What Model Transmission Do I Have
Alright, let's dive into figuring out what transmission you're rocking in your ride. Identifying your transmission model is crucial for a whole host of reasons. Whether you're planning a simple fluid change, tackling a more complex repair, considering performance upgrades, or just trying to understand your vehicle better, knowing the specific transmission model is absolutely essential. This article will guide you through the process, touching on key components, operation, and potential issues. And remember, while we're covering a lot of ground, this article is meant as a guide. Always consult your vehicle's service manual or a qualified professional for specific procedures and safety precautions.
Why Knowing Your Transmission Matters
Understanding your transmission model isn't just about bragging rights. It's a fundamental piece of knowledge that unlocks a world of information. Here's why it's so important:
- Repairs and Maintenance: Different transmissions have different service intervals, fluid requirements, and common failure points. Knowing your transmission means using the correct fluids, filters, and parts, preventing costly mistakes and extending the transmission's lifespan.
- Performance Upgrades: Planning to boost your vehicle's horsepower? Your transmission needs to be able to handle the added torque. Knowing your transmission's specifications allows you to choose compatible upgrades like shift kits, torque converters, or even a complete transmission swap.
- Troubleshooting: When your transmission starts acting up – slipping, hard shifting, or making strange noises – knowing the model helps you narrow down the potential causes and find the right diagnostic information.
- Parts Identification: From filters to solenoids to valve bodies, every transmission has unique parts. Knowing your transmission model ensures you order the correct replacements.
- Learning and Understanding: Delving into your transmission's specifics gives you a deeper understanding of how your vehicle works. It empowers you to be a more informed car owner and DIY enthusiast.
Key Specifications and Main Parts
Before we start digging into diagrams, let's familiarize ourselves with some key transmission specifications and components. These terms will pop up frequently as you research your transmission model.
Key Specs:
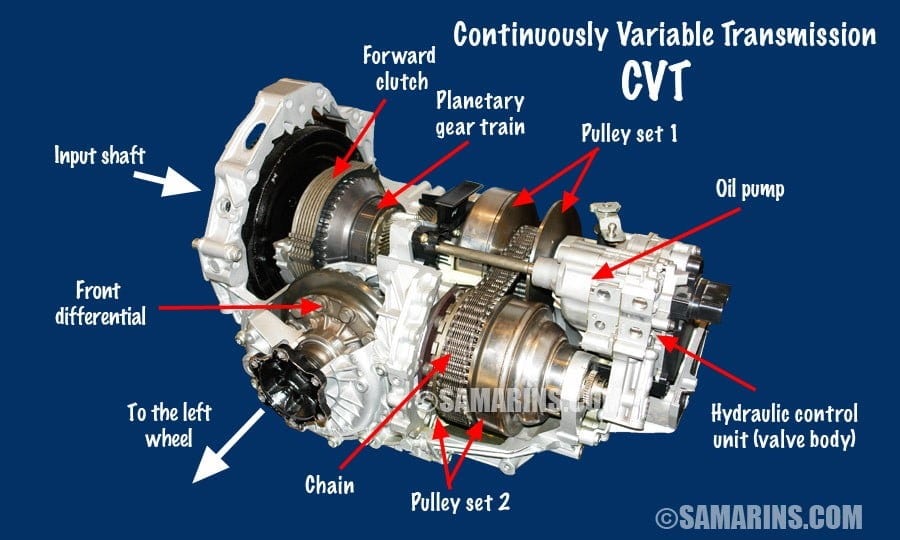
- Type: Automatic, Manual, CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission), DCT (Dual Clutch Transmission). This is the broadest classification.
- Number of Gears: 4-speed, 5-speed, 6-speed, 8-speed, 10-speed, etc. More gears generally mean better fuel economy and smoother acceleration.
- Gear Ratios: The ratio between the engine's RPM and the wheels' RPM for each gear. These ratios determine the vehicle's acceleration and top speed.
- Torque Capacity: The maximum amount of torque the transmission can handle without failing. This is crucial for performance upgrades.
- Fluid Type: Each transmission requires a specific type of fluid (e.g., Dexron VI, Mercon V, ATF+4). Using the wrong fluid can cause serious damage.
- Manufacturer: GM, Ford, Aisin Warner, ZF, etc. Knowing the manufacturer helps narrow down the possibilities.
