What Two Colors Make Brown Paint
Ever needed to touch up a spot on your car, customize its interior, or even just repaint a small trim piece and found yourself without the exact shade of brown you need? Understanding the color mixing process, specifically how to create brown paint, can be a lifesaver. This article will delve into the technical aspects of color mixing to produce brown, providing you with the knowledge to accurately and consistently achieve your desired hue.
Why Understanding Color Theory for Automotive Applications Matters
Knowing how to mix your own paint isn't just a fun project; it's a practical skill for any serious car enthusiast or DIY mechanic. Here's why understanding the principles of color theory, particularly for creating brown paint, is essential:
- Cost Savings: Mixing your own paint can be significantly cheaper than purchasing pre-mixed colors, especially for smaller touch-up jobs.
- Precise Color Matching: Achieving an exact match to your vehicle's existing paint color is crucial for seamless repairs. Knowing how to adjust the color allows for perfect blending.
- Customization: Whether you're painting brake calipers, interior trim, or creating a custom pin-stripe, the ability to mix your own colors opens up a world of customization possibilities.
- Availability: Sometimes, the exact shade of brown you need might be discontinued or unavailable. Mixing your own ensures you can always get the color you want.
- Enhanced Skillset: Understanding color theory elevates your skills as a DIY mechanic and gives you more control over your projects.
Key Specs and Main Parts (Primary and Secondary Colors)
The foundation of color mixing lies in understanding primary and secondary colors. Primary colors are the foundational colors that cannot be created by mixing other colors. They are:
- Red
- Yellow
- Blue
Secondary colors are created by mixing two primary colors in equal proportions. They are:
- Green (Blue + Yellow)
- Orange (Red + Yellow)
- Violet (Red + Blue)
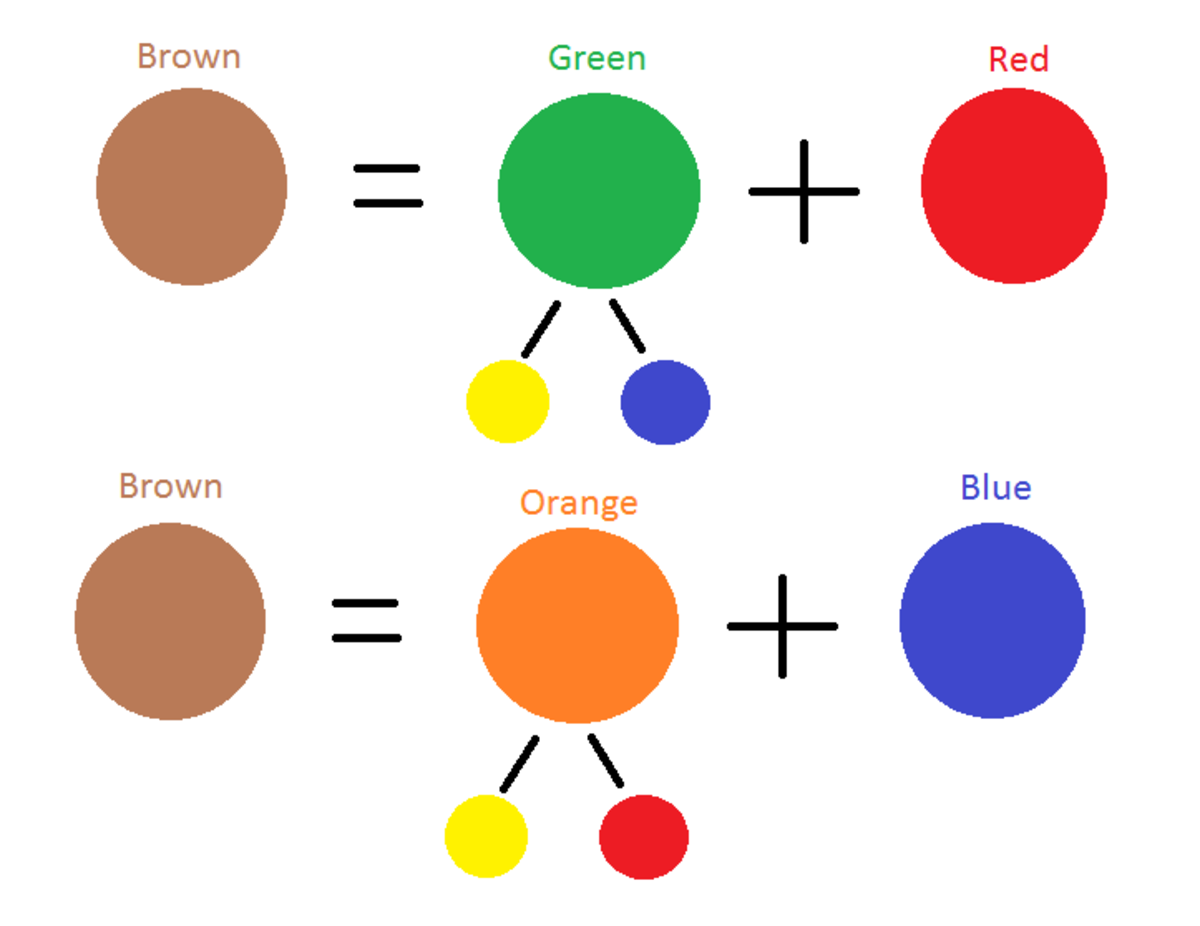
The key to making brown isn't direct mixing of the primary colors (red, yellow and blue). Brown is typically achieved by mixing all three primary colors or by mixing complementary colors.
