What Is Gap Coverage On A Vehicle
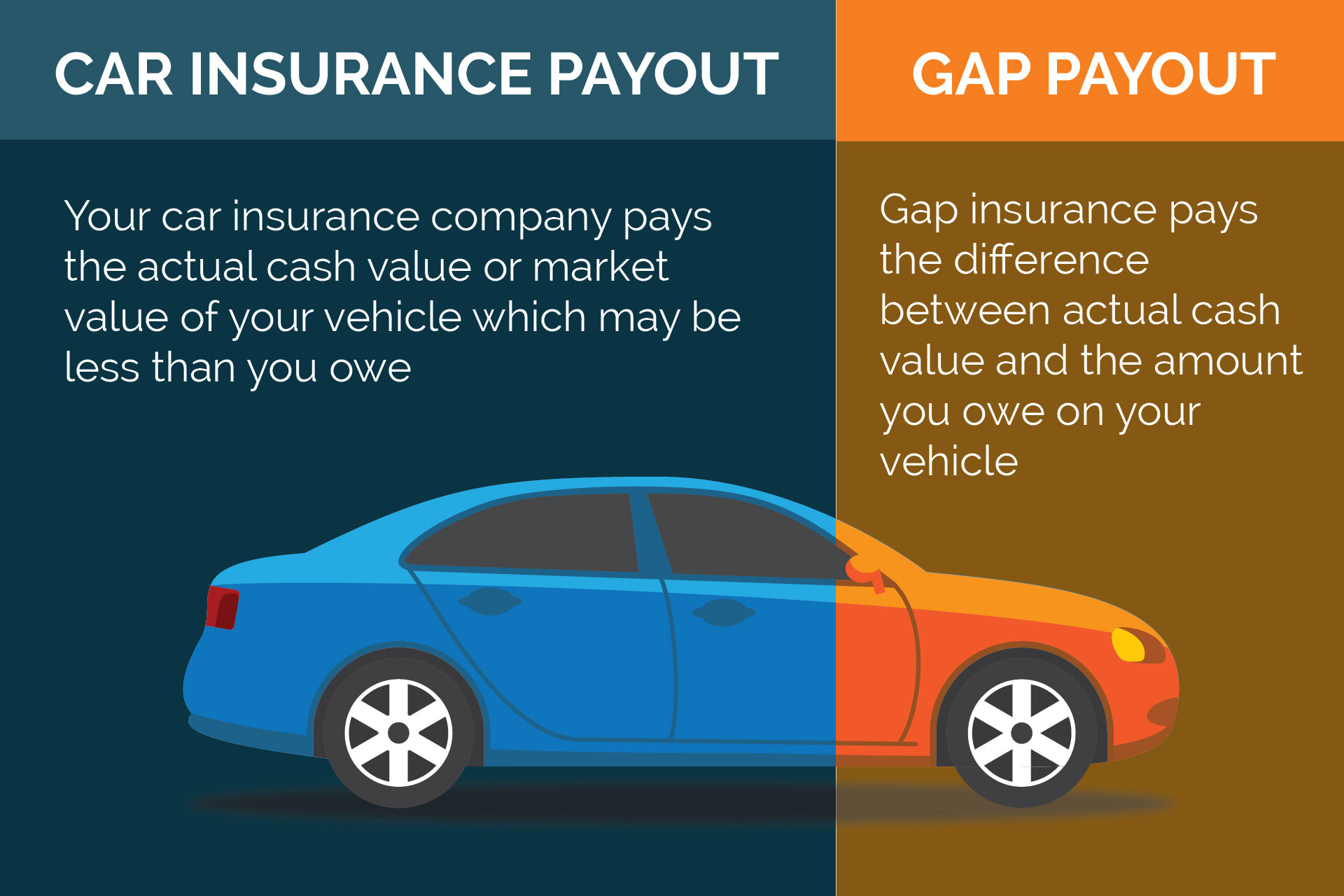
Gap insurance, also known as Guaranteed Asset Protection, is a specialized form of vehicle insurance designed to protect you financially when your car is totaled or stolen and you owe more on your loan or lease than the vehicle's actual cash value (ACV). Let's break down exactly what that means and why it's important, especially in today's automotive market.
Purpose of Gap Coverage
The primary purpose of gap insurance is to bridge the "gap" between what your standard auto insurance policy will pay out in the event of a total loss and the outstanding balance on your auto loan or lease. New cars depreciate rapidly – a phenomenon known as accelerated depreciation. It's entirely possible to owe significantly more on your car than it's worth within the first year or two of ownership. If your car is totaled, your regular insurance will only pay its current market value, leaving you responsible for the remaining loan balance. This is where gap insurance steps in.
