04 Expedition 2004 Ford Expedition Fuse Box Diagram
Alright, let's dive into the often-overlooked but absolutely critical component of your 2004 Ford Expedition: the fuse box. This article is your comprehensive guide to understanding its intricacies, deciphering its diagram, and using it to troubleshoot electrical issues. Whether you're tackling a dead headlight, a malfunctioning radio, or planning to add some aftermarket accessories, knowing your way around the fuse box is indispensable.
Purpose of the Fuse Box Diagram
Why bother with a fuse box diagram? Simple: it's the roadmap to your Expedition's electrical system. Think of it as the electrical equivalent of a street map, guiding you to the exact point where a potential problem resides. The fuse box diagram is essential for:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Problems: Identifying and replacing blown fuses is often the first step in resolving electrical issues. The diagram pinpoints the fuse associated with a specific circuit.
- Adding Aftermarket Accessories: When installing new equipment like lights, stereos, or alarms, you'll likely need to tap into the vehicle's electrical system. The diagram helps you find appropriate power sources and fuse them correctly to prevent damage.
- Understanding Your Vehicle's Electrical System: Familiarizing yourself with the diagram provides a deeper understanding of how different components are powered and protected within your Expedition.
- Preventative Maintenance: Regularly checking fuses for corrosion or damage can prevent future electrical failures.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the 2004 Expedition Fuse Box
The 2004 Ford Expedition typically has two main fuse box locations:
- Under-Hood Fuse Box: Located in the engine compartment, this box houses fuses and relays that control critical engine and chassis functions, such as the fuel pump, ignition system, headlights, ABS, and cooling fan. This is also often referred to as the Power Distribution Box (PDB).
- Passenger Compartment Fuse Box: Usually found under the dashboard on the driver's side, this box protects circuits for interior components like the radio, power windows, power locks, climate control, and interior lighting.
Key Specs:
- Fuse Types: The 2004 Expedition uses a variety of fuse types, including ATO/ATC (standard blade fuses), Mini blade fuses, and potentially Maxi fuses (high-amperage fuses). The diagram will specify the type and amperage rating for each fuse.
- Relays: Relays are electromechanical switches that control high-current circuits using a low-current signal. They are used for components like the starter motor, fuel pump, and headlights. You'll find relays in both fuse box locations.
- Fuse Puller: A small plastic tool (usually included in the fuse box) used to safely remove and install fuses without damaging them.
Understanding Fuse Box Diagram Symbols
The fuse box diagram uses a standardized set of symbols to represent different components and electrical connections. While the exact layout and symbols may vary slightly depending on the specific trim level and options of your Expedition, the basic principles remain the same.
Lines and Colors:
- Solid Lines: Represent direct electrical connections.
- Dashed Lines: May indicate a connection that is optional or only present in certain configurations.
- Colors: While the diagram itself is typically black and white, knowing the color-coding of the wiring in your Expedition is helpful. Wire colors often correspond to specific functions (e.g., red for power, black for ground). Refer to a separate wiring diagram for comprehensive color-coding information.
Icons:
- Fuse Symbol: A zigzag line inside a rectangle. The amperage rating is usually indicated next to the symbol.
- Relay Symbol: A square or rectangle with internal markings representing the coil and contacts of the relay.
- Diode Symbol: A triangle pointing to a vertical line, indicating the direction of current flow.
- Ground Symbol: A series of downward-pointing lines, indicating a connection to the vehicle's chassis ground.
The diagram typically labels each fuse and relay with a number or letter designation, along with a brief description of the circuit it protects (e.g., "Radio," "Headlights," "Fuel Pump"). This is the key to identifying the correct fuse for a specific problem.
How It Works: The Fuse Box as Circuit Protector
The fuse box serves as the central protection point for your Expedition's electrical system. Each fuse is designed to protect a specific circuit from overcurrent. An overcurrent occurs when the current flowing through a circuit exceeds its safe operating limit, which can be caused by a short circuit, a faulty component, or an overload.
A fuse contains a thin wire that melts and breaks the circuit when an overcurrent occurs. This "blowing" of the fuse prevents damage to the wiring and components connected to that circuit. The amperage rating of the fuse determines the amount of current it can handle before blowing. It is crucial to replace a blown fuse with one of the same amperage rating. Using a higher-amperage fuse can bypass the protection mechanism and lead to serious damage or even a fire.
Relays, on the other hand, act as remotely controlled switches. A small current flowing through the relay's coil energizes an electromagnet, which pulls a set of contacts together, completing a high-current circuit. This allows a small switch on the dashboard to control a high-current device like the headlights without requiring heavy-gauge wiring to run all the way to the switch.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's how to use the fuse box diagram for basic troubleshooting:
- Identify the Problem: Determine which component is not working (e.g., the radio, headlights, power windows).
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse box diagram (either in your owner's manual or a downloadable version). Find the fuse that corresponds to the malfunctioning component.
- Inspect the Fuse: Use a fuse puller to remove the fuse. Visually inspect it for a broken filament. A blown fuse will have a visible gap in the wire. You can also use a multimeter to test the fuse for continuity.
