What Is Drive Belt In A Car
Let's talk about drive belts – a seemingly simple component in your car's engine bay that's actually responsible for powering a whole host of vital accessories. This article will give you a deep dive into understanding what a drive belt is, how it works, and how to troubleshoot common issues. Knowing this stuff is crucial, whether you're planning on tackling some DIY repairs, customizing your ride, or just want to be a more informed car owner. We'll cover the key specs, explain how it all works, and even give you some real-world troubleshooting tips.
Understanding the Purpose of the Drive Belt
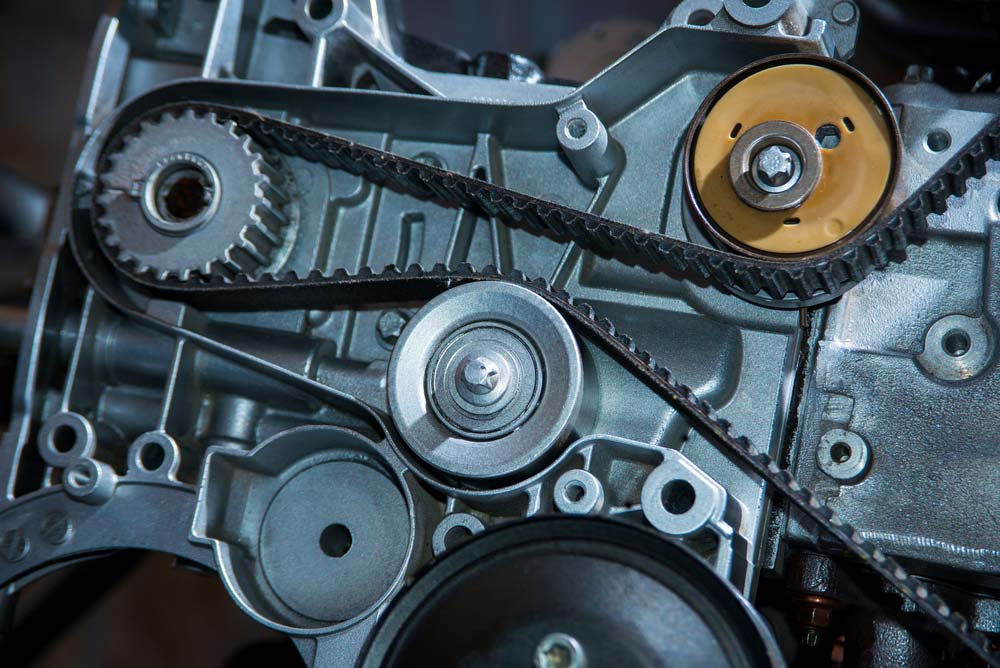
The drive belt, sometimes called the serpentine belt or accessory belt, is a crucial component responsible for transferring rotational power from the engine's crankshaft to various accessories. Without it, these accessories wouldn't function, rendering your car practically unusable. Understanding its function is paramount for several reasons:
- Preventative Maintenance: Knowing how the drive belt works and the signs of wear allows you to perform preventative maintenance, preventing breakdowns and costly repairs down the line.
- Troubleshooting: If your car is experiencing issues with power steering, air conditioning, or the charging system, a faulty drive belt could be the culprit. Understanding its role helps you diagnose the problem effectively.
- DIY Repairs: Replacing a drive belt is a relatively straightforward DIY project, saving you money on labor costs.
- Performance Upgrades: When upgrading your car's accessories (e.g., installing a high-output alternator), you might need to consider a different drive belt length or material to handle the increased load.
Key Specs and Main Parts of a Drive Belt System
The drive belt system comprises several key components, each playing a critical role in power transmission:
- Drive Belt (Serpentine Belt): The main component, typically made of reinforced rubber, that connects the crankshaft pulley to the accessory pulleys.
- Crankshaft Pulley: Attached to the crankshaft, this pulley receives power directly from the engine and drives the belt.
- Accessory Pulleys: These pulleys are connected to various accessories, such as:
- Alternator: Generates electricity to power the car's electrical system and charge the battery.
- Power Steering Pump: Provides hydraulic assistance for easier steering.
