What Is The Exhaust In A Car
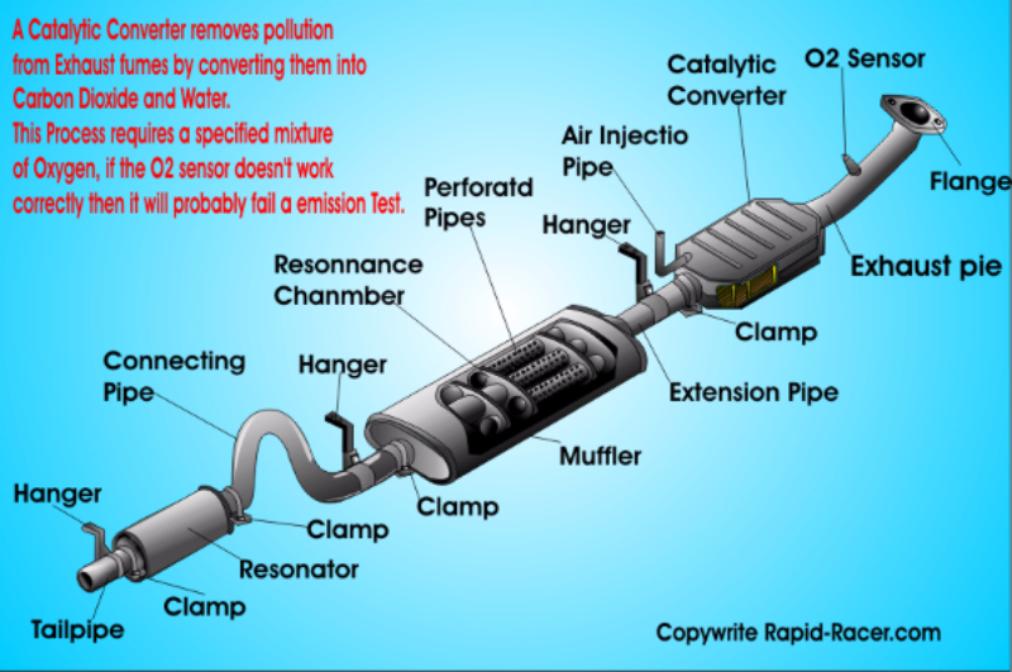
Let's dive into the exhaust system, that unsung hero tucked beneath your car. Understanding it isn't just about passing emissions tests; it's crucial for performance, fuel efficiency, and even the overall sound of your ride. Whether you're planning a simple repair, considering an aftermarket upgrade, or just curious about how your car works, knowing the ins and outs of the exhaust system is essential. This article is designed to equip you with that knowledge, explained in a way that's both technically accurate and easy to grasp.
Purpose of Understanding the Exhaust System
Why bother learning about your exhaust? Well, a solid grasp of its function and components empowers you to:
- Diagnose Problems: Identify unusual noises, reduced performance, or increased fuel consumption that could be related to exhaust issues.
- Perform Basic Repairs: Replace a rusty muffler, tighten loose connections, or patch small leaks yourself, saving on labor costs.
- Make Informed Modifications: Understand the impact of aftermarket exhaust components on your car's performance, sound, and emissions. This helps avoid costly mistakes and choose parts that actually deliver the desired results.
- Pass Emissions Tests: Address problems that could lead to failing an emissions test, keeping your car legal and environmentally friendly.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The exhaust system is more than just a pipe; it's a carefully engineered series of components working in concert. Here's a breakdown of the main players:
- Exhaust Manifold: The starting point. Bolted directly to the engine's cylinder head, it collects exhaust gases from each cylinder. These manifolds are often made of cast iron or, in performance applications, stainless steel for better flow and heat resistance.
- Catalytic Converter: This is the environmental guardian. It uses catalysts (platinum, palladium, and rhodium) to convert harmful pollutants like hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and nitrogen (N2). Catalytic converters are required by law in most vehicles.
- Oxygen Sensors (O2 Sensors): Crucial for engine management. Typically, there's one before (upstream) and one after (downstream) the catalytic converter. The upstream sensor monitors the exhaust gas composition and provides feedback to the engine control unit (ECU) to adjust the air-fuel ratio. The downstream sensor monitors the converter's efficiency.
- Resonator (Optional): A chamber designed to cancel out certain frequencies, helping to reduce unwanted droning or raspiness in the exhaust note.
- Muffler: The primary sound deadener. It uses baffles and chambers to reduce the noise level of the exhaust gases before they exit the tailpipe. Mufflers come in various designs, each affecting the sound characteristics differently.