- Replace the Fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage rating.
- Test the Circuit: After replacing the fuse, test the component to see if it is now working. If the fuse blows again immediately, there is likely a short circuit in the wiring or a faulty component that needs further investigation.
Common Issues:
- Repeatedly Blown Fuses: Indicates a short circuit or an overload in the circuit. Do not simply replace the fuse with a higher amperage one. Find and fix the underlying problem.
- Corrosion: Corrosion on fuse terminals can cause poor connections and intermittent problems. Clean the terminals with a wire brush or contact cleaner.
- Incorrect Fuse Size: Always use the correct amperage rating for each fuse. Using the wrong size can lead to damage or fire.
Safety: Identifying Risky Components
Working with electrical systems involves inherent risks. Here are some key safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on the fuse box, disconnect the negative (-) battery terminal to prevent accidental shorts and electrical shocks.
- Avoid Working in Wet Conditions: Water conducts electricity, increasing the risk of electric shock.
- Be Careful with High-Amperage Circuits: Circuits protected by high-amperage fuses (e.g., those for the starter motor or alternator) can deliver a significant shock. Exercise extreme caution when working with these circuits.
- Do Not Bypass Fuses: Never bypass a fuse by using a piece of wire or other conductive material. This eliminates the circuit protection and can lead to serious damage or fire.
- If Unsure, Seek Professional Help: If you are not comfortable working with electrical systems, consult a qualified mechanic.
Specifically, the circuits controlling airbags and ABS systems are extremely sensitive and potentially dangerous. Incorrect handling of these systems can result in unintended airbag deployment or ABS malfunction. If you suspect a problem with these systems, it is best to consult a qualified technician.
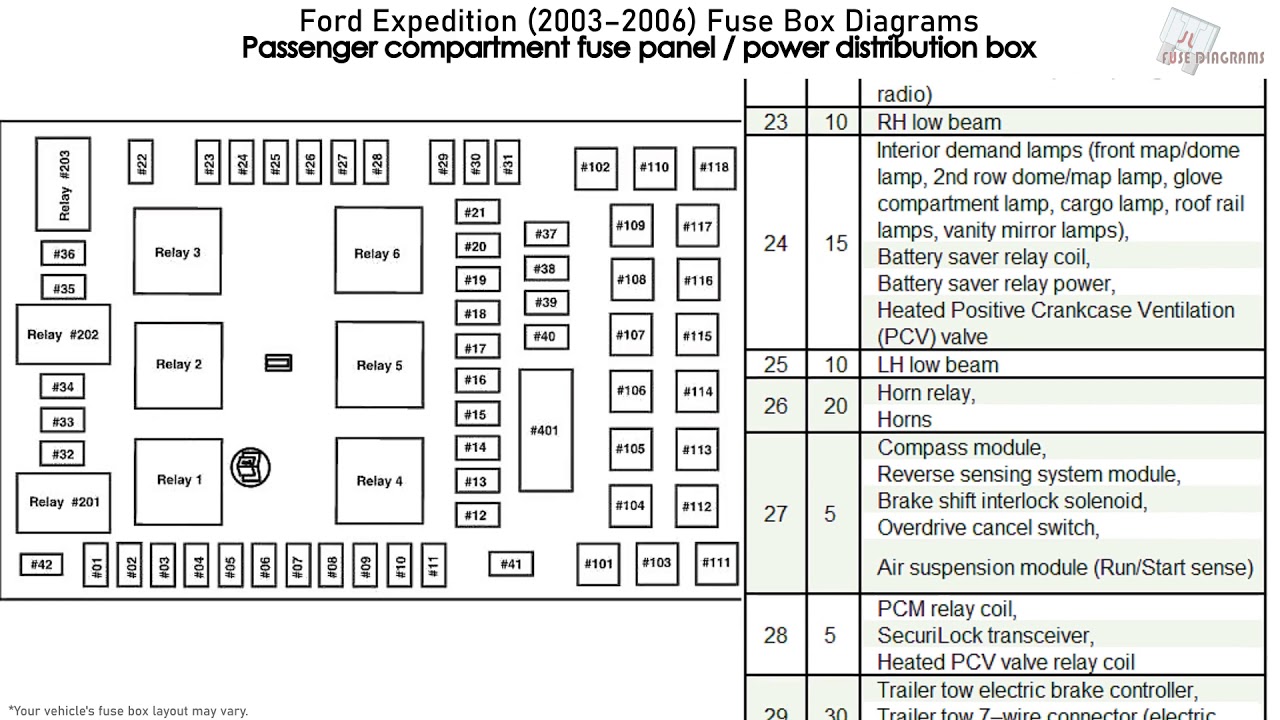
We have the 2004 Ford Expedition fuse box diagram available for download. This diagram provides a detailed layout of both the under-hood and passenger compartment fuse boxes, including fuse locations, amperage ratings, and circuit descriptions. Download it, keep it handy, and you'll be well-equipped to tackle most electrical issues that may arise in your Expedition.
