What Weight Should I Be At 6ft
Determining the ideal weight for someone who is 6 feet tall isn't an exact science. Unlike diagnosing a car engine problem, where a diagnostic code directly points to a faulty sensor, body weight involves a complex interplay of factors. However, just as understanding a car's wiring diagram helps you pinpoint electrical issues, understanding the concepts and metrics involved in healthy weight ranges can guide you towards a healthier and more fulfilling lifestyle. Think of this article as your guide to understanding the “weight diagram” – a roadmap to interpreting the various metrics that help determine a healthy weight range for your height.
Purpose: Understanding Your Personal “Weight Diagram”
Why bother figuring out a target weight? Just like understanding a car's electrical system allows for effective repairs and performance enhancements, knowing your healthy weight range offers several benefits:
- Health Optimization: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers. This is akin to performing preventive maintenance on your car to avoid costly breakdowns later.
- Improved Physical Performance: Whether you're modifying your car for better handling or improving your fitness, both require an understanding of optimal conditions. A healthy weight can enhance your energy levels, stamina, and overall physical capability.
- Enhanced Body Composition: It's not just about the number on the scale. Understanding healthy weight ranges helps you focus on building lean muscle mass and reducing body fat. Think of it as optimizing your car's power-to-weight ratio.
- Increased Longevity: Studies show a correlation between maintaining a healthy weight and living a longer, healthier life, much like proper care and maintenance can extend the lifespan of your vehicle.
Key Specs and Main Parts: Decoding the Metrics
Several metrics are used to determine a healthy weight range. Just as a car's specifications include engine displacement, horsepower, and torque, human body metrics include BMI, body fat percentage, and waist circumference.
Body Mass Index (BMI)
The Body Mass Index (BMI) is a widely used, though imperfect, measure. It’s calculated using your weight and height. The formula is weight (kg) / [height (m)]2. Alternatively, using US customary units: weight (lb) / [height (in)]2 x 703.
BMI categories are:
- Underweight: BMI less than 18.5
- Normal weight: BMI between 18.5 and 24.9
- Overweight: BMI between 25 and 29.9
- Obese: BMI of 30 or greater
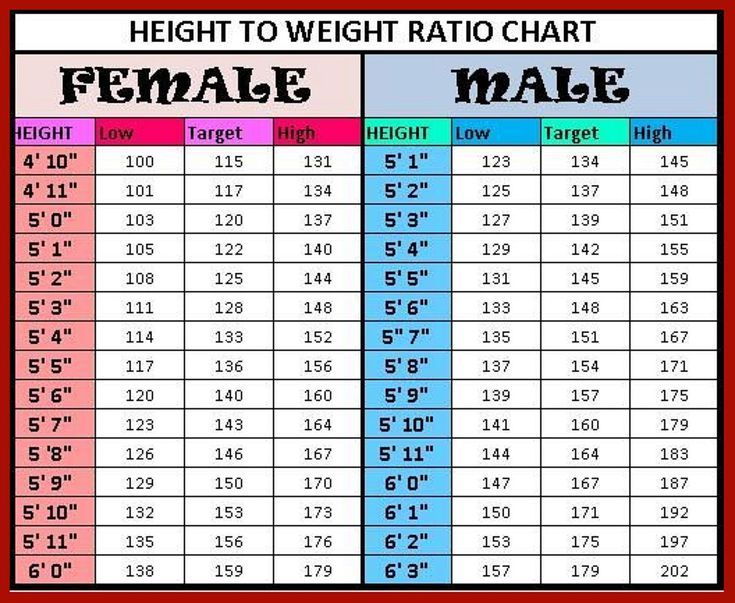
For a 6-foot (72 inches or approximately 1.83 meters) individual, a "normal" BMI would translate to the following weight range:
Minimum weight: 18.5 x (1.83 m)2 = 61.9 kg (approximately 136.5 lbs)
Maximum weight: 24.9 x (1.83 m)2 = 83.3 kg (approximately 183.7 lbs)
Therefore, according to BMI, a healthy weight range for a 6-foot individual is roughly 136.5 lbs to 183.7 lbs. But remember, this is just a starting point. BMI has limitations. It doesn't differentiate between muscle mass and fat mass. A muscular athlete might have a BMI in the "overweight" range despite having very little body fat. This is similar to a modified car with a powerful engine – its stock appearance might mislead an observer about its true performance capabilities.
