What Is S Gear In A Car
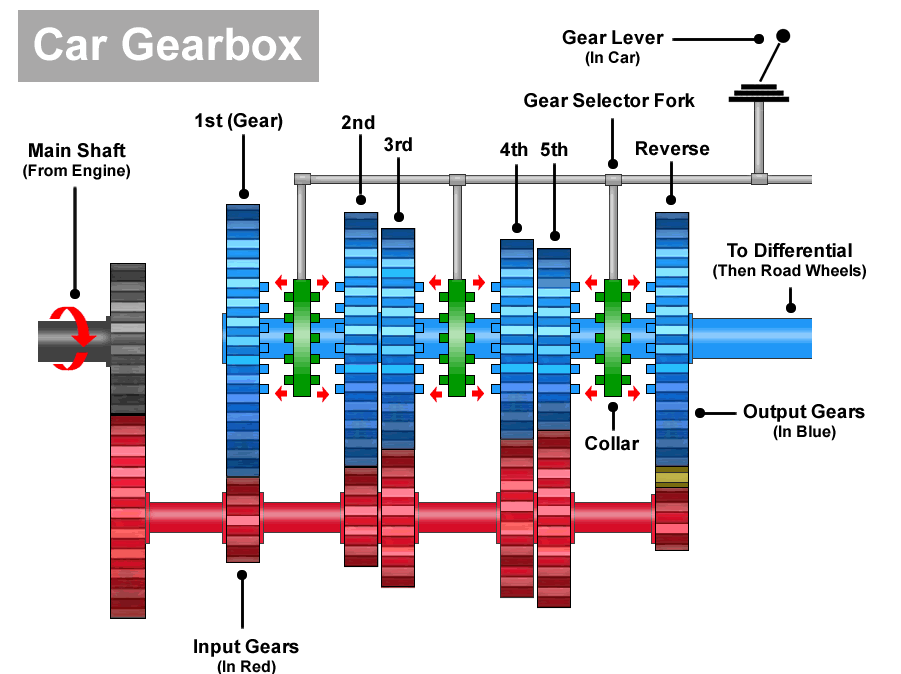
Alright, let's talk about "S" gear in your car. While not every vehicle features an "S" selection on the gear shifter, it's become increasingly common, especially in modern automatic transmissions. Understanding what "S" gear actually does is crucial, whether you're diagnosing performance issues, considering modifications, or simply want to get the most out of your vehicle. This article provides a breakdown to help you understand its inner workings. Think of this as a mini-service manual explanation – helpful for DIYers looking to go beyond basic maintenance.
Purpose and Relevance
Why bother understanding "S" gear? Simple. Knowledge is power. Misunderstanding its function can lead to inefficient driving, unnecessary wear and tear, or even misdiagnosis of transmission problems. Knowing the specifics allows you to:
- Optimize Performance: Properly using "S" gear can improve acceleration and responsiveness in specific driving situations.
- Diagnose Issues: A malfunction in the "S" gear system (including its electronic controls) can point to more extensive transmission or engine management problems.
- Understand Modifications: If you're considering performance modifications (ECU tuning, transmission upgrades), understanding "S" gear's behavior is essential for calibrating those changes.
This knowledge is particularly valuable when troubleshooting drivability issues or interpreting scan tool data. If you notice erratic shifting, delayed engagement, or a lack of response in "S" mode, understanding how it’s *supposed* to work helps pinpoint the problem.
Key Specs and Main Parts (Depending on the Car)
The specifics of "S" gear vary depending on the vehicle manufacturer and transmission type. However, some common elements are:
- Transmission Control Module (TCM): The TCM is the brain of the automatic transmission. It receives inputs from various sensors (throttle position, vehicle speed, engine speed, etc.) and controls the transmission's shifting behavior. "S" gear is essentially a different operating mode programmed into the TCM.
- Shift Solenoids: These are electronically controlled valves inside the transmission that direct hydraulic fluid to engage different gear ratios. The TCM activates specific solenoids based on the selected gear (including "S").
- Throttle Position Sensor (TPS): The TPS provides the TCM with information about how far the accelerator pedal is depressed. This is a critical input for determining shift points in "S" mode.
- Engine Speed Sensor (Crankshaft Position Sensor): Also key as it provides engine speed information to the TCM.
- Gear Selector Switch: Sends a signal to the TCM indicating that "S" gear has been selected.
- Valve Body: The hydraulic control center of the transmission, containing channels and valves that direct fluid to the appropriate clutches and bands.
