What Types Of Cars Are There
Alright, let's dive deep into the world of cars! Knowing the fundamental types of vehicles and their defining characteristics is crucial whether you're planning a restoration project, diagnosing a tricky engine problem, or just want to sound knowledgeable at the next car meet. This overview is designed for those of you who already know your way around a wrench but want a more structured understanding of vehicle classifications.
Why Understanding Car Types Matters
Why bother knowing all this? Well, for starters, a solid grasp of vehicle types directly impacts your ability to:
- Diagnose problems accurately: Knowing the typical drivetrain layout (FWD, RWD, AWD) immediately narrows down potential issues.
- Select the right parts: Accidentally ordering a sway bar link for a sedan when you own a pickup truck is a common (and costly) mistake.
- Understand repair manuals: Repair manuals often assume you know the basics. Knowing the type of car ensures you understand the manual's terminology and instructions.
- Choose the right modifications: Lift kits for SUVs? Performance exhaust for sports cars? Understanding the platform dictates the feasible modifications.
In short, understanding car types saves you time, money, and frustration in the long run.
Classifying Cars: A Breakdown
There are several ways to classify cars. We'll cover the most common:
1. By Body Style
This is the most visually obvious classification.
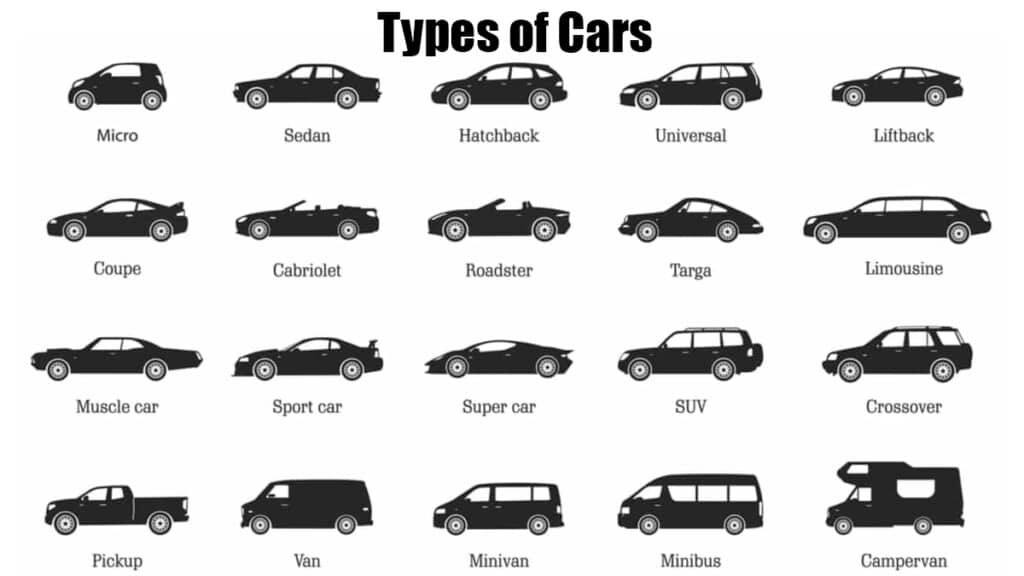
- Sedan: A three-box configuration with a distinct engine compartment, passenger compartment, and trunk. Key specs: Typically 4 doors, seating for 5, separate trunk space. Main parts: Unibody construction, front and rear independent suspension (though solid rear axles exist on older models).
- Coupe: Similar to a sedan, but with a sloping roofline and typically only 2 doors. Key specs: 2 doors, sporty appearance, often smaller rear seats. Main parts: Shorter wheelbase compared to sedans, potentially stiffer suspension.
- Hatchback: A car with a rear door that swings upward, providing access to a cargo area integrated with the passenger compartment. Key specs: 3 or 5 doors (including the hatch), foldable rear seats for increased cargo space. Main parts: Often based on sedan platforms, but with a modified rear structure.
- Station Wagon: An extended version of a sedan or hatchback, with a longer roofline and a larger cargo area behind the rear seats. Key specs: Similar to sedans but with increased cargo capacity. Main parts: Reinforced rear suspension to handle heavier loads.
- SUV (Sport Utility Vehicle): Characterized by a taller ride height, a spacious interior, and often, all-wheel drive. Key specs: High ground clearance, ample cargo space, seating for 5-7 passengers. Main parts: Body-on-frame or unibody construction, often with independent front suspension and a solid rear axle (though independent rear suspension is increasingly common).
- Truck (Pickup): Designed for hauling cargo, with an open cargo bed at the rear. Key specs: High payload capacity, often with 4x4 capability. Main parts: Body-on-frame construction for strength and durability, leaf spring rear suspension for heavy loads.
