2014 Nissan Maxima Fuse Box Diagram
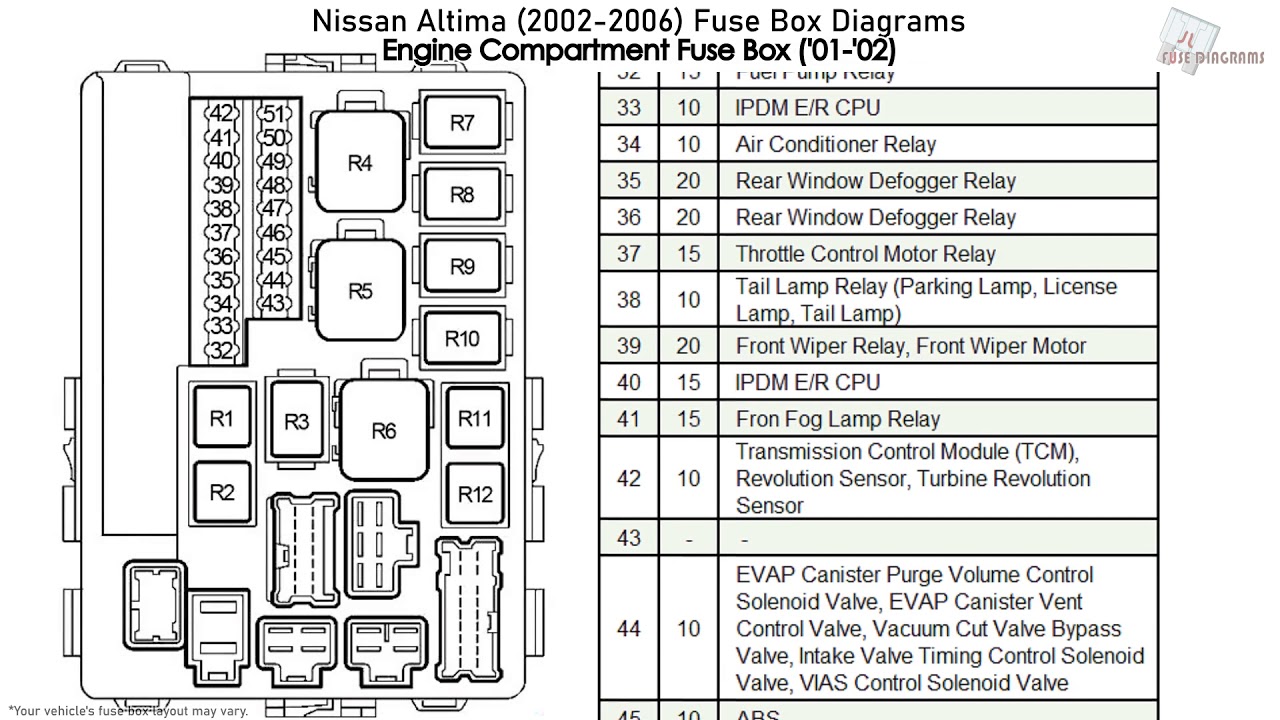
The 2014 Nissan Maxima, like any modern vehicle, relies heavily on a complex electrical system. Fuses are a critical safety component, protecting delicate circuits from overcurrent and potential damage. Understanding the 2014 Maxima's fuse box diagram is crucial for performing basic electrical repairs, diagnosing problems, and even adding aftermarket accessories. This article will provide an in-depth look at the fuse box diagram, explaining its key features, how it works, and how to use it for effective troubleshooting. We're assuming you have some basic automotive knowledge and are comfortable working on your car, but we'll avoid overly technical jargon where possible.
Purpose of Understanding the Fuse Box Diagram
Why bother with the fuse box diagram? Several reasons. First, it's invaluable for troubleshooting electrical issues. If a specific component isn't working – say, the radio, a power window, or even the engine not starting – the first place to check is the corresponding fuse. A blown fuse is a relatively simple and inexpensive fix compared to diagnosing a wiring problem or a faulty component. Second, the diagram is essential for safely installing aftermarket accessories. Tapping into the wrong circuit can overload it and cause damage, or worse, a fire. The diagram helps you identify appropriate circuits and the correct fuse rating to use. Finally, studying the diagram provides a deeper understanding of your vehicle's electrical architecture, which can be helpful for future repairs and modifications.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the Fuse Box
The 2014 Nissan Maxima typically has two main fuse boxes: one located in the engine compartment and another inside the passenger cabin, usually under the dashboard on the driver's side. Each fuse box houses a variety of fuses, each protecting a specific circuit or group of circuits. The engine compartment fuse box generally handles high-current circuits related to engine management, headlights, and other critical systems. The interior fuse box typically handles lower-current circuits like interior lights, the radio, and power windows. The exact layout and fuse assignments can vary slightly depending on the vehicle's trim level and options, so it's always best to consult the specific diagram for your car.