- Air Conditioning Compressor: Compresses refrigerant to cool the cabin.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant to regulate engine temperature.
- Tensioner Pulley: Maintains proper tension on the drive belt, preventing slippage and ensuring efficient power transfer. There are two main types:
- Spring-loaded Tensioner: Automatically adjusts tension using a spring mechanism.
- Manual Tensioner: Requires manual adjustment to set the proper tension.
- Idler Pulley: A smooth pulley used to guide the belt around the engine components, preventing interference and optimizing belt routing.
Key specifications to consider when dealing with drive belts include:
- Length: The total length of the belt, usually measured in millimeters or inches. Correct length is critical for proper tension.
- Width: The width of the belt, which must match the width of the grooves on the pulleys.
- Number of Ribs: The number of V-shaped ribs on the belt. This also needs to match the pulley grooves.
- Material: Most belts are made from EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer) rubber, known for its durability and resistance to heat and wear. Some high-performance belts are made from more exotic materials for increased strength and heat resistance.
How the Drive Belt System Works
The operation of the drive belt system is relatively straightforward but crucial for the functionality of your car. The process unfolds as follows:
- The engine's crankshaft rotates, driving the crankshaft pulley.
- The rotating crankshaft pulley turns the drive belt, which is wrapped around all the accessory pulleys.
- As the drive belt moves, it spins the pulleys of the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and water pump.
- Each accessory pulley, in turn, drives its respective component, allowing it to perform its function.
- The tensioner pulley maintains constant tension on the belt, ensuring that it doesn't slip and that all the accessories are driven efficiently.
- The idler pulley simply guides the belt, ensuring proper routing and preventing interference with other engine components.
Proper belt tension is critical. Too loose, and the belt will slip, causing accessories to malfunction. Too tight, and it can put excessive strain on the bearings of the accessories and the tensioner itself, leading to premature failure. The tensioner pulley plays a vital role in managing this tension, either automatically (spring-loaded) or through manual adjustment.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some common problems you might encounter with your drive belt and how to troubleshoot them:
- Squealing Noise: A common sign of a slipping drive belt, often caused by wear, contamination (oil or coolant), or incorrect tension.
- Troubleshooting: Inspect the belt for cracks, glazing, or missing ribs. Check the tensioner for proper operation. Clean the belt and pulleys with a belt dressing or degreaser. If the belt is old or damaged, replace it.
- Cracked or Frayed Belt: Indicates that the belt is deteriorating and needs replacement.
- Troubleshooting: Visually inspect the belt for cracks, frayed edges, or missing chunks. Replace the belt immediately if any of these signs are present.
- Accessories Not Working: If you notice that your power steering is stiff, your air conditioning is not cooling, or your battery is not charging, a broken or slipped drive belt could be the cause.
- Troubleshooting: Visually inspect the drive belt to ensure it's properly routed and in good condition. Check the tensioner to ensure it's functioning correctly. If the belt is broken, replace it.
- Excessive Vibration: Can be caused by a worn tensioner pulley or an imbalanced accessory pulley.
- Troubleshooting: Inspect the tensioner pulley for play or noise. Check the accessory pulleys for damage or imbalance. Replace any faulty components.
Safety Considerations
Working on the drive belt system can be risky if you're not careful. Here are some important safety precautions to keep in mind:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any part of the engine, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical shock.
- Ensure the Engine is Cool: Never work on the drive belt system when the engine is hot. Allow the engine to cool down completely to avoid burns.
- Keep Hands and Clothing Clear: Always keep your hands, clothing, and tools clear of the moving belt and pulleys when the engine is running. A running engine is extremely dangerous.
- Use Proper Tools: Use the correct tools for the job, such as a belt tensioner tool, to avoid damaging the belt or other components.
- Follow the Service Manual: Always refer to your car's service manual for specific instructions and torque specifications.
The drive belt system is a critical part of your vehicle. It is best to approach repairs with caution, or seek professional help from a qualified mechanic.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the drive belt system. With this knowledge, you can better maintain your vehicle, troubleshoot common issues, and even tackle some DIY repairs with confidence.
