What Is The Exhaust On A Car
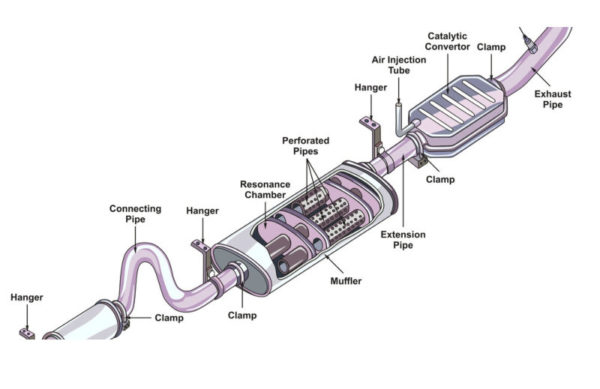
So, you're looking to understand the exhaust system on your car. That's great! Knowing the ins and outs of this often-overlooked system can save you money on repairs, help you diagnose performance issues, and even guide you in making smart modifications. We're going to break down the components, how they work together, and even some basic troubleshooting. Think of this as a deep dive, but in a way that makes sense even if you're not a seasoned mechanic. Plus, we have a detailed diagram you can download to really get a good visual of everything we discuss.
Purpose of Understanding Your Exhaust System
Why bother learning about your exhaust system? Well, for starters, it's crucial for proper engine function. A faulty exhaust can lead to reduced power, poor fuel economy, and even engine damage. Understanding the system allows you to:
- Diagnose Problems: Recognize symptoms like unusual noises, smells, or performance drops.
- Perform Basic Repairs: Replace mufflers, catalytic converters (where legally allowed), or exhaust pipes yourself.
- Make Informed Modifications: Choose the right aftermarket parts to improve performance or sound without causing issues.
- Understand Emissions Regulations: Stay compliant with local laws regarding exhaust modifications and pollution control.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The exhaust system is more than just a pipe sticking out the back. It's a carefully engineered system designed to safely remove exhaust gases from your engine while minimizing pollution and noise. Here's a breakdown of the main components:
1. Exhaust Manifold
The exhaust manifold is the first part of the system, bolted directly to the engine's cylinder head. Its purpose is to collect exhaust gases from each cylinder and funnel them into a single pipe. It's exposed to extremely high temperatures and pressures.
2. Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter is a crucial emissions control device. It uses chemical reactions to convert harmful pollutants like carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC), and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and nitrogen (N2). It contains a ceramic honeycomb coated with precious metals like platinum, palladium, and rhodium, which act as catalysts.
3. Oxygen Sensors (O2 Sensors)
Oxygen sensors (usually one before and one after the catalytic converter) measure the amount of oxygen in the exhaust stream. This data is sent to the engine control unit (ECU), which uses it to fine-tune the air-fuel mixture for optimal combustion and emissions control. The upstream sensor is critical for fuel trim, while the downstream sensor monitors the efficiency of the catalytic converter.
4. Muffler
The muffler is designed to reduce exhaust noise. It uses a series of chambers and baffles to cancel out sound waves without significantly restricting exhaust flow. There are different types of mufflers, each with varying levels of noise reduction and performance characteristics.
5. Resonator (Optional)
A resonator is another noise reduction device, often used in conjunction with a muffler. It's designed to target specific frequencies of sound, further reducing unwanted noise or drone. Some performance exhaust systems omit the resonator for a louder sound.
6. Exhaust Pipes
Exhaust pipes connect all the components together, carrying the exhaust gases from the manifold to the tailpipe. They are typically made of steel or stainless steel and are designed to withstand high temperatures and corrosion.
7. Tailpipe
The tailpipe is the final section of the exhaust system, directing the exhaust gases away from the vehicle and into the atmosphere.
Symbols and Lines on an Exhaust Diagram
Exhaust system diagrams use standard symbols and lines to represent the various components and connections. Here’s a quick guide:
- Solid Lines: Indicate exhaust pipes.
- Dashed Lines: Might indicate vacuum lines (related to emissions control) or electrical wiring for sensors.
- Rectangles: Often represent catalytic converters or mufflers.
- Circles: Can represent sensors (O2 sensors, temperature sensors).
- Arrows: Show the direction of exhaust gas flow.
Color-coding is rare on basic diagrams but more common on interactive or electronic versions. Color might indicate temperature zones or the type of material used.
How It Works: The Exhaust Process
The exhaust system works in a sequence of steps:
- Combustion: Fuel and air are burned inside the engine cylinders, producing power and exhaust gases.
- Collection: The exhaust manifold collects the hot gases from each cylinder.
- Conversion: The catalytic converter reduces harmful pollutants.
- Monitoring: Oxygen sensors provide feedback to the ECU about the air-fuel mixture and catalytic converter efficiency.
- Noise Reduction: The muffler and resonator (if present) reduce exhaust noise.
- Discharge: The tailpipe expels the exhaust gases into the atmosphere.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting
Here are some common exhaust system problems and how to diagnose them:
- Loud Exhaust Noise: Could indicate a hole in the exhaust pipe, a damaged muffler, or a loose connection. Visually inspect the system for rust, cracks, or damage.
- Reduced Engine Power: A clogged catalytic converter or a restriction in the exhaust system can reduce engine performance. Consider a backpressure test to check for restrictions.
- Poor Fuel Economy: A faulty oxygen sensor can cause the engine to run rich (too much fuel), leading to poor fuel economy. Use an OBD-II scanner to check for O2 sensor codes.
- Check Engine Light: Many exhaust system problems will trigger the check engine light. Use an OBD-II scanner to read the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and pinpoint the problem. Common codes relate to O2 sensors or catalytic converter efficiency.
- Rattling Noise: Often caused by a loose heat shield or a broken hanger. Check for loose or damaged components.
Important Note: Remember that modifications to your exhaust system might be subject to local laws and regulations. Check your local guidelines before making any changes.
Safety Considerations
Working on an exhaust system can be dangerous due to high temperatures and the presence of harmful gases. Here are some safety precautions:
- Hot Surfaces: Always allow the exhaust system to cool completely before working on it. Exhaust pipes can reach extremely high temperatures and cause severe burns.
- Harmful Gases: Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling exhaust gases. Carbon monoxide is odorless and deadly.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris and rust.
- Gloves: Wear gloves to protect your hands from cuts and burns.
- Lifting: Use jack stands to support the vehicle safely. Never work under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
- Welding: If welding is required, take proper precautions, including wearing a welding helmet, gloves, and protective clothing.
The catalytic converter is a particularly risky component. It contains harmful materials, and disturbing it without proper knowledge can be dangerous. If you suspect a catalytic converter issue and are not experienced, consider taking your car to a professional.
By understanding your car's exhaust system, you can keep your car running efficiently, safely, and in compliance with regulations. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult with a qualified mechanic if you're unsure about any repairs or modifications.
To help you even further, we have a detailed exhaust system diagram available for download. This diagram provides a visual representation of all the components and their relationships. With this resource and the information provided here, you'll be well-equipped to tackle exhaust system maintenance and repairs!
