What Is The Drive Belt On A Car
Alright, let's dive into the heart of your engine and talk about something crucial but often overlooked: the drive belt. This isn't just some rubber band; it's a vital component that keeps many of your car's accessories running. Understanding the drive belt is essential for preventative maintenance, diagnosing weird noises, and even performing certain repairs yourself. Consider this your comprehensive guide.
Purpose of Understanding the Drive Belt System
Why should you care about the drive belt? Well, think about it. Without it, you'd be without power steering, air conditioning, and your alternator wouldn't charge the battery. That means no tunes, no cool air on a hot day, and eventually, a dead car. More practically, a solid understanding helps with:
- Troubleshooting: Squealing noises, dimming lights, or a lack of power steering can all be symptoms of a drive belt issue.
- Maintenance: Knowing when and how to inspect and replace the belt saves you money and prevents breakdowns.
- DIY Repairs: Certain repairs require removing or adjusting the drive belt, so knowledge is power (and wrenching power!).
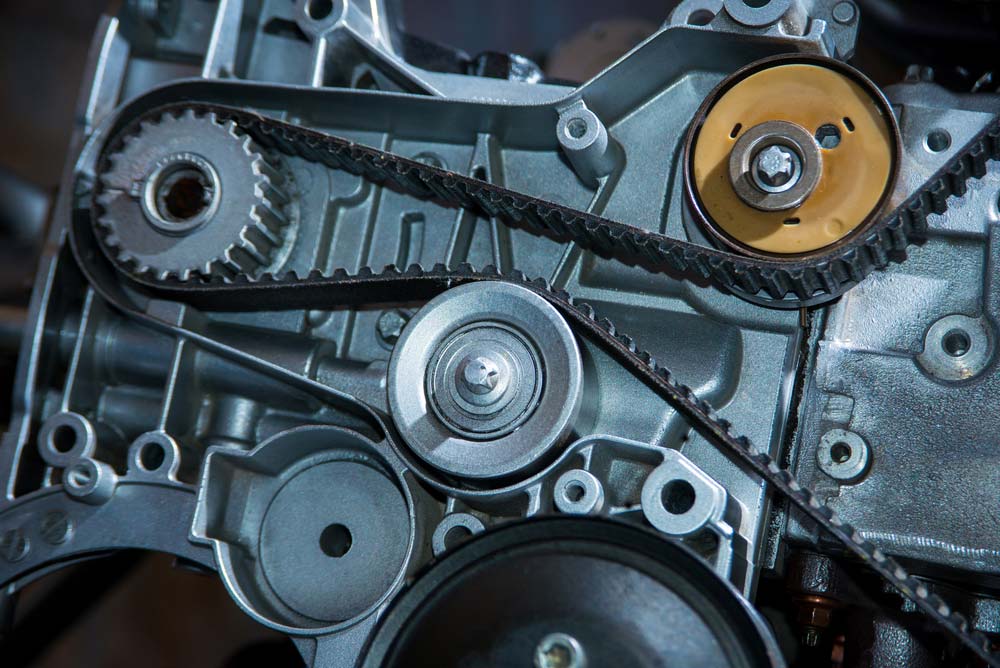
Key Specs and Main Parts
The drive belt system isn't just a single belt. It's a collection of components working together. Here's a breakdown:
- Drive Belt (or Serpentine Belt): This is the main actor, a long, continuous belt made of reinforced rubber. Older cars might have multiple V-belts, but modern vehicles predominantly use a single serpentine belt.
- Crankshaft Pulley (or Damper): This pulley is attached to the crankshaft – the main rotating shaft in the engine. It's what provides the initial rotational force that drives the belt.
- Alternator Pulley: Connected to the alternator, this pulley spins the alternator, which generates electricity to charge your battery and power your car's electrical system.
- Power Steering Pump Pulley: If your car has hydraulic power steering, this pulley drives the pump that provides assist to make steering easier.
- Air Conditioning Compressor Pulley: Spins the compressor, which is a key part of the air conditioning system.
- Idler Pulley(s): These smooth, non-driven pulleys guide the belt and maintain proper tension.
- Tensioner Pulley: Crucially important, the tensioner pulley automatically maintains the correct tension on the drive belt. It usually contains a spring-loaded mechanism or hydraulic damper. A failing tensioner is a common cause of belt problems.
Key specs you might encounter include the belt length (measured in inches or millimeters) and the number of ribs (for serpentine belts). This is important when ordering a replacement belt; make sure you get the right one for your vehicle's make, model, and engine. Using the wrong belt can cause it to slip, wear out prematurely, or even break.
How It Works
The principle is simple: the engine's crankshaft turns the crankshaft pulley, which then turns the drive belt. The belt wraps around the various accessory pulleys (alternator, power steering pump, AC compressor), transferring the rotational force to them. The tensioner pulley keeps the belt tight, preventing slippage. Think of it like a chain on a bicycle, but instead of transferring power to the rear wheel, it's powering your car's accessories.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting
Here are some common problems and how to diagnose them:
- Squealing Noise: This is often the most common symptom. It usually indicates a slipping belt.
- Possible Causes: Worn belt, loose belt (tensioner failing), contaminated belt (oil or coolant), misaligned pulleys.
- Troubleshooting: Inspect the belt for cracks, glazing (shiny surface), or missing chunks. Check the tensioner to ensure it's moving freely and applying pressure to the belt. Clean the belt and pulleys with a degreaser if they're contaminated.
- Cracked or Frayed Belt: This is a sign of wear and tear. The belt needs to be replaced ASAP.
- Possible Causes: Age, excessive heat, misalignment, over-tensioning.
- Troubleshooting: Visually inspect the entire belt for cracks, fraying, or missing ribs. Run your fingers along the belt to feel for any damage.
- Dimming Lights or Battery Not Charging: This could indicate a slipping alternator pulley, which means the alternator isn't generating enough power.
- Possible Causes: Slipping belt, faulty alternator.
- Troubleshooting: Check the belt tension and condition. If the belt seems okay, have the alternator tested.
- Loss of Power Steering or Air Conditioning: If the belt snaps, you'll immediately lose these functions.
- Possible Causes: Broken belt.
- Troubleshooting: Visually inspect the belt. If it's broken, replace it immediately. Also, check for what caused the failure, a seized pulley can put excessive stress on the belt.
Important Tip: A belt dressing product can be used to temporarily silence a squealing belt, but it's just a band-aid. Address the underlying problem, or the noise will return (and the problem will likely worsen).
Safety First
Working on the drive belt system can be dangerous. Never work on the engine while it's running. Even with the engine off, be careful around the belt and pulleys, as they can be sharp and pinch your fingers. The spring tensioner has a lot of force behind it; always use the correct tools to relieve tension before removing the belt. If the tensioner slips out of your control, it could cause serious injury. A breaker bar with correct socket is crucial when dealing with the tensioner.
Also, the engine compartment gets hot, and components can remain hot for a while even after the engine is turned off. Wear gloves to protect your hands.
Finally, always disconnect the negative battery cable before working on any electrical components, including the alternator.
Wrapping Up
Understanding the drive belt system is a crucial step in becoming a more knowledgeable and capable car owner or DIY mechanic. By knowing the components, how they work, and common problems, you can save yourself time, money, and potential headaches down the road. Regularly inspect your drive belt, and replace it when necessary, to keep your car running smoothly and reliably.
We have a detailed diagram of a typical serpentine belt system that you can download for reference. It includes labeled components and routing information to help you visualize the system. Just let us know you are interested!