Key components include:
- Fuses: These are the sacrificial links that break the circuit when the current exceeds a safe level. They are rated in amperes (amps), which indicates the maximum current they can handle before blowing.
- Relays: These are electromechanical switches that allow a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit. They're commonly used for components like headlights, the starter motor, and the fuel pump.
- Fuse Box Housing: This is the physical container that houses the fuses and relays, providing a organized and protected environment.
- Fuse Puller: A small plastic tool designed to safely remove fuses without damaging them or the fuse box. Often located within the fuse box itself.
Understanding the Symbols, Lines, Colors, and Icons on the Diagram
Fuse box diagrams aren't just random arrangements of numbers. They use a standardized set of symbols and conventions to convey information efficiently. Here's a breakdown:
- Lines: Solid lines typically represent the electrical circuits protected by the fuses. Dashed lines might indicate a shared ground or a control circuit.
- Colors: While not always present on every diagram, colors can be used to differentiate between circuits or to highlight specific functions. For example, a red line might indicate a circuit connected directly to the battery.
- Icons: Icons are used to represent the components protected by each fuse. Common icons include:
- A light bulb (for headlights, taillights, interior lights)
- A radio antenna (for the radio)
- A steering wheel (for power steering)
- A window (for power windows)
- An engine (for engine control systems)
- Fuse Numbers: Each fuse is typically labeled with a number, which corresponds to a legend on the diagram that lists the component or circuit it protects.
- Amperage Rating: Each fuse location will also indicate the required amperage rating for that fuse. It is critical to use the correct amperage fuse. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating than specified can allow excessive current to flow, potentially damaging the circuit and causing a fire. Using a fuse with a lower amperage rating will cause the fuse to blow prematurely.
The diagram will typically show the layout of the fuses in the fuse box, with each fuse identified by its number and amperage rating. A separate table or legend will then list the component or system that each fuse protects.
How It Works: The Fuse Protection Mechanism
A fuse is essentially a thin wire designed to melt and break the circuit when the current flowing through it exceeds its rated amperage. This melting action, called "blowing," interrupts the flow of electricity and prevents damage to the protected component or the wiring in the circuit. The fuse is the weakest link in the circuit, designed to fail first to protect the more expensive and critical components. When a circuit experiences an overcurrent condition – often caused by a short circuit (an unintended path for current to flow with little resistance) – the current flow increases dramatically. This increased current generates heat in the fuse, causing the wire to melt and open the circuit.
Relays work differently. They use a small electrical current to activate an electromagnet. This electromagnet pulls a switch closed, allowing a larger current to flow through a separate circuit. This allows a low-current circuit, such as a signal from the car's computer, to control a high-current device, such as the headlights or starter motor.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's how to use the fuse box diagram for basic troubleshooting:
- Identify the Problem: Determine which component is not working.
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse that protects that component in the fuse box diagram.
- Locate the Fuse: Find the corresponding fuse in the appropriate fuse box (engine compartment or interior).
- Inspect the Fuse: Carefully remove the fuse using the fuse puller. Inspect the fuse to see if the wire inside is broken or blackened. A blown fuse will have a visible gap in the wire.
- Replace the Fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the exact same amperage rating.
- Test the Component: Turn on the component to see if it now works.
- If the Fuse Blows Again: If the new fuse blows immediately, there is a short circuit or overload in the circuit. Do not continue replacing fuses. This indicates a more serious problem that requires professional diagnosis.
Safety Precautions When Working with Fuses
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous if proper precautions are not taken. Here are some safety tips:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical system, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery. This will prevent accidental shorts and electric shock.
- Use the Correct Fuse: Never replace a fuse with one of a higher amperage rating. This can overload the circuit and cause a fire.
- Inspect Wiring: When replacing a blown fuse, inspect the wiring and components in the circuit for signs of damage or wear. A blown fuse is often a symptom of a larger problem.
- Avoid Water: Never work on electrical systems in wet conditions.
- Relays and High-Current Fuses: Be especially careful around relays and fuses that protect high-current circuits (e.g., the starter motor, alternator). These circuits can carry a significant amount of current and pose a greater risk of electric shock. Consider having a professional handle work on these systems if you are not comfortable.
By following these safety precautions, you can minimize the risk of injury and damage when working with your vehicle's electrical system.
Remember, while this guide provides a comprehensive overview, it's not a substitute for professional advice. If you're unsure about any aspect of working with your car's electrical system, consult a qualified mechanic.
We have a digital copy of the 2014 Nissan Maxima fuse box diagram available for download. It contains a more detailed and precise view of the fuse layout and component assignments than what we can describe here. This diagram will be invaluable for diagnosing and repairing electrical issues in your vehicle.
