What Is Typical Apr On Car Loans
Alright, let's talk about Annual Percentage Rates (APRs) on car loans. It's a crucial aspect of car ownership that can significantly impact your wallet, so understanding the nitty-gritty is essential, whether you're a seasoned DIY mechanic, a modder, or just a car owner looking to make informed decisions.
Purpose - Why APR Matters
Understanding car loan APRs is vital for several reasons:
- Budgeting & Financial Planning: Knowing your APR helps you accurately predict your monthly payments and the total cost of the vehicle over the life of the loan. This allows for better budgeting and financial planning.
- Comparing Loan Offers: APR provides a standardized way to compare different loan offers. A lower APR translates to less interest paid over the loan term.
- Negotiating Power: Understanding APR and the factors that influence it gives you more leverage when negotiating loan terms with lenders.
- Refinancing Opportunities: Knowing your current APR allows you to assess whether refinancing your loan could save you money.
- Avoiding Financial Pitfalls: A high APR can quickly lead to financial stress. Understanding the implications helps you avoid taking on unaffordable debt.
Key Specs and Main Parts of a Car Loan APR
The APR isn't just the interest rate. It's the true cost of borrowing money, expressed as a yearly percentage. This includes the interest rate itself, plus any additional fees associated with the loan. Let's break down the key components:
- Nominal Interest Rate: This is the stated interest rate on the loan. It's the base percentage used to calculate interest accrual.
- Fees: These can include origination fees (charged by the lender for processing the loan), application fees, and other administrative costs. These fees are factored into the APR calculation.
- Loan Term: The length of time you have to repay the loan (e.g., 36 months, 60 months, 72 months). A longer term usually means lower monthly payments but higher total interest paid.
- Principal: The amount of money you borrow. This is the purchase price of the car minus any down payment.
- Down Payment: The amount of money you pay upfront towards the purchase of the car. A larger down payment reduces the principal and can often lead to a lower APR.
Important Terminology:
Amortization: This refers to the process of gradually paying off a loan over time through regular payments. Each payment includes both principal and interest.
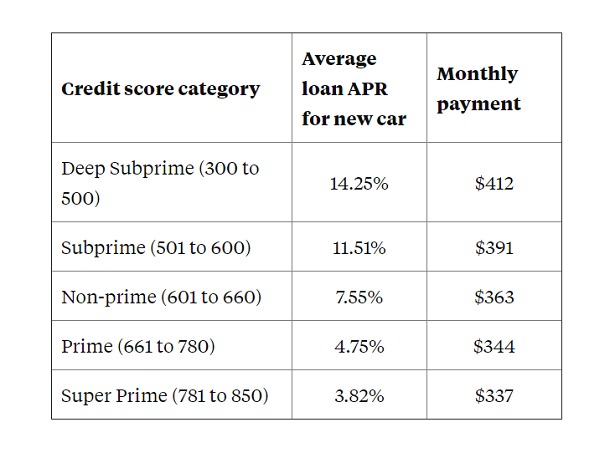
Credit Score: A numerical representation of your creditworthiness. A higher credit score typically results in a lower APR. Lenders use your credit score to assess the risk of lending you money.
Loan-to-Value (LTV) Ratio: This is the ratio of the loan amount to the value of the asset (in this case, the car). A lower LTV ratio (meaning you're borrowing less compared to the car's value) can result in a lower APR.
How APR Works - The Technical Stuff
The APR calculation is actually a bit more complex than simply adding the interest rate and fees. It's designed to reflect the time value of money. This means that money received today is worth more than the same amount of money received in the future, due to its potential earning capacity.
The formula for calculating APR is fairly intricate and usually involves financial calculators or software. However, understanding the core principles is key.
The APR calculation essentially finds the single interest rate that, when applied to the loan principal and fees, would result in the same total cost as the loan with its specific interest rate and fees paid over the loan term. The formula adjusts the interest rate to account for the timing of cash flows (the loan disbursement and the subsequent payments).
Many online APR calculators are available. To use them effectively, you'll need to know:
- The loan amount (principal).
- The loan term (in months).
- The stated interest rate.
- All loan-related fees (origination fees, application fees, etc.).
The calculator will then iterate through different APR values until it finds one that satisfies the present value equation, effectively accounting for all the costs associated with the loan.
Real-World Use – Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Let's look at some practical scenarios:
- High APR: If you're quoted a high APR, the first step is to check your credit report for any errors or negative items. Correct any inaccuracies and work to improve your credit score. You can also shop around for loan offers from different lenders.
- Hidden Fees: Carefully review the loan agreement to identify any hidden fees. Ask the lender to explain any charges you don't understand. Don't be afraid to negotiate these fees.
- Long Loan Term: While a longer loan term lowers your monthly payments, it significantly increases the total interest you pay. If possible, opt for a shorter loan term to save money in the long run.
- Refinancing: If interest rates have dropped since you took out your car loan, consider refinancing to a lower APR. This can save you a substantial amount of money over the life of the loan.
- Dealer Financing vs. Direct Lending: Dealers often offer financing, but it's crucial to compare their offers with those from banks and credit unions directly. Sometimes, direct lending can offer better rates and terms.
Safety – Risky APR Components
Be aware of these potential risks:
- Variable APRs: Some car loans have variable APRs, which means the interest rate can change over the life of the loan. This can make budgeting difficult and potentially lead to higher payments. If you opt for a variable APR, understand how the rate is determined and what factors could cause it to increase.
- Predatory Lending: Be wary of lenders who offer loans with extremely high APRs or unreasonable terms. These lenders often target borrowers with poor credit and can trap them in a cycle of debt.
- Balloon Payments: Some loans have a large lump-sum payment due at the end of the loan term. This can be difficult to manage and may require you to refinance the loan.
It's always a good idea to consult with a financial advisor before taking out a car loan, especially if you have any concerns about your credit or ability to repay the loan.
Remember, understanding the APR on your car loan is crucial for making informed financial decisions. Don't be afraid to ask questions and shop around for the best possible rates and terms. A little bit of research can save you a significant amount of money in the long run.
We have a detailed APR calculation spreadsheet available for download. This tool can help you analyze different loan scenarios and make informed decisions about your car financing.
