What Is Good Mpg For A Sedan
Let's dive into the often-asked question: What constitutes "good" MPG (miles per gallon) for a sedan? There's no simple, one-size-fits-all answer, as it depends on several factors. This article will provide a technical breakdown of those factors, helping you assess your sedan's fuel efficiency and potentially identify areas for improvement.
Why Understanding MPG Matters
Understanding your sedan's MPG isn't just about bragging rights. It's critical for several reasons:
- Budgeting: Knowing your fuel consumption directly impacts your transportation expenses.
- Vehicle Health: A sudden drop in MPG can indicate underlying mechanical issues needing attention. Addressing these early can prevent more significant, and costly, repairs.
- Environmental Impact: Lower MPG means higher emissions. Understanding and improving your fuel efficiency contributes to a smaller carbon footprint.
- Resale Value: Fuel-efficient vehicles often command a higher resale value.
Key Specs and Main Factors Affecting MPG
Several key specifications and operational factors determine a sedan's fuel efficiency:
Engine Size and Type
Smaller engines (e.g., inline-4 or I4) generally offer better MPG than larger engines (e.g., V6 or V8). Turbocharging or supercharging, while increasing power, can also impact fuel consumption, especially if the driver frequently utilizes the boosted power.
Transmission Type
Traditionally, manual transmissions (MT) were considered more fuel-efficient, as they allow the driver greater control over gear selection and engine RPM. However, modern automatic transmissions (AT), particularly those with eight or more gears, often achieve comparable or even superior MPG due to their optimized shift patterns and torque converter lockup. CVTs (Continuously Variable Transmissions) are designed for maximum efficiency by keeping the engine in its optimal operating range.
Vehicle Weight
Heavier sedans require more energy to accelerate and maintain speed, leading to lower MPG. Lighter materials like aluminum and carbon fiber, though more expensive, are increasingly used to reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency.
Aerodynamics
A car's aerodynamic profile affects how easily it moves through the air. A lower drag coefficient (Cd) results in less air resistance and better MPG, especially at higher speeds. Factors like vehicle height, body shape, and underbody panels contribute to the Cd. Spoilers and other body modifications can improve or degrade aerodynamics depending on their design.
Tire Rolling Resistance
Tires with lower rolling resistance require less energy to turn, improving MPG. These tires often have specific tread patterns and use specialized rubber compounds. However, low rolling resistance tires may offer less grip, which can impact handling and braking performance. Consider tires marked with "Low Rolling Resistance" indicators.
Driving Habits
Aggressive driving habits, such as rapid acceleration and hard braking, significantly decrease MPG. Maintaining a consistent speed, anticipating traffic conditions, and avoiding unnecessary idling can improve fuel efficiency. The use of cruise control on the highway is a simple but effective way to maintain a consistent speed.
Vehicle Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for maintaining optimal MPG. Dirty air filters, worn spark plugs, and old engine oil can all reduce fuel efficiency. Proper tire inflation is also essential, as underinflated tires increase rolling resistance. Pay attention to your vehicle's maintenance schedule.
Fuel Type
Using the correct octane fuel as specified by the manufacturer is vital. Using a lower octane fuel than recommended can lead to engine knocking and reduced performance, while using a higher octane fuel than needed offers no benefit and simply costs more. E85 (a blend of 85% ethanol and 15% gasoline) can reduce MPG compared to regular gasoline due to its lower energy content, even though the vehicle is designed to use it. Diesel engines are generally more fuel-efficient than gasoline engines. Check your owner's manual for fuel recommendations.
External Factors
Weather conditions, terrain, and traffic congestion also impact MPG. Cold weather increases engine friction and requires more energy to warm up the engine. Hilly terrain requires more power, reducing MPG. Stop-and-go traffic is inherently inefficient.
