What Is Parking Assist On A Car
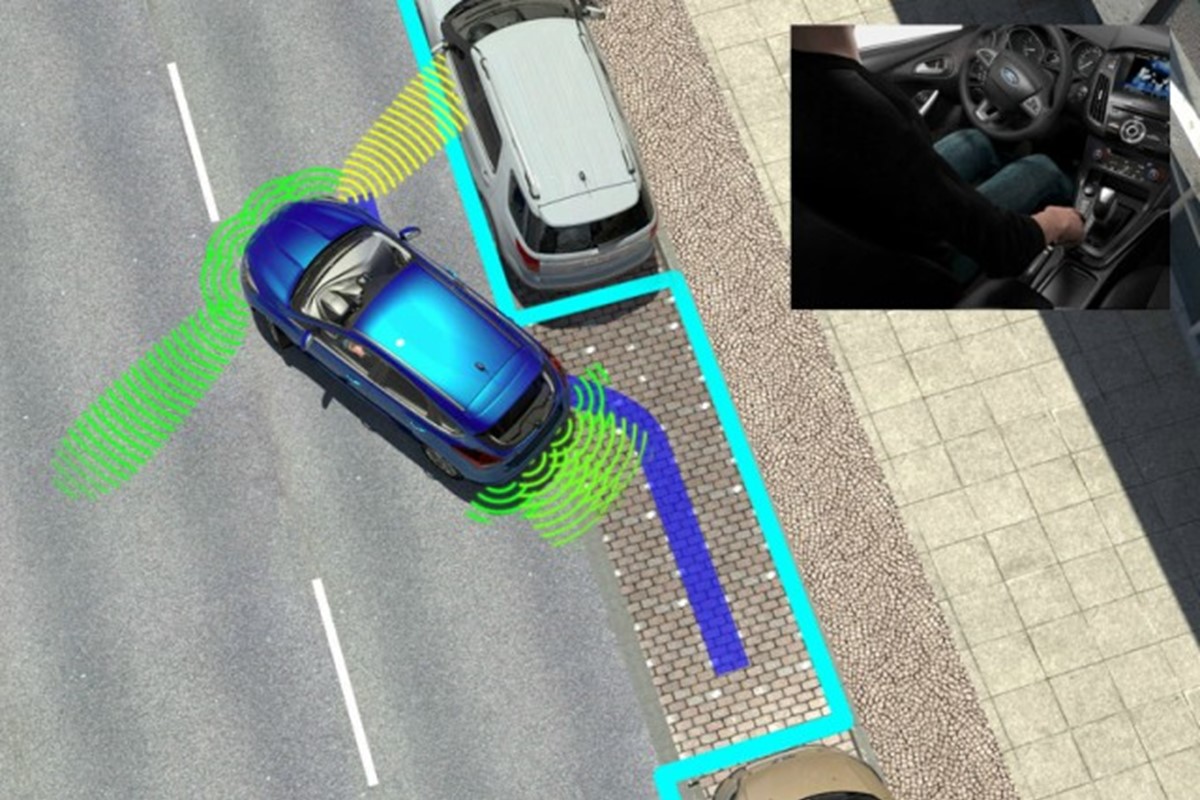
Alright, let's dive into parking assist systems. For experienced DIYers like yourselves, understanding these systems is becoming increasingly vital. Modern cars are packed with electronic aids, and parking assist is a prime example. Whether you're planning to add aftermarket sensors, diagnose a malfunctioning system, or simply want to know how it all works, this deep dive will equip you with the knowledge you need. We'll break down the components, the underlying technology, and even cover some basic troubleshooting.
Purpose and Components
The primary purpose of a parking assist system is to help drivers safely and efficiently maneuver into parking spaces, particularly in tight or challenging conditions. It reduces the risk of collisions with other vehicles, objects, or pedestrians. This diagram is invaluable for diagnosing faults, understanding the location and function of components, and even planning custom modifications. Think of it as your roadmap to navigating the inner workings of the system.
Key Specs and Main Parts:
Parking assist systems typically involve the following key components. These can vary slightly between manufacturers, but the core principles remain the same:
- Ultrasonic Sensors: These are the workhorses of the system. They emit high-frequency sound waves (typically in the 40-50 kHz range) and measure the time it takes for the echoes to return. This allows the system to calculate the distance to nearby objects. You'll find these sensors usually embedded in the front and rear bumpers.
- Control Unit (ECU): The Electronic Control Unit is the brain of the operation. It receives data from the ultrasonic sensors, processes it using sophisticated algorithms, and then provides audible or visual alerts to the driver. This ECU may be dedicated solely to parking assist or integrated into a larger vehicle control module.