Key Specs to consider (though these are very car-dependent, so consult your car's service manual):
- Shift Points: The RPM at which the transmission shifts up or down in "S" mode. These are usually higher than in "D" (Drive).
- Throttle Sensitivity: How much the transmission responds to changes in throttle position in "S" mode.
- Gear Ratios: While the gear ratios themselves don't change, the selection of those ratios is altered in "S" mode.
Symbols and Indicators
While there isn't a standardized diagram or symbol specific to "S" gear itself (you won't find it on an electrical wiring diagram, for example), understanding the broader symbols related to the transmission control system is essential. Common symbols you *might* encounter when diagnosing related issues include:
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of fluid flow (in hydraulic diagrams) or signal flow (in electrical diagrams).
- Circles/Squares: Represent components like solenoids, sensors, or switches.
- Lines: Represent wires (electrical diagrams) or hydraulic lines (hydraulic diagrams). Different line thicknesses can indicate wire gauge or pressure levels.
- Colors: Standardized color coding is used for wiring to identify circuits. Consult your vehicle's wiring diagram for specific color codes.
- Icons (on instrument panel): If a transmission problem is detected (related to "S" gear or otherwise), the check engine light (CEL) or a specific transmission warning light may illuminate.
How It Works
In essence, "S" gear remaps the transmission's shifting behavior. Here’s a breakdown:
- Selection: When you select "S" gear, the gear selector switch sends a signal to the TCM.
- Remapped Shift Logic: The TCM switches to a different set of programming instructions. This typically involves:
- Higher Shift Points: The transmission holds gears longer, allowing the engine to rev higher and produce more power before shifting.
- More Aggressive Downshifts: The transmission is more likely to downshift when you lift off the throttle or apply the brakes, providing engine braking and improved responsiveness.
- Faster Shift Times: Some transmissions are programmed for quicker shifts in "S" mode.
- Adaptive Learning Adjustments: The TCM might limit "adaptive learning" in S mode, meaning it is less likely to change its shifting behavior based on your driving style to optimize for consistent performance.
- Throttle Sensitivity: The TCM becomes more sensitive to throttle input, meaning even small changes in accelerator pedal position can result in immediate gear changes.
- Manual Control (Optional): Some vehicles with "S" gear also offer a manual shift mode (often using paddle shifters or the gear lever itself). In this mode, you have direct control over gear selection.
The key is that "S" gear doesn't magically change the transmission's gear ratios. It simply tells the TCM to select those ratios in a different way, optimized for performance.
Real-World Use and Basic Troubleshooting
When to Use: "S" gear is best suited for situations where you need maximum performance and responsiveness, such as:
- Merging onto highways.
- Passing other vehicles.
- Driving on winding roads.
- Towing (consult your vehicle's manual).
Troubleshooting Tips:
- No Response: If the transmission doesn't seem to change behavior when you select "S" gear, start by checking the gear selector switch and its wiring. A faulty switch might not be sending the signal to the TCM.
- Erratic Shifting: If the transmission shifts erratically or harshly in "S" mode, suspect a problem with the TCM, shift solenoids, or a faulty sensor (TPS, vehicle speed sensor). A scan tool can help you read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Lack of Power: If the engine bogs down or lacks power in "S" mode, it could be related to the higher shift points (the engine might be outside its optimal power band). Also, check for engine-related issues (e.g., faulty spark plugs, clogged air filter).
Safety Considerations
While "S" gear itself isn't inherently dangerous, be aware of the following:
- Increased Engine Wear: Driving in "S" mode constantly can lead to increased engine wear due to the higher RPMs.
- Reduced Fuel Economy: The more aggressive shifting in "S" mode will typically reduce fuel economy.
- Overheating: Prolonged use of "S" gear, especially when towing or driving in hot conditions, can increase the risk of transmission overheating. Monitor your vehicle's temperature gauge.
- Hydraulic Pressures: Working inside a transmission without proper knowledge is extremely risky due to high pressure hydraulic fluid. De-pressurize the system before attempting any repairs.
Never attempt to disassemble or repair the transmission without proper training and experience. The transmission is a complex and precision-engineered component. Incorrect repairs can lead to serious damage or injury.
Remember to consult your vehicle's service manual for specific information and diagrams related to your particular make and model. These manuals often include detailed schematics of the transmission control system, which can be invaluable for troubleshooting. They'll provide specifics that are impossible to list in a general article like this one.
We have additional resources, including a detailed transmission control system diagram, available for download. This diagram provides a visual representation of the system's components and wiring, which can be extremely helpful for diagnosis and repair.
