What Type Of Cars Are There
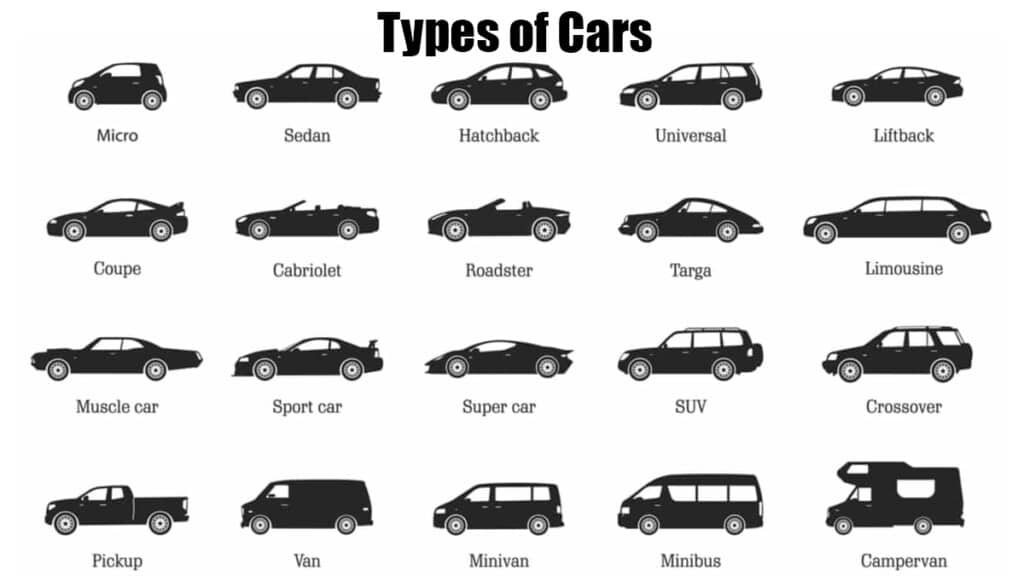
Okay, gearheads, let's dive into a fundamental topic: the diverse landscape of car types. Understanding these categories isn't just trivia; it's crucial for everything from choosing the right replacement parts to diagnosing performance issues and even planning modifications. Think of this as your roadmap to automotive knowledge. We'll break down the key characteristics, functionalities, and even a few safety considerations for each major car type.
Why Understanding Car Types Matters
Knowing your car's classification goes beyond simply knowing its make and model. It impacts:
- Repairs and Maintenance: Different car types have different components and systems. For example, a pickup truck's suspension is drastically different from a compact car's.
- Modifications: Understanding the vehicle's inherent limitations and strengths is essential before attempting any performance enhancements. You wouldn't try to turn a fuel-efficient hybrid into a drag racer without significant (and likely impractical) modifications.
- Troubleshooting: Recognizing the typical behavior of your car type can help you pinpoint problems faster. A subtle vibration in a truck might indicate a U-joint issue, while a similar vibration in a sedan could point to a wheel balance problem.
- Safety: Knowing your vehicle's center of gravity, weight distribution, and braking characteristics is vital for safe driving, especially in adverse conditions.
The Major Car Types
Here's a breakdown of the most common car types:
Sedans
Sedans are typically characterized by their three-box configuration: engine compartment, passenger cabin, and trunk. They generally offer a balance of comfort, fuel efficiency, and practicality.
- Key Specs: Seating for 5, typically front-wheel drive (FWD) or all-wheel drive (AWD). Engine options usually range from fuel-efficient inline-4s to more powerful V6s.
- Main Parts: Unibody construction, independent suspension (often MacPherson struts in the front and multi-link in the rear), hydraulic or electric power steering.
- How It Works: Sedans prioritize ride comfort and handling, making them suitable for daily commuting and family trips. Suspension systems are tuned to absorb bumps and minimize body roll.
Coupes
Coupes are typically two-door vehicles with a sporty or performance-oriented design. They often sacrifice some rear passenger space for a sleeker appearance.
- Key Specs: Seating for 2 or 4 (often with limited rear legroom), RWD or AWD options are common, more powerful engine options compared to sedans (e.g., turbocharged engines, larger displacement).
- Main Parts: Similar construction to sedans but often with a stiffer chassis, sport-tuned suspension, and upgraded braking systems.
- How It Works: Coupes emphasize driving enjoyment. They tend to have quicker acceleration, sharper handling, and a more aggressive exhaust note.
Hatchbacks
Hatchbacks feature a rear liftgate that provides access to a cargo area integrated with the passenger cabin. This design offers enhanced versatility and cargo-carrying capacity compared to sedans.
