What Is An Exhaust On A Car
Alright, let's dive into the exhaust system – that network of pipes and components that carries spent gases away from your engine. For any serious DIYer, understanding the exhaust is crucial. Whether you're chasing performance gains, diagnosing a pesky rattle, or just trying to keep your ride on the road, knowing your way around the exhaust system is invaluable. We're going to break down everything you need to know, from its basic purpose to common troubleshooting scenarios.
Purpose of the Exhaust System
The primary function of the exhaust system is pretty straightforward: it directs harmful exhaust gases away from the engine and out of the vehicle. But it does much more than just that. Here’s a breakdown:
- Removes Exhaust Gases: This is the core function. Combustion inside the engine creates a cocktail of gases, including carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and carbon dioxide (CO2). The exhaust system safely channels these gases away from the passenger compartment.
- Reduces Emissions: Modern exhaust systems are equipped with catalytic converters to significantly reduce the levels of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere. These converters use chemical reactions to transform CO, HC, and NOx into less harmful substances like water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), and nitrogen (N2).
- Muffles Engine Noise: Without an exhaust system, your engine would sound like a monster truck rally – all the time! The muffler is designed to reduce the intensity of the engine's noise pulses, making your driving experience far more pleasant.
- Improves Engine Performance (Potentially): A well-designed exhaust system can improve engine performance by reducing backpressure. Backpressure is the resistance to exhaust flow, and excessive backpressure can hinder the engine's ability to efficiently expel spent gases, ultimately reducing power.
Key Specs and Main Parts
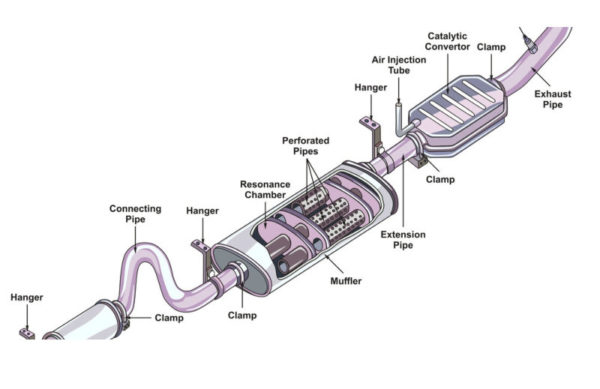
Let's look at the main components of a typical exhaust system. Keep in mind that the specific design and configuration can vary depending on the vehicle's make, model, and engine type.
- Exhaust Manifold: This is the first component in the system. Bolted directly to the engine's cylinder head, the manifold collects exhaust gases from each cylinder. Cast iron or stainless steel are common materials. Some high-performance vehicles use headers instead of manifolds. Headers are individually tuned pipes designed to improve exhaust flow and reduce backpressure.
- Downpipe: Connecting the exhaust manifold (or header) to the rest of the system, the downpipe directs exhaust gases downwards.
- Catalytic Converter: As mentioned earlier, the catalytic converter is a crucial component for reducing emissions. It uses a catalyst (usually platinum, palladium, and rhodium) to convert harmful gases into less harmful substances. Catalytic converters are sensitive components and can be damaged by engine misfires or contaminated fuel.
- Resonator (Optional): Some vehicles include a resonator to further dampen noise and tune the exhaust note. Resonators typically consist of a chamber with internal baffles.
- Muffler: The muffler is the primary noise-reducing component in the exhaust system. It uses a series of chambers and baffles to cancel out sound waves.
- Tailpipe: The final section of the exhaust system, the tailpipe directs exhaust gases away from the vehicle's body.
- Exhaust Hangers: These rubber or metal hangers suspend the exhaust system from the vehicle's undercarriage, absorbing vibrations and preventing excessive movement.
- Gaskets and Clamps: Gaskets seal the joints between exhaust components, preventing leaks. Clamps securely fasten sections of the exhaust system together.
How It Works
Here's a simplified overview of how the exhaust system works:
- When the engine's exhaust valves open, the high-pressure exhaust gases are released from the combustion chamber into the exhaust manifold.
- The exhaust manifold collects these gases and directs them into the downpipe.
- The downpipe carries the gases to the catalytic converter, where harmful pollutants are converted into less harmful substances.
- From the catalytic converter, the gases may pass through a resonator (if equipped) for further noise reduction.
- Finally, the gases enter the muffler, where sound waves are dampened, and then exit the vehicle through the tailpipe.
Real-World Use – Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Let's talk about some common exhaust system problems and how to diagnose them.
- Loud Exhaust Noise: This is often caused by a hole or crack in the exhaust system, especially in the muffler or pipes. Carefully inspect the entire system for signs of damage. You might be able to temporarily patch a small hole with exhaust tape, but a proper repair (welding or replacement) is usually necessary.
- Rattling Noise: A rattling noise could indicate a loose exhaust hanger, a broken heat shield, or a damaged internal component within the muffler or catalytic converter. Check the hangers first, as they are the easiest to inspect and replace.
- Reduced Engine Performance: A clogged catalytic converter can significantly restrict exhaust flow, leading to reduced engine power and poor fuel economy. A mechanic can use a backpressure test to determine if the catalytic converter is clogged.
- Smell of Exhaust in the Cabin: This is a serious issue and should be addressed immediately. It indicates an exhaust leak, which can allow harmful carbon monoxide to enter the passenger compartment. Inspect the exhaust manifold gasket, downpipe, and other joints for leaks.
- Check Engine Light: Many exhaust-related issues, such as a faulty oxygen sensor or a malfunctioning catalytic converter, can trigger the check engine light. Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the trouble codes and diagnose the problem.
Safety – Highlight Risky Components
Working on the exhaust system can be dangerous if you don't take proper precautions. Here are some safety considerations:
- Hot Surfaces: The exhaust system gets incredibly hot, especially after the engine has been running. Allow the system to cool completely before working on it.
- Burns: Wear gloves and long sleeves to protect your skin from burns.
- Eye Protection: Use safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris and welding sparks.
- Carbon Monoxide: Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling carbon monoxide. Never run the engine in an enclosed space.
- Lifting the Vehicle: Use jack stands to support the vehicle securely. Never work under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
- Welding: If you're welding on the exhaust system, follow proper welding safety procedures, including wearing a welding helmet and gloves.
Catalytic Converters Contain Hazardous Materials: Handle catalytic converters with care. They contain platinum, palladium, and rhodium, which are valuable but also potentially harmful. Avoid inhaling dust from damaged converters.
Remember, when in doubt, consult a qualified mechanic. Some exhaust system repairs, such as welding or catalytic converter replacement, require specialized tools and expertise.