Main Parts:
- Torque Converter (Automatic Transmissions): Replaces the clutch in a manual transmission, allowing the engine to spin independently of the transmission at low speeds.
- Clutch (Manual Transmissions): Disengages the engine from the transmission, allowing you to shift gears.
- Gears: Different-sized gears provide different gear ratios.
- Valve Body (Automatic Transmissions): Controls the flow of hydraulic fluid to actuate clutches and bands, controlling gear shifts.
- Solenoids (Automatic Transmissions): Electrically controlled valves that direct fluid flow in the valve body.
- Planetary Gear Sets: Complex gear arrangements that provide multiple gear ratios in a compact space.
- Transmission Control Module (TCM): The computer that controls the automatic transmission's operation, including shift points and torque converter lockup.
- Input Shaft: Connects the engine to the transmission.
- Output Shaft: Connects the transmission to the driveshaft or axles.
- Transmission Housing: The main body of the transmission, which houses all the internal components.
Identifying Your Transmission
Okay, let's get down to the nitty-gritty. How do you actually figure out what transmission you have?
- Check Your Vehicle's Service Manual: This is the most reliable source of information. The manual will usually list the transmission model under the "Specifications" section.
- Look for a Transmission Identification Tag: Many transmissions have a metal tag or sticker attached to the transmission housing. This tag will contain the transmission model number and other relevant information. Look carefully, as these tags can be small and easily overlooked. Locations vary, but common spots include the side of the transmission case or near the bellhousing (where the transmission bolts to the engine).
- VIN Decoder: Use an online VIN decoder to find out the original specifications of your vehicle. While this might not be accurate if the transmission has been replaced, it's a good starting point. Most decoders will provide the original transmission type.
- Visual Inspection: Compare your transmission to images and diagrams of different models. This can be tricky, but with practice, you can often narrow down the possibilities based on the transmission's shape, size, and the location of various components.
- Consult a Mechanic: If you're still unsure, take your vehicle to a trusted mechanic. They will have the expertise and tools to identify your transmission model.
How It Works (Briefly)
A simplified explanation is needed here, because each transmission type is a vast topic. Let’s just touch on the basics of automatic and manual transmission operation:
- Automatic Transmissions: Use hydraulic pressure to engage clutches and bands, which control the planetary gear sets. The valve body and solenoids regulate this pressure based on engine speed, vehicle speed, and throttle position. The TCM tells the solenoids what to do, based on sensor inputs. The torque converter multiplies engine torque at low speeds.
- Manual Transmissions: Rely on the driver to manually select gears using a clutch and a shifter. The clutch disengages the engine from the transmission, allowing the driver to move the gear selector. Shifting forks move synchronizers, which mesh the desired gear with the output shaft.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting
Now that you know what kind of transmission you have, here are some basic troubleshooting tips:
- Slipping: Could be low fluid, worn clutches (automatic), or a worn clutch disc (manual). Check fluid levels first.
- Hard Shifting: Could be low fluid, a malfunctioning valve body (automatic), or worn synchronizers (manual).
- No Shifting: Could be a faulty solenoid (automatic), a broken shift linkage (manual), or a major internal failure.
- Unusual Noises: Grinding, whining, or clunking sounds can indicate various problems, from worn bearings to damaged gears.
Important Note: These are just general guidelines. Always consult your vehicle's service manual or a qualified professional for specific diagnostic procedures.
Safety
Working on transmissions can be dangerous. Here are some key safety precautions:
- Always disconnect the battery before working on any electrical components. This prevents accidental shocks.
- Support the vehicle securely on jack stands. Never work under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
- Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from flying debris.
- Be careful when handling transmission fluid. It can be hot and slippery.
- Be aware of the potential for stored energy in springs and other components. Release this energy carefully to avoid injury.
- Hydraulic fluid can be injected under pressure. Avoid direct contact with skin. This requires immediate medical treatment.
- The torque converter contains a lot of oil, and is very heavy. Support properly when removing.
Transmission work often involves dealing with heavy parts, pressurized fluids, and intricate mechanical components. If you're not comfortable with any aspect of the job, it's best to leave it to a professional. A mistake can be costly and even dangerous.
We have a detailed transmission diagram available for download. This diagram provides a visual representation of a typical automatic transmission, highlighting the location of key components and their relationships to each other. While it may not be specific to your exact transmission model, it offers a valuable overview of transmission architecture and function. Good luck!