- Key Specs: Seating for 5, FWD or AWD, typically compact or subcompact in size, often prioritize fuel efficiency.
- Main Parts: Unibody construction, rear suspension designed to maximize cargo space (e.g., torsion beam or multi-link), liftgate with integrated glass.
- How It Works: Hatchbacks are practical and fuel-efficient, making them ideal for city driving and carrying cargo. The rear liftgate allows for easy loading and unloading of larger items.
SUVs (Sport Utility Vehicles)
SUVs are characterized by their higher ground clearance, larger size, and often 4WD or AWD capabilities. They offer a blend of passenger comfort, cargo space, and off-road capability (depending on the specific model).
- Key Specs: Seating for 5-7, AWD or 4WD options, higher ground clearance, body-on-frame or unibody construction. Engine options range from fuel-efficient 4-cylinders to powerful V8s.
- Main Parts: Independent front suspension (often double wishbone), solid axle or independent rear suspension, transfer case (for 4WD models), larger tires, robust braking systems.
- How It Works: SUVs are designed to handle a variety of driving conditions, from city streets to unpaved roads. Their higher ground clearance and optional 4WD make them suitable for off-roading, while their spacious interiors and comfortable ride make them ideal for family trips.
Trucks (Pickups)
Trucks are characterized by their open cargo bed, rugged construction, and towing/hauling capabilities. They are typically available in various cab configurations (e.g., regular cab, extended cab, crew cab) and bed lengths.
- Key Specs: Seating for 2-6, RWD or 4WD, body-on-frame construction, heavy-duty suspension, powerful engine options (e.g., V6, V8, diesel).
- Main Parts: Ladder frame, solid rear axle, leaf spring or coil spring rear suspension, heavy-duty brakes, transfer case (for 4WD models), towing hitch.
- How It Works: Trucks are designed for hauling cargo and towing trailers. Their body-on-frame construction provides strength and durability, while their heavy-duty suspension and powerful engines allow them to handle heavy loads.
Minivans
Minivans are designed for maximum passenger and cargo capacity. They typically feature sliding doors and a spacious interior.
- Key Specs: Seating for 7-8, FWD or AWD, unibody construction, sliding rear doors, focus on passenger comfort and convenience.
- Main Parts: Independent suspension, spacious interior with flexible seating configurations, entertainment systems, power sliding doors and liftgate.
- How It Works: Minivans prioritize passenger comfort and cargo capacity. Their sliding doors make it easy to access the rear seats, and their spacious interiors provide ample room for passengers and luggage.
Hybrids and Electric Vehicles (EVs)
These are *not* car types per se, but powertrain types that can be found in almost any of the above categories. Hybrids combine an internal combustion engine (ICE) with an electric motor, while EVs rely solely on electric power.
- Key Specs: Hybrid models use a battery pack and electric motor to assist the ICE, improving fuel efficiency. EVs have a large battery pack and electric motor(s) for propulsion.
- Main Parts: Battery pack, electric motor(s), regenerative braking system, power electronics, specialized cooling systems.
- How It Works: Hybrids use regenerative braking to capture energy during deceleration, recharging the battery. EVs are powered entirely by electricity, offering zero tailpipe emissions.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are a few basic troubleshooting tips based on car type:
- SUV with 4WD: If the 4WD system isn't engaging, check the transfer case fluid level and the condition of the vacuum lines (if applicable).
- Truck with Leaf Springs: Squeaking from the rear suspension often indicates worn leaf spring bushings.
- Sedan with Independent Suspension: Clunking noises when going over bumps can point to worn ball joints or tie rod ends.
Safety: Highlight Risky Components
Certain components are inherently risky to work on. Always exercise extreme caution and consult a professional if you're unsure.
- High-Voltage Systems (Hybrids/EVs): Battery packs and power electronics operate at extremely high voltages and can be lethal. Only qualified technicians should work on these systems.
- Airbags: Airbags can deploy unexpectedly if handled improperly. Disconnect the battery and follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully.
- Fuel Systems: Gasoline is highly flammable. Work in a well-ventilated area and take precautions to prevent sparks or flames.
- Suspension Components Under Load: Springs can release with tremendous force if not properly compressed. Use appropriate spring compressors and safety equipment.
This information provides a solid foundation for understanding the diverse world of car types. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult a qualified mechanic when dealing with complex or potentially dangerous repairs.
And finally, for those who want a quick-reference diagram to keep on hand, we have a printable PDF file that visually organizes this information. Consider it your handy cheat sheet in the garage.
