2015 Nissan Rogue Fuse Box Diagram
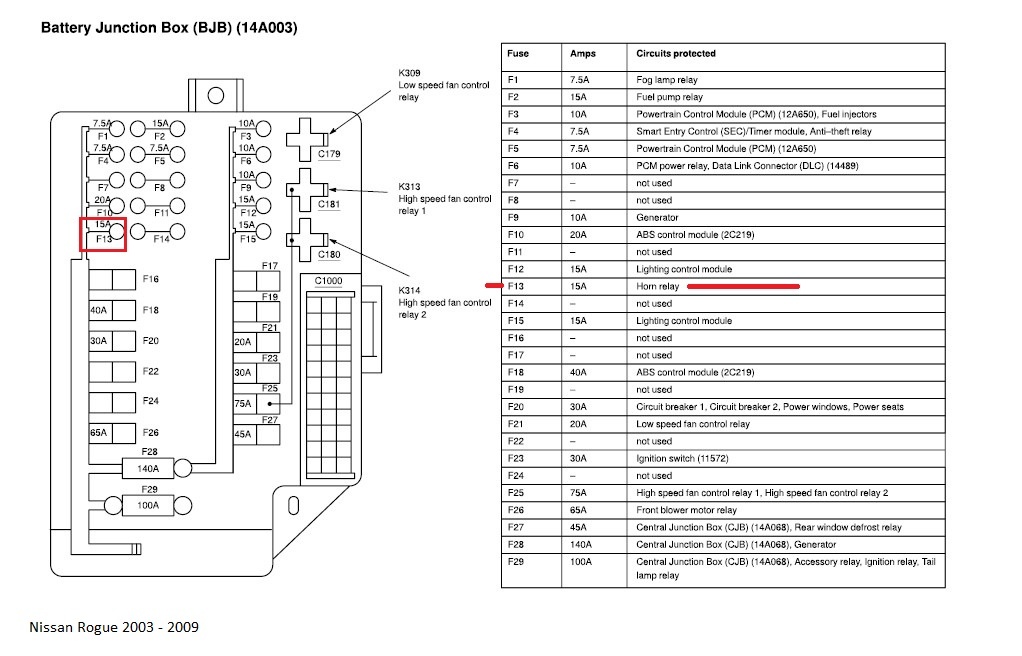
If you're tackling electrical repairs or modifications on a 2015 Nissan Rogue, understanding its fuse box diagram is absolutely essential. Think of the fuse box as the central nervous system of your Rogue's electrical system. It protects individual circuits from overcurrent, preventing potentially damaging shorts and fires. This article provides a comprehensive breakdown of the 2015 Nissan Rogue's fuse box layout, conventions, and practical uses.
Why This Diagram Matters
A fuse box diagram isn't just a pretty picture; it's your roadmap to safely and effectively diagnose and repair electrical issues. Here's why it's indispensable:
- Troubleshooting: When an electrical component stops working (e.g., a light, the radio, or a power window), the first place to check is the corresponding fuse. The diagram tells you exactly which fuse to inspect.
- Modifications: If you're adding electrical accessories like aftermarket lights, a new stereo, or a dashcam, you'll need to tap into the existing electrical system. The diagram helps you identify suitable circuits and fuse ratings to avoid overloading.
- Learning the System: Understanding the fuse box layout provides a deeper understanding of your vehicle's overall electrical architecture.
- Preventing Damage: Replacing a blown fuse with the correct amperage rating is crucial. Using a fuse with a higher rating than specified can bypass the circuit protection and potentially cause serious damage, including fires.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2015 Nissan Rogue typically has two main fuse boxes:
- Interior Fuse Box: Located inside the cabin, usually on the driver's side, behind a small panel near the dashboard or under the steering wheel. This box primarily houses fuses for interior components like lights, entertainment system, power windows, and the climate control system.
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box: Situated under the hood, usually near the battery. This box contains fuses for critical engine components like the fuel pump, ignition system, and cooling fan, as well as other essential vehicle systems like the headlights and ABS.
Each fuse box consists of several key components:
- Fuse Block (or Fuse Panel): The main housing that holds the fuses.
- Fuses: Small, replaceable devices designed to protect circuits from overcurrent. They contain a thin wire that melts and breaks the circuit when the current exceeds the rated amperage.
