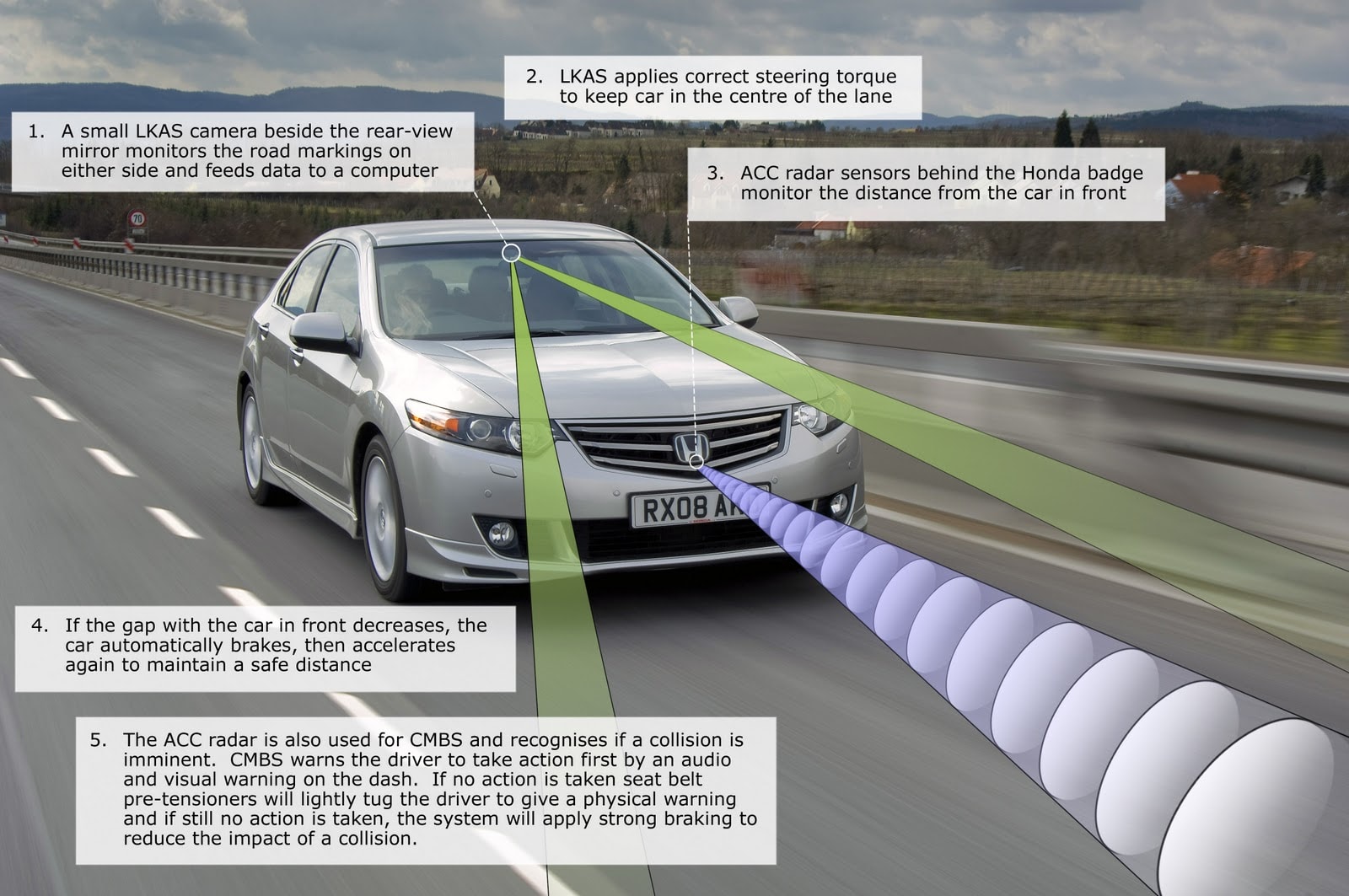
Let's dive into Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB), a crucial safety feature increasingly common in modern vehicles. As someone who's likely already comfortable with vehicle maintenance and modifications, you understand the importance of knowing your car inside and out. This explanation will give you a solid understanding of AEB systems, covering their purpose, components, operation, and basic troubleshooting.
Purpose of Understanding AEB
Understanding AEB systems is essential for several reasons:
- Repairs and Maintenance: Identifying faults in the AEB system allows for precise repairs, saving time and money. You might not be fixing circuit boards, but you can diagnose sensor issues or mechanical problems with the braking components.
- Modifications: When modifying other systems (e.g., suspension, tires), understanding how they might interact with the AEB system is crucial to prevent unintended consequences. For instance, changing tire sizes could affect the radar system's calculations.
- Learning Vehicle Technology: AEB is a stepping stone to understanding more advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and eventually autonomous driving technologies. It builds on the fundamentals of sensor technology, control algorithms, and vehicle dynamics.
- Safety Awareness: Knowing how AEB works helps you understand its limitations and use it effectively in different driving conditions.
Key Specs and Main Parts of AEB
AEB systems vary in complexity, but they generally consist of these key components:
- Radar Sensor: Typically located in the front grille or bumper, the radar sensor emits radio waves to detect the distance and relative speed of objects ahead. Think of it as the system's eyes. The radar sensor's range and field of view are critical specifications.