Body Fat Percentage
Body fat percentage provides a more accurate picture of body composition. It represents the proportion of your body weight that is fat. Healthy body fat ranges vary by age and gender. Generally:
- Men: 10-20% is considered healthy.
- Women: 18-28% is considered healthy.
Measuring body fat percentage requires specialized equipment, such as skinfold calipers, bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) scales, or DEXA scans. These methods, while more accurate than BMI, also have their limitations in terms of precision and accessibility. Think of these methods as different diagnostic tools for your car – some are more precise than others, and some are more readily available.
Waist Circumference
Waist circumference is another important indicator of health risk. Excess abdominal fat (visceral fat) is strongly linked to increased risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and other health problems. Recommendations generally state that:
- Men: Waist circumference should be less than 40 inches (102 cm).
- Women: Waist circumference should be less than 35 inches (88 cm).
Waist circumference is easily measured with a tape measure. A high waist circumference, even with a "normal" BMI, should be a red flag to address dietary and lifestyle habits. This is akin to noticing a strange noise coming from your engine, even if all the gauges appear normal.
Other Factors
Remember that your ideal weight is also influenced by factors such as:
- Age
- Genetics
- Activity Level
- Overall Health Condition
Symbols: Interpreting the "Weight Diagram"
In this "weight diagram", there aren't literal symbols like resistors or diodes in an electrical schematic. Instead, consider the following:
- Ranges: Instead of a single ideal weight, think of a healthy range. This is analogous to a torque spec for a bolt – it’s not a single number, but a range that ensures proper tightening without damage.
- Trends: Monitor trends over time, not just single measurements. A gradual increase or decrease in weight, body fat, or waist circumference can be more informative than a single snapshot. Think of it as monitoring your car’s fuel efficiency over time to detect potential issues.
- Individual Variation: Recognize that everyone is different. What's healthy for one person might not be healthy for another. This is similar to how different car models have different performance characteristics and maintenance needs.
How It Works: Putting It All Together
Determining your ideal weight is an iterative process, much like tuning a car engine. Start with the BMI range as a guideline. Then, assess your body fat percentage and waist circumference. Consider your activity level and overall health. Are you an athlete with a significant amount of muscle mass? Are you sedentary with a high body fat percentage? Adjust your target weight range accordingly.
Focus on making sustainable lifestyle changes. A healthy diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep are essential for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight. This is analogous to performing regular maintenance on your car – it's a long-term commitment, not a quick fix.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some common scenarios and how to address them:
- BMI is high, but you have low body fat: You likely have a significant amount of muscle mass. Focus on maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine.
- BMI is normal, but your waist circumference is high: Focus on reducing visceral fat through diet and exercise. Pay particular attention to reducing processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated fats.
- You're struggling to lose weight despite diet and exercise: Consult a healthcare professional to rule out underlying medical conditions that might be affecting your metabolism.
Safety: Components Requiring Expert Attention
Attempting drastic weight loss measures can be dangerous. Just as modifying your car without proper knowledge can lead to serious problems, rapid weight loss can have adverse health consequences. Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making significant changes to your diet or exercise routine. They can help you create a safe and effective plan tailored to your individual needs.
Be wary of fad diets and weight loss supplements. Many of these products are ineffective and some can be harmful. Stick to evidence-based strategies that prioritize long-term health and well-being.
We have a detailed "Weight Diagram" file containing further resources, calculators, and information on healthy weight management. This file allows you to input your height, weight, and other relevant factors to estimate your healthy weight range and provides tools for tracking your progress. You can download the diagram here.