- Display Unit: The display provides visual feedback to the driver, often showing a graphical representation of the vehicle and its surroundings. It may be integrated into the infotainment system or a dedicated display screen.
- Audible Warning System: A series of beeps or tones that increase in frequency and intensity as the vehicle gets closer to an obstacle.
- Steering Assist Module (in some systems): More advanced systems feature automatic steering. This module takes control of the electric power steering (EPS) system to guide the vehicle into the parking space.
- Camera System (in some systems): Many modern systems supplement the ultrasonic sensors with cameras, providing a visual representation of the surroundings. This enhances accuracy and provides a wider field of view.
Symbols and Diagram Interpretation
Understanding the schematic diagram is crucial. While specifics vary, here are common conventions:
- Solid Lines: Typically represent electrical wiring. Thicker lines might indicate power or ground wires.
- Dashed Lines: Often used for communication buses, like CAN (Controller Area Network) bus lines, which transmit data between different ECUs.
- Colors: Wire colors are usually specified (e.g., "RD" for red, "BL" for blue, "BK" for black). This helps in identifying specific wires during troubleshooting.
- Ground Symbols: Indicate connection to the vehicle's chassis ground.
- Sensor Symbols: Represent the ultrasonic sensors. These may vary in shape, but usually have a distinctive marking to denote their function.
- ECU Symbols: Typically represented as rectangles with labeled input and output pins.
Pay close attention to the connector pinouts. These show which wire connects to which pin on the ECU and other components. Incorrect connections can cause malfunctions or even damage to the system.
How It Works
The parking assist system operates in several stages:
- Activation: The system is typically activated when the vehicle is in reverse gear or by pressing a dedicated button.
- Scanning: The ultrasonic sensors emit sound waves and listen for the returning echoes. The system calculates the distance to objects based on the time it takes for the echoes to return.
- Data Processing: The ECU receives the distance data from the sensors and uses algorithms to determine the location and size of available parking spaces. It also identifies potential obstacles.
- Alerts: If the system detects an obstacle, it provides audible and visual alerts to the driver. The frequency and intensity of the alerts increase as the vehicle gets closer to the obstacle.
- Steering Assist (if equipped): In systems with automatic steering, the ECU calculates the optimal steering angle and controls the EPS system to guide the vehicle into the parking space. The driver typically controls the acceleration and braking.
The algorithms used by the ECU are complex and take into account factors such as vehicle speed, steering angle, and sensor readings. These algorithms are constantly being refined to improve accuracy and reliability.
Real-World Use and Basic Troubleshooting
Here are some basic troubleshooting tips:
- Clean Sensors: Dirty or obstructed sensors can cause inaccurate readings. Clean them regularly with a soft cloth.
- Check Wiring: Inspect the wiring and connectors for damage or corrosion. Use a multimeter to check for continuity and voltage.
- Scan for Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to check for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the parking assist system. These codes can provide valuable clues about the source of the problem.
- Sensor Calibration: Some systems require sensor calibration after replacement or repair. Consult the vehicle's service manual for the correct procedure.
- Check for Obstructions: Ensure there are no loose objects or debris interfering with the sensor's field of view.
For example, a common issue is a "phantom obstacle" warning. This could be caused by a faulty sensor, damaged wiring, or even a dirty sensor. Start by cleaning the sensors and checking the wiring. If the problem persists, you may need to replace the sensor. Using the diagram, you can easily identify the sensor location and trace the wiring back to the ECU.
Safety Considerations
Working with electrical systems always carries risks. Here are some key safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on the electrical system. This will prevent accidental shorts and electric shock.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools to avoid electric shock.
- Avoid Water: Never work on the electrical system in wet conditions.
- Handle Sensors Carefully: Ultrasonic sensors are delicate and can be damaged by mishandling.
- Be Mindful of Airbags: Some parking assist components may be located near airbag sensors or modules. Be careful not to disturb these components.
The ECU itself can be sensitive to static electricity. Use an anti-static wrist strap when handling the module to prevent damage.
Warning: Never rely solely on the parking assist system. Always use your mirrors and look around to ensure it is safe to maneuver. Parking assist systems are aids, not replacements for attentive driving.
We hope this breakdown has been helpful. You now have a solid foundation for understanding parking assist systems. Remember to always consult the vehicle's service manual for specific instructions and safety precautions.
For your convenience, we have the detailed schematic diagram available for download. It provides a comprehensive overview of the system's components and wiring. Happy wrenching!