How It Works: Creating Brown Paint
There are two primary methods for creating brown paint:
1. Mixing All Three Primary Colors (Subtractive Color Mixing)
This method involves combining red, yellow, and blue. This is subtractive color mixing – as you add more pigment, you're subtracting more light, resulting in a darker color. Here's the general process:
- Start with a Base: Choose one color as your base. Often, a small amount of red is a good starting point.
- Add Yellow: Gradually add yellow to the red. This will create a shade of orange.
- Introduce Blue: Slowly incorporate blue into the orange mixture. The blue will neutralize the vibrancy of the orange, pushing it towards brown. This is where the magic happens. The amount of blue added will determine the final shade of brown. Too little blue and you'll have an orange-ish brown; too much, and you'll have a blue-ish brown.
- Adjust and Refine: Continue adding small amounts of each color until you achieve the desired shade of brown. This requires careful observation and incremental adjustments.
2. Mixing Complementary Colors
Complementary colors are colors that sit opposite each other on the color wheel. Mixing complementary colors also creates brown. Some common complementary color pairings include:
- Blue and Orange
- Red and Green
- Yellow and Violet
The process is similar to the first method, but using two colors instead of three. For example, when mixing blue and orange:
- Start with Orange: Begin with a base of orange paint.
- Add Blue Gradually: Introduce blue slowly, mixing thoroughly. The blue will neutralize the orange, creating a brown color.
- Adjust for Desired Hue: Fine-tune the color by adding more orange for a warmer brown or more blue for a cooler brown.
Important Considerations:
- The Quality of Pigments: Use high-quality pigments specifically formulated for automotive use (if you're painting a car). These pigments will provide better color retention, UV resistance, and overall durability. Cheap pigments may fade quickly or have poor coverage.
- The Medium: The type of paint medium (e.g., acrylic lacquer, enamel, urethane) will influence the final color and how it dries. Always use a compatible medium.
- Sheen/Finish: The sheen of the paint (matte, satin, gloss) will also affect how the color appears. Matte finishes tend to make colors appear deeper and richer, while gloss finishes reflect more light, making colors appear brighter.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some common issues you might encounter when mixing brown paint and how to address them:
- Too Orange: Add more blue.
- Too Red: Add more green (if using complementary colors) or blue and yellow (if using the primary colors).
- Too Blue/Purple: Add more orange (if using complementary colors) or red and yellow (if using the primary colors).
- Too Dark: Add white or a lighter shade of yellow to lighten the color. Be very careful with white, as it can quickly desaturate the color.
- Not Opaque Enough: Ensure you're using enough pigment in your mixture. Consider adding an opaque white base coat for better coverage, especially when painting over a darker surface.
- Inconsistent Color: Thoroughly mix the paint before and during application. Inconsistent mixing can lead to color variations.
Safety: Handling Automotive Paints
Working with automotive paints requires certain safety precautions. Many paints contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that can be harmful if inhaled or absorbed through the skin.
- Ventilation: Always work in a well-ventilated area. Consider using a spray booth or working outdoors.
- Respiratory Protection: Wear a respirator specifically designed for paint fumes. A simple dust mask is not sufficient. Look for respirators with organic vapor cartridges.
- Skin Protection: Wear gloves to prevent paint from coming into contact with your skin. Some paint solvents can be absorbed through the skin and cause irritation or other health problems.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses or goggles to protect your eyes from paint splatters.
- Flammability: Be aware that many automotive paints and solvents are highly flammable. Keep them away from open flames, sparks, and heat sources. Dispose of used rags and materials properly to prevent spontaneous combustion.
- Disposal: Dispose of leftover paint and solvents according to local regulations. Do not pour them down the drain.
Diagram Available for Download
We have compiled a comprehensive color mixing diagram that visually demonstrates the ratios and techniques discussed in this article. This diagram serves as a quick reference guide, illustrating the steps required to create various shades of brown paint. You can download the diagram here.
Understanding the principles of color mixing, specifically how to create brown paint, empowers you to take greater control over your automotive projects. With careful practice and attention to detail, you can achieve professional-quality results and customize your vehicle to your exact specifications.