- Camera Sensor: Often mounted near the rearview mirror, the camera sensor provides visual information about the road ahead, including lane markings, traffic signs, and pedestrians. The camera's resolution and frame rate are important specs.
- Control Module (ECU): The "brain" of the AEB system. It processes data from the radar and camera sensors, analyzes the driving situation, and determines whether to intervene. The ECU's processing power and software algorithms are crucial.
- Brake Actuator: This component applies the brakes automatically when the ECU determines a collision is imminent. It interfaces directly with the vehicle's braking system, often using the existing ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) and ESC (Electronic Stability Control) systems.
- Warning System: Alerts the driver to a potential collision through visual (e.g., dashboard light) and audible (e.g., beep) warnings.
AEB System Diagram Symbols: An Explanation
A schematic diagram of an AEB system will use standard electronic symbols. Here’s a breakdown of some common ones:
- Solid Lines: Represent electrical wiring. Thicker lines indicate higher current carrying capacity.
- Dashed Lines: Often represent data communication lines (e.g., CAN bus) where information is transmitted between different modules.
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of current flow or data flow.
- Resistors: Zigzag lines. Their value (in ohms) is usually indicated nearby.
- Capacitors: Two parallel lines. Their capacitance (in farads) is usually indicated nearby.
- Diodes: Triangle pointing to a line. They allow current to flow in one direction only.
- Transistors: Various symbols depending on the type (BJT, MOSFET). They act as electronic switches or amplifiers.
- Ground Symbols: Indicate a connection to the vehicle's chassis ground.
- ECU Symbols: Usually a rectangular box with pins representing input and output connections. The name of the module (e.g., "AEB ECU") is often written inside the box.
- Sensor Symbols: Varied, but often depict the type of sensor (e.g., radar wave for a radar sensor).
Color Coding: Wire colors are often indicated on the diagram (e.g., "Red," "Blue," "Green"). This is crucial for identifying specific wires during troubleshooting.
How AEB Works: A Step-by-Step Explanation
Here’s a simplified explanation of how a typical AEB system operates:
- Sensor Data Acquisition: The radar and camera sensors constantly monitor the environment in front of the vehicle. The radar measures the distance and speed of objects, while the camera identifies objects (e.g., vehicles, pedestrians, traffic signs).
- Data Processing: The sensors send their data to the AEB ECU. The ECU uses sophisticated algorithms to analyze the data and determine the risk of a collision. This involves calculating the time to collision (TTC), which is the estimated time until the vehicle would collide with an object if no action is taken.
- Risk Assessment: The ECU compares the TTC to predefined thresholds. If the TTC falls below a certain threshold, the system initiates a warning. If the TTC falls below an even lower threshold, the system initiates emergency braking.
- Warning Stage: The system first warns the driver of the impending collision. This can be through a visual warning on the dashboard, an audible warning (e.g., a beep), or a haptic warning (e.g., a brief brake pulse).
- Automatic Braking: If the driver does not respond to the warning, or if the collision is deemed unavoidable, the AEB system automatically applies the brakes. The system may apply partial braking to reduce the impact speed, or full braking to attempt to avoid the collision altogether.
- ABS/ESC Integration: During automatic braking, the AEB system works in conjunction with the vehicle's ABS and ESC systems to maintain stability and prevent wheel lockup.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
While in-depth AEB troubleshooting requires specialized equipment and expertise, here are some basic checks you can perform:
- Check for Obstructions: Ensure that the radar and camera sensors are clean and free from obstructions (e.g., dirt, snow, ice). Even a small amount of debris can significantly impair sensor performance.
- Inspect Wiring: Visually inspect the wiring harnesses and connectors associated with the AEB system for damage or corrosion. Pay close attention to connections near the sensors and the ECU.
- Check Fuses: Consult the vehicle's owner's manual to locate the fuses associated with the AEB system. Check these fuses for continuity.
- Scan for Error Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to check for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the AEB system. These codes can provide valuable clues about the nature of the problem. Common codes relate to sensor failures or communication errors. Be aware that clearing certain codes might require specialized software.
- Battery Voltage: AEB systems are sensitive to voltage fluctuations. Ensure the battery is in good condition and providing stable voltage.
Safety Considerations
Working with AEB systems involves potential risks. Here are some safety precautions to keep in mind:
- High-Voltage Components: Some AEB systems integrate with the vehicle's high-voltage system (especially in hybrid and electric vehicles). Never attempt to repair or modify high-voltage components without proper training and equipment.
- Braking System: The braking system is a critical safety component. If you are not comfortable working on the braking system, consult a qualified mechanic.
- Airbag System: The AEB system may be integrated with the airbag system. Improper handling of these systems can lead to accidental airbag deployment. Disconnect the battery and wait several minutes before working on any electrical components related to the airbags.
- Software Updates: Incorrect software updates can cause the AEB system to malfunction. Always use the correct software and follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully.
- Sensor Calibration: After replacing or adjusting sensors, the AEB system may need to be recalibrated. This typically requires specialized equipment and software. Don't assume that a sensor is working correctly just because it appears to be functioning.
Remember that AEB is a supplemental safety feature and should not be relied upon as a substitute for safe driving practices. Always maintain a safe following distance and pay attention to your surroundings.
This overview should provide a solid foundation for understanding AEB systems. Always consult the vehicle's service manual for specific information and procedures related to your vehicle. We have an AEB system diagram file available for download; it provides a more detailed and technical schematic of a common AEB setup.