- Piping: Connects all the components. Usually made of steel (aluminized or stainless), its diameter and routing can affect exhaust flow and performance.
- Flanges and Gaskets: These provide sealed connections between exhaust components. They are susceptible to leaks due to heat and corrosion.
- Hangers: Rubber or metal mounts that support the exhaust system and prevent vibrations from being transmitted to the chassis.
Understanding Common Symbols in Exhaust Diagrams
Exhaust system diagrams often use specific symbols to represent components and features. Here's a quick guide:
- Solid Lines: Represent the main exhaust pipes carrying gases. The thickness of the line might indicate the pipe diameter.
- Dashed Lines: Often indicate vacuum lines related to exhaust control systems or secondary air injection systems.
- Boxes or Rectangles: Usually represent components like the catalytic converter, muffler, or resonator.
- Circles: May represent sensors (O2 sensors, temperature sensors) or small components like vacuum actuators.
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of exhaust gas flow.
- Shading or Colors: Sometimes used to differentiate between materials (e.g., stainless steel vs. aluminized steel) or to highlight specific parts in the system. Consult the diagram's legend for specific meanings.
How It Works: The Exhaust Process
The exhaust system's function is to efficiently remove combustion byproducts from the engine while minimizing noise and harmful emissions. Here's the step-by-step process:
- Exhaust Stroke: During the engine's exhaust stroke, the exhaust valve opens, and the piston pushes the burnt gases out of the cylinder.
- Collection in the Manifold: The exhaust gases from all cylinders enter the exhaust manifold. Manifold design can significantly impact exhaust flow and engine performance. A well-designed manifold minimizes backpressure.
- Catalytic Conversion: The exhaust gases pass through the catalytic converter, where harmful pollutants are chemically converted into less harmful substances. This process requires high temperatures to function effectively.
- Oxygen Sensor Feedback: Upstream O2 sensors monitor the exhaust gas composition and send signals to the ECU, which adjusts the air-fuel mixture to optimize combustion and catalytic converter efficiency. Downstream sensors verify the converter's performance.
- Sound Attenuation: The exhaust gases then flow through the resonator (if equipped) and the muffler, where sound waves are dampened to reduce noise levels.
- Exit Through the Tailpipe: Finally, the treated exhaust gases exit the system through the tailpipe into the atmosphere.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some common exhaust system problems and troubleshooting tips:
- Loud Exhaust: Often indicates a leak in the system, commonly at flanges or around the muffler. Visually inspect for rust, holes, or cracks. Check for loose connections.
- Reduced Performance/Poor Fuel Economy: Could be caused by a clogged catalytic converter, a leaking exhaust manifold, or a faulty O2 sensor. Have the system professionally inspected if you suspect a clogged converter.
- Check Engine Light (CEL): Many exhaust-related issues can trigger the CEL. Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the error code and diagnose the problem. Common codes include those related to O2 sensors and catalytic converter efficiency.
- Rattling or Vibration: Could indicate a loose exhaust hanger, a broken internal component in the muffler, or an exhaust pipe contacting the chassis. Inspect the hangers and the entire system for physical contact.
- Smell of Exhaust Inside the Cabin: Extremely dangerous! Indicates a leak in the exhaust system allowing toxic gases to enter the vehicle. Have it repaired immediately.
Safety Precautions
Working on the exhaust system presents several safety hazards:
- Heat: The exhaust system gets incredibly hot. Always allow the system to cool completely before working on it. Touching a hot exhaust pipe can cause severe burns.
- Exhaust Gases: Exhaust gases contain carbon monoxide, which is odorless, colorless, and deadly. Never run the engine in an enclosed space while working on the exhaust system. Ensure adequate ventilation.
- Rust and Corrosion: Exhaust systems are prone to rust and corrosion, which can weaken components and make fasteners difficult to remove. Use penetrating oil and appropriate tools to avoid damaging parts. Wear gloves to protect your hands from sharp edges and debris.
- Jack Stands: Always use jack stands to support the vehicle when working underneath it. Never rely solely on a jack.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from flying debris and rust particles.
The exhaust system is a vital part of your car's operation, impacting performance, emissions, and even your driving experience. By understanding its components, function, and potential problems, you can better maintain your vehicle and make informed decisions about repairs and modifications. Remember to always prioritize safety when working on any automotive system.
We have a detailed diagram of a generic exhaust system available for download. This diagram provides a visual representation of the components discussed in this article, along with annotations and explanations. It's a valuable resource for anyone looking to further their understanding of automotive exhaust systems. You can download it here.
