What Should My Rpm Be At 80 Mph
Alright, let's talk about engine RPM at 80 mph. It's a question that pops up a lot, and the answer, as with most things automotive, is "it depends." But we can definitely narrow it down and give you a good understanding of what's normal, what's not, and what factors influence it.
Purpose: Understanding Your Engine's Sweet Spot
Why does knowing your RPM at a given speed matter? Several reasons. First, it's a good indicator of your vehicle's overall health and efficiency. A sudden, unexplained change in RPM at a constant speed could point to a problem like a slipping transmission, a dragging brake, or even engine issues. Second, it's valuable for diagnosing potential mechanical problems or for tuning your car after modifications. Third, understanding the relationship between RPM, speed, and gear ratio is fundamental to becoming a better DIY mechanic. You can use this knowledge to better understand how all of your vehicle's systems interact.
Key Specs and Main Parts
To understand RPM at 80 mph, we need to consider several key specifications and components. These are intertwined and affect the final RPM reading you'll see:
- Engine Size and Characteristics: Larger engines generally produce more torque at lower RPMs. However, factors like engine design (inline, V, rotary), forced induction (turbocharging, supercharging), and valve timing all play significant roles.
- Transmission Gear Ratios: This is perhaps the most critical factor. Each gear in your transmission has a specific ratio. This ratio determines how many times the engine needs to rotate for the wheels to rotate once. Lower gear ratios (numerically larger, like 4.10:1) provide more torque for acceleration but result in higher RPMs at a given speed. Higher gear ratios (numerically smaller, like 2.73:1) offer better fuel economy at highway speeds but less acceleration.
- Final Drive Ratio: Located in the differential, the final drive ratio is another fixed gear reduction. It multiplies the torque coming from the transmission before sending it to the wheels.
- Tire Size: The overall diameter of your tires affects the distance traveled per revolution. Larger diameter tires will result in lower RPMs at a given speed, while smaller tires will increase RPMs. This is because a larger tire covers more ground in a single revolution.
- Lock-up Torque Converter (Automatic Transmissions): Most modern automatic transmissions have a lock-up torque converter. When locked, there's a direct mechanical connection between the engine and transmission, eliminating slippage within the torque converter and improving fuel efficiency. This often results in a noticeable drop in RPM at highway speeds when the lock-up engages.
How It Works: The Math Behind the Motion
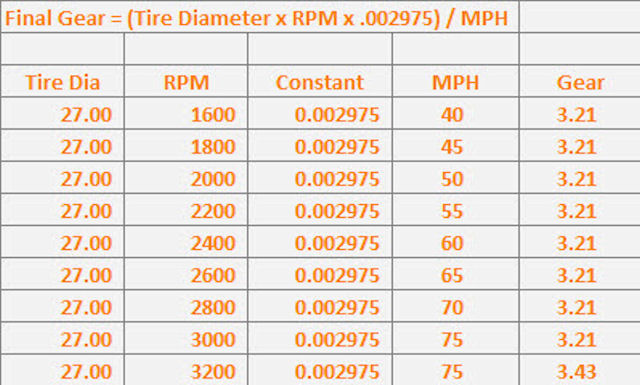
Here’s the basic formula to calculate theoretical RPM at a given speed:
RPM = (Speed (mph) * Gear Ratio * Final Drive Ratio * 336) / Tire Diameter (inches)
Where:
- Speed is the desired speed in miles per hour.
- Gear Ratio is the transmission gear ratio for the gear you are in (usually top gear for highway cruising).
- Final Drive Ratio is the final drive ratio in the differential.
- 336 is a constant used to convert units.
- Tire Diameter is the overall diameter of your tires in inches. You can calculate this from the tire sidewall markings. For example, a tire marked 225/50R17 means: 225mm section width, 50% aspect ratio (sidewall height is 50% of the section width), and 17-inch wheel diameter. You'd calculate the sidewall height as 225mm * 0.50 = 112.5mm. Then, the overall diameter would be (112.5mm * 2) + (17 inches * 25.4 mm/inch) = 656.8mm. Convert that to inches by dividing by 25.4: 656.8 / 25.4 = 25.86 inches (approximately).
Let's do an example. Suppose we have a car with the following specs:
- Speed: 80 mph
- Gear Ratio (top gear): 0.8:1
- Final Drive Ratio: 3.55:1
- Tire Diameter: 26 inches
RPM = (80 * 0.8 * 3.55 * 336) / 26 = 2920 RPM (approximately)
This is a theoretical value. In reality, there will be slight variations due to tire slippage, aerodynamic drag, and drivetrain losses.
Real-World Use and Troubleshooting
Now, let's get practical. What if your RPM at 80 mph seems off? Here are some basic troubleshooting tips:
- Verify Your Speedometer: Ensure your speedometer is accurate. Use a GPS app or a known mile marker to check. An inaccurate speedometer will throw off your RPM readings.
- Check Tire Size: Make sure your tires are the correct size for your vehicle. Using the wrong size tires can significantly affect RPM and speedometer readings.
- Listen for Unusual Noises: Whining, grinding, or clunking sounds from the transmission or differential could indicate a problem.
- Monitor Transmission Fluid: Check the level and condition of your transmission fluid. Low or dirty fluid can cause slipping and erratic RPM behavior. A burnt smell means there is a serious problem.
- Scan for Error Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to check for any trouble codes. Some transmission problems will trigger a code.
- Consider a Transmission Service: If your transmission hasn't been serviced in a while, a fluid and filter change might be in order.
If you notice a significant and persistent difference between your actual RPM and the theoretical RPM, consult a qualified mechanic. It could be a sign of a serious problem that needs professional attention.
Safety: High-Stress Components
When dealing with drivetrain components, safety is paramount. Here are a few risky areas to be aware of:
- Rotating Parts: Never work around rotating parts (like the driveshaft or wheels) while the engine is running. Even at low speeds, these parts can cause serious injury.
- Hot Exhaust: The exhaust system gets extremely hot. Allow it to cool completely before working near it.
- Jacking Up the Car: Always use jack stands when working under a vehicle. Never rely solely on a jack. Ensure the vehicle is on a level surface.
- Transmission Fluid: While not highly toxic, used transmission fluid can contain contaminants. Wear gloves and avoid getting it on your skin. Dispose of used fluid properly at a recycling center.
Diagram and Further Resources
We've put together a detailed diagram illustrating the relationship between engine RPM, gear ratios, tire size, and vehicle speed. This diagram provides a visual representation of the calculations we discussed and can be a valuable tool for understanding how these factors interact. It also includes typical RPM ranges for various vehicles at 80 mph. This comprehensive document, in PDF format, is available for download. Refer to it often as you explore these concepts further.
Remember, understanding your engine's operating characteristics is key to keeping it running smoothly and efficiently. By paying attention to details like RPM at a given speed, you can catch potential problems early and prevent costly repairs down the road. Happy wrenching!