This matters because being stuck with a loan for a car you no longer possess is a financially crippling situation. Gap insurance prevents this, allowing you to walk away from the loss without a substantial debt burden.
Key Specs and Main Parts of a Gap Insurance Policy
While there isn't a physical "diagram" in the traditional sense (like a wiring diagram or a parts breakdown), understanding the components of a gap insurance policy is crucial. Think of these components as the "parts" of the agreement:
- Policy Coverage Limit: This is the maximum amount the gap insurance will pay out. It's vital to know this limit and ensure it's sufficient to cover the potential gap between your car's ACV and your loan balance.
- Covered Losses: Gap insurance typically covers total losses due to collision, theft, fire, and other events covered by your comprehensive and collision insurance.
- Excluded Losses: Know what's not covered. Typical exclusions include mechanical breakdowns, normal wear and tear, negative equity rolled over from a previous loan, and situations where you're in violation of your primary insurance policy (e.g., driving under the influence).
- Deductible: Some gap policies have a deductible, which is the amount you'll pay out-of-pocket before the gap insurance kicks in.
- Waiting Period: Some policies have a waiting period, meaning you're not covered for a certain period after purchasing the policy.
- ACV (Actual Cash Value): This is the estimated market value of your vehicle at the time of the loss, determined by your primary insurance company. It's a critical factor in calculating the "gap."
"Symbols" - Interpreting Policy Language
Instead of traditional symbols, understanding gap insurance involves interpreting policy language. Here's how to approach some common "symbols":
- Fine Print (Tiny Text): This is where exclusions, limitations, and conditions are often buried. Read it carefully.
- Dollar Signs ($): Pay close attention to coverage limits, deductibles, and premium costs.
- Percentages (%): Some policies may cap coverage based on a percentage of the vehicle's original MSRP (Manufacturer's Suggested Retail Price) or the loan amount.
- Dates: Note the effective date and expiration date of the policy.
- "Subject to the terms and conditions of the policy": This phrase means everything is governed by the detailed policy wording.
How It Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
- Loss Occurs: Your vehicle is totaled or stolen.
- Primary Insurance Claim: You file a claim with your primary auto insurance company.
- ACV Determination: Your primary insurer determines the Actual Cash Value (ACV) of your vehicle.
- Loan Balance Assessment: You determine the outstanding balance on your auto loan or lease.
- Gap Calculation: The "gap" is calculated by subtracting the ACV from the loan balance, and then subtracting your primary insurance deductible (if applicable).
- Gap Insurance Claim: You file a claim with your gap insurance provider, providing documentation from your primary insurer and your loan or lease provider.
- Claim Processing: The gap insurance company reviews your claim and verifies the information.
- Payment: If approved, the gap insurance company pays the remaining loan balance, up to the policy coverage limit.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
While gap insurance is relatively straightforward, issues can arise. Here are some troubleshooting tips:
- Coverage Limit Exceeded: If the gap between the ACV and the loan balance exceeds the policy limit, you'll still be responsible for the difference. Solution: Choose a gap policy with a sufficient coverage limit.
- Excluded Loss: If the loss is due to an excluded event (e.g., drunk driving), the claim will be denied. Solution: Understand the exclusions before purchasing the policy and avoid activities that violate your primary insurance.
- Claim Denied Due to Insufficient Documentation: Missing documents can delay or deny the claim. Solution: Gather all necessary documentation (police report, insurance settlement, loan statement) before filing the claim.
- Dispute Over ACV: You might disagree with the ACV determined by your primary insurer. Solution: Research comparable vehicles for sale in your area to support your argument for a higher ACV. Consider an independent appraisal.
Safety: Avoiding Financial Pitfalls
Gap insurance isn't inherently risky in terms of physical safety, but it's crucial to avoid these financial pitfalls:
- Overlapping Coverage: Don't purchase gap insurance if you already have loan/lease payoff coverage as part of your primary insurance policy.
- Unnecessary Coverage: If you're making a large down payment or paying off your loan quickly, the risk of being "upside down" on your loan decreases. Gap insurance may not be necessary in these situations.
- Ignoring Policy Details: Failing to read and understand the policy terms can lead to unexpected claim denials or financial liabilities.
- Relying Solely on Dealer-Offered Gap: Dealers often mark up gap insurance significantly. Shop around for the best rates from independent insurers or your bank.
Remember, gap insurance is designed to protect you from a specific financial risk. Evaluate your individual circumstances and determine if it's the right choice for you.
For a detailed sample gap insurance policy document, including all the terms and conditions mentioned above, you can download it by clicking here. (Example Link - Replace with actual file download link).