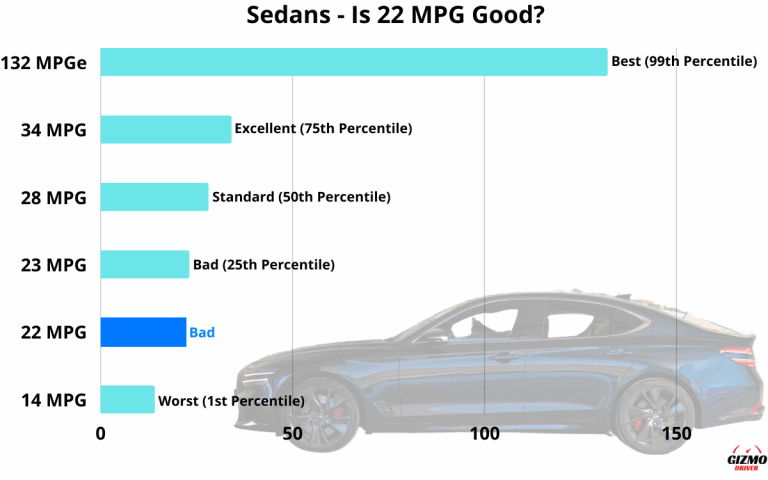
What's a "Good" MPG for a Sedan?
As a general guideline, here’s a breakdown:
- Below 25 MPG: Poor MPG, potentially indicating a problem or an older, less efficient vehicle.
- 25-30 MPG: Average MPG for older or larger sedans.
- 30-35 MPG: Good MPG, typical for many modern mid-size sedans.
- 35 MPG and Above: Excellent MPG, often achieved by hybrid or particularly fuel-efficient sedans.
However, these are just averages. Compare your sedan's MPG to its EPA fuel economy ratings (city and highway) to get a more accurate assessment. Remember that the EPA ratings are achieved under controlled conditions and may not perfectly reflect real-world driving.
Real-World Use - Basic Troubleshooting Tips
If you notice a sudden drop in your sedan's MPG, here are some basic troubleshooting steps:
- Check Tire Pressure: Ensure all tires are properly inflated to the recommended pressure (found on the sticker inside the driver's side door jamb or in the owner's manual).
- Inspect Air Filter: A dirty air filter restricts airflow to the engine, reducing MPG. Replace it if it's visibly dirty.
- Check for Leaks: Inspect the engine and fuel lines for any signs of fuel leaks. Even a small leak can significantly impact MPG and presents a fire hazard.
- Review Driving Habits: Be honest with yourself about your driving habits. Are you accelerating aggressively or braking hard?
- Consider a Tune-Up: If your vehicle hasn't had a tune-up recently, it might be time to replace spark plugs, check ignition timing, and clean fuel injectors.
- OBDII Scanner: Use an OBDII scanner to check for any diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that could indicate engine problems.
Safety Considerations
When working on your vehicle to improve MPG, always prioritize safety:
- Fuel System: The fuel system is highly flammable. Never work on the fuel system near open flames or sparks. Always disconnect the negative battery cable before working on any electrical components.
- Exhaust System: The exhaust system can get extremely hot. Allow it to cool completely before working on it.
- Jacking Up the Vehicle: Always use jack stands to support the vehicle when working underneath it. Never rely solely on a jack.
- Electrical System: Be cautious when working with the electrical system, especially around the battery and alternator. Disconnect the negative battery cable before working on any electrical components.
Conclusion
Determining "good" MPG for a sedan is nuanced, influenced by factors ranging from engine size to driving habits. By understanding these elements and employing the troubleshooting tips outlined above, you can accurately assess your vehicle's fuel efficiency and take steps to optimize it. Remember, consistent monitoring and preventative maintenance are key to maintaining optimal MPG and extending the life of your vehicle.
We have a detailed diagram illustrating the interconnectedness of the engine and fuel systems, showing how adjustments to one affects the other, and of course, your MPG. Click here to download the diagram.