- Minivan: A van-like vehicle designed for transporting passengers and cargo. Key specs: Sliding side doors, seating for 7-8 passengers, ample cargo space. Main parts: Unibody construction, front-wheel drive (though AWD is available).
- Convertible: A car with a retractable roof, allowing for open-air driving. Key specs: Retractable soft or hard top, often with a sporty appearance. Main parts: Reinforced chassis to compensate for the lack of a fixed roof.
- Roadster: A two-seat convertible. Key specs: Open-top driving experience, sporty handling. Main parts: Lightweight construction, often with a focus on performance.
2. By Drivetrain
This refers to how engine power is transmitted to the wheels.
- FWD (Front-Wheel Drive): The engine powers the front wheels. Key specs: Lighter weight, generally better fuel economy. Main parts: Transaxle (transmission and differential combined), constant velocity (CV) joints.
- RWD (Rear-Wheel Drive): The engine powers the rear wheels. Key specs: Better weight distribution for handling, often used in sports cars and trucks. Main parts: Transmission, driveshaft, differential.
- AWD (All-Wheel Drive): The engine powers all four wheels. Key specs: Improved traction in all weather conditions. Main parts: Transfer case, differentials on both axles.
- 4WD (Four-Wheel Drive): Similar to AWD, but typically designed for off-road use with a selectable low-range gear. Key specs: Increased torque at low speeds for off-road driving. Main parts: Transfer case with low-range gear, locking differentials.
3. By Engine Type
The type of engine also defines the vehicle.
- Gasoline (Petrol): Internal combustion engine using gasoline as fuel. Key specs: Wide range of power outputs, generally responsive throttle. Main parts: Fuel injectors, spark plugs, catalytic converter.
- Diesel: Internal combustion engine using diesel fuel. Key specs: High torque at low speeds, good fuel economy. Main parts: Fuel injectors (often common rail), turbocharger, diesel particulate filter (DPF).
- Electric (EV): Powered by an electric motor and battery pack. Key specs: Zero tailpipe emissions, instant torque. Main parts: Battery pack, electric motor, inverter.
- Hybrid: Combines a gasoline engine with an electric motor. Key specs: Improved fuel economy compared to gasoline-only vehicles. Main parts: Gasoline engine, electric motor, battery pack, regenerative braking system.
Symbols and Conventions (General)
While there isn't a universal diagram for all car types, some conventions are common:
- Solid lines: Typically represent physical connections, like hoses or wires.
- Dashed lines: Often indicate vacuum lines or control signals.
- Colors: Can vary, but red often indicates power (positive battery cable), blue/green for sensors, and black for ground.
- Icons: Specific icons represent components like sensors, actuators, and control modules. A square often represents a sensor, a circle can mean a pump or motor.
Consult the specific wiring diagrams or schematics for the vehicle you're working on for accurate symbol definitions.
How It Works: Putting It All Together
Understanding how different systems interact is key. For example, in a modern car:
- The engine (gasoline, diesel, or electric) generates power.
- The transmission (manual or automatic) manages the engine's power output to the wheels.
- The drivetrain (FWD, RWD, AWD, 4WD) transmits the power to the wheels.
- The suspension system provides a comfortable ride and stable handling.
- The braking system allows the driver to slow down or stop the vehicle.
- Electronic sensors and control modules monitor and adjust various systems for optimal performance and safety.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting
Let's say your RWD sedan is experiencing poor traction in wet conditions. Understanding the drivetrain immediately points you toward:
- Tire condition: Are the tires worn?
- Tire pressure: Is it correct?
- Suspension components: Are the shocks or struts worn?
- Differential condition: Is there excessive wear or damage?
Compare that to a FWD vehicle with the same issue, where the focus would be on the front tires, suspension, and transaxle.
Safety: Risky Components
Always prioritize safety when working on cars!
- High-voltage electrical systems (EVs and Hybrids): Extremely dangerous. Always disconnect the high-voltage battery according to the manufacturer's instructions and wait the specified time for capacitors to discharge. Never assume a system is safe.
- Fuel system: Gasoline and diesel are flammable. Work in a well-ventilated area and avoid sparks.
- Brake system: Brake fluid is corrosive. Wear eye protection and gloves.
- Airbags: Can deploy unexpectedly if mishandled. Disconnect the battery and wait before working near airbags.
Never underestimate the potential dangers of working on cars. When in doubt, consult a qualified professional.
We have a detailed vehicle type diagram available for download. It covers more detail on sub-types and examples. This reference diagram provides a visual aid to help you further understand these classifications.