- Relays: Electrically operated switches that control higher-current circuits. Relays allow a low-current circuit (like a switch) to control a high-current circuit (like headlights).
- Diagram Label: Usually a sticker inside the fuse box cover that identifies each fuse and relay and its corresponding function. This is the crucial piece of information we're discussing.
Symbols – Deciphering the Diagram
Fuse box diagrams use a variety of symbols to represent different components and their functions. Understanding these symbols is key to interpreting the diagram correctly.
- Lines: Lines represent electrical circuits or wires. Thicker lines may indicate higher-current circuits.
- Colors: Wire colors are often indicated on the diagram, though this isn't always the case on the fuse box sticker itself. Knowing the wire color can be extremely helpful when tracing circuits for troubleshooting. Common colors include red (power), black (ground), and various other colors for signal and control circuits.
- Icons: Icons represent specific components or systems. Common icons include:
- Light Bulb: Represents a lighting circuit (headlights, taillights, interior lights).
- Fan: Represents a cooling fan circuit.
- Radio Speaker: Represents the audio system circuit.
- Window: Represents a power window circuit.
- Cigar Lighter: Represents the accessory power outlet (cigarette lighter) circuit.
- Engine: Represents engine-related circuits (fuel pump, ignition).
- Numbers: Each fuse and relay is typically assigned a number, which corresponds to the number on the diagram.
- Amperage (A): The amperage rating of each fuse is indicated, usually next to the fuse number or within the description. Common fuse ratings include 5A, 7.5A, 10A, 15A, 20A, 25A, and 30A. Always replace a blown fuse with one of the same amperage rating.
How It Works
The fuse box acts as a central distribution point for electrical power. The battery provides power to the fuse box, and from there, power is distributed to various circuits throughout the vehicle. Each circuit is protected by a fuse. If a circuit experiences an overcurrent condition (e.g., a short circuit), the fuse will blow, interrupting the flow of electricity and preventing damage to the wiring and components connected to that circuit.
Relays are used to control circuits that require a higher current than a typical switch can handle. For example, the headlights might be controlled by a relay. When you turn on the headlight switch, it activates the relay, which then closes the circuit to the headlights, allowing them to draw power directly from the battery.
Real-World Use – Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's how to use the fuse box diagram for basic troubleshooting:
- Identify the Problem: Determine which electrical component is malfunctioning.
- Locate the Relevant Fuse: Consult the fuse box diagram to identify the fuse associated with the problematic component.
- Inspect the Fuse: Remove the fuse from the fuse block and visually inspect it. A blown fuse will have a broken filament (the thin wire inside). You can also use a multimeter to check for continuity across the fuse. If there's no continuity, the fuse is blown.
- Replace the Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the exact same amperage rating.
- Test the Component: Turn on the ignition and test the component to see if it's working.
- If the Fuse Blows Again: If the new fuse blows immediately or shortly after being replaced, it indicates a more serious problem in the circuit, such as a short circuit. Further diagnosis is required to identify and repair the underlying issue. This might involve tracing wires, checking for damaged components, or consulting a professional mechanic.
Safety – Risky Components
Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous if proper precautions aren't taken. Here are some key safety considerations:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical component, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent accidental shocks or short circuits.
- Use Insulated Tools: Use tools with insulated handles to protect yourself from electric shock.
- Never Bypass a Fuse: Never attempt to bypass a fuse by using a piece of wire or other conductive material. This removes the circuit protection and can lead to serious damage or fire.
- Avoid Water: Never work on electrical components in wet conditions.
- High-Current Relays: Be especially careful when working around relays, particularly those controlling high-current circuits like the starter motor or headlights. These circuits can deliver a significant electrical shock.
- Airbag System: The airbag system is a sensitive and potentially dangerous component. Incorrect handling can cause accidental deployment, which can result in serious injury. If you need to work near the airbag system, consult a qualified technician.
Remember to consult your 2015 Nissan Rogue's owner's manual for specific details about the fuse box locations and diagrams. While this article provides general guidance, the exact layout and fuse assignments may vary depending on the vehicle's trim level and options.
We have a high-resolution PDF file containing the 2015 Nissan Rogue fuse box diagram available for download. This detailed diagram will provide an invaluable resource for your troubleshooting and modification projects.
