04 Nissan Sentra Fuse Box Diagram
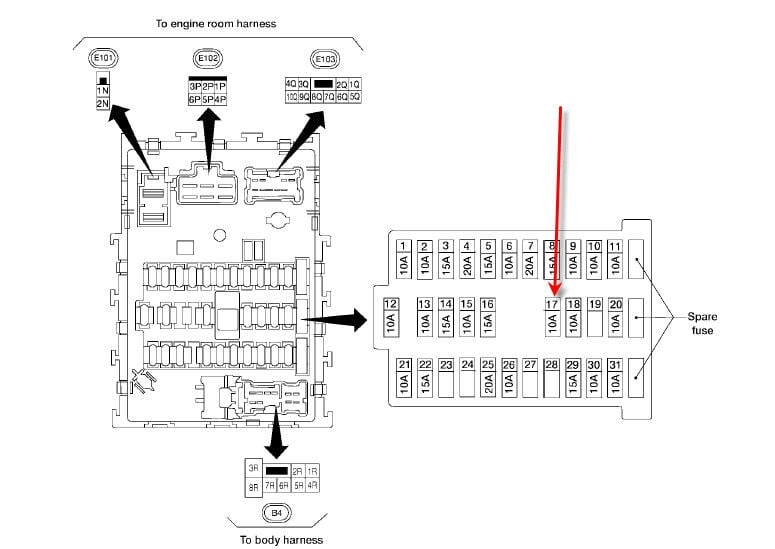
So, you're diving into the electrical system of your 2004 Nissan Sentra? Smart move! Understanding your fuse box diagram is absolutely crucial, whether you're tackling a faulty radio, a dead cigarette lighter, or diagnosing more complex electrical issues. Think of it as the roadmap to your car's electrical nervous system. It allows you to quickly identify and isolate potential problems without blindly poking around and potentially causing more damage. This article will give you a comprehensive breakdown of the 04 Sentra's fuse box diagram, empowering you to troubleshoot effectively and safely.
Why Bother with the Fuse Box Diagram?
Honestly, knowing your fuse box is a game-changer. Here’s why this diagram is so valuable:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Problems: The primary purpose is to quickly identify which fuse corresponds to a specific circuit. If something electrical isn't working, the first step is always to check the associated fuse. A blown fuse indicates an overload or short circuit somewhere in that system.
- Performing Electrical Modifications: Planning to add an aftermarket stereo, install auxiliary lighting, or upgrade other electrical components? You'll need to know which circuits you can tap into safely and without overloading the system. The diagram helps you avoid accidentally shorting out something important.
- Preventing Further Damage: Replacing a fuse with one of the wrong amperage can cause serious damage to the circuit and the components it powers. The diagram tells you the correct amperage rating for each fuse.
- Understanding Your Car's Systems: Just familiarizing yourself with the diagram can deepen your understanding of how your car's electrical systems are interconnected. This knowledge can be invaluable for future repairs and modifications.
Key Specs and Main Fuse Box Locations
The 2004 Nissan Sentra typically has two main fuse box locations:
- Interior Fuse Box: Located inside the cabin, usually under the dashboard on the driver's side. This box typically houses fuses for interior components like the radio, lights, power windows, and other convenience features. Access might involve removing a small panel or opening a glove compartment.
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box: Situated in the engine bay, often near the battery. This box contains fuses and relays for engine-related functions, headlights, and other critical systems. It's usually clearly labeled.
The most important spec to note is the amperage rating of each fuse. This is typically printed on the fuse itself and indicated on the fuse box diagram. Using a fuse with a higher amperage than specified can bypass the circuit protection and lead to overheating and potentially a fire. Using a lower amperage fuse might cause nuisance tripping (the fuse blowing unnecessarily). Always replace a blown fuse with one of the exact same amperage rating.
Decoding the Diagram: Symbols, Lines, and Colors
The fuse box diagram isn't just a random collection of lines and numbers; it's a standardized representation of the electrical circuit layout. Here’s how to interpret it:
- Fuses: Represented by a rectangular symbol, often with a number indicating the amperage rating (e.g., "10A," "15A").
- Relays: Typically shown as a square or rectangular box with terminals. Relays are electromechanical switches that use a small current to control a larger current. They are used to protect sensitive circuits and allow low-current switches to control high-current devices (like headlights or starter motors).
- Lines: Solid lines indicate direct electrical connections. Dotted lines may indicate connections through a switch or relay.
- Colors: Diagrams *might* use color coding to differentiate between different types of circuits (e.g., red for power, black for ground). However, color coding is less common on fuse box diagrams themselves and more prevalent in wiring schematics. If your diagram does have color coding, there will be a legend explaining what each color represents.
- Labels: Each fuse and relay is clearly labeled with a description of the circuit it protects (e.g., "RADIO," "HEAD LP," "IGN COIL"). These labels are often abbreviated.
It's crucial to match the physical location of the fuse within the fuse box to its representation on the diagram. The diagram provides a precise map of which fuse protects which component.
How It All Works: Circuit Protection 101
The fuse box is essentially a circuit breaker panel for your car. Each fuse is a safety device containing a thin wire designed to melt and break the circuit if the current exceeds a predetermined level. This protects the wiring and components connected to that circuit from overheating and potential damage. If a component malfunctions and draws excessive current (a short circuit), the fuse will blow, interrupting the flow of electricity and preventing a fire or further damage. Think of it as a sacrificial lamb, protecting the rest of the electrical system.
The amperage rating of a fuse determines how much current it can handle before blowing. If you try to draw more current than the fuse is rated for (by, say, connecting too many devices to a single circuit), the fuse will blow, cutting off the power supply. This is why it's so important to use the correct amperage fuse for each circuit.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here’s how to use the fuse box diagram to diagnose and fix common electrical problems:
- Identify the Problem: Determine which component is not working. For example, the cigarette lighter is dead.
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse box diagram for your 2004 Nissan Sentra. Find the fuse labeled for the cigarette lighter (it might be labeled something like "CIGAR," "ACC," or "POWER OUTLET").
- Inspect the Fuse: Physically locate the fuse in the fuse box. Visually inspect it. A blown fuse will usually have a broken filament inside. Sometimes, it's difficult to see, so use a multimeter set to continuity to test the fuse. If the multimeter doesn't beep or show a low resistance reading, the fuse is blown.
- Replace the Fuse: Remove the blown fuse using a fuse puller (a small plastic tool designed for this purpose). Replace it with a new fuse of the exact same amperage rating. Do not use a higher amperage fuse.
- Test the Component: Turn on the ignition and test the component. If it now works, you've solved the problem.
- If the Fuse Blows Again: If the new fuse immediately blows again, there is a short circuit or overload in the circuit. This requires further investigation by a qualified mechanic. Do not keep replacing the fuse with the same result.
A multimeter is an invaluable tool for electrical troubleshooting. It allows you to measure voltage, current, and resistance, helping you pinpoint the location of a short circuit or open circuit.
Safety First: Handle with Care!
Working with electrical systems always carries a risk. Here are some critical safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Whenever possible, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery before working on the electrical system. This will prevent accidental short circuits and electrical shocks.
- Never Bypass a Fuse: Never replace a fuse with a wire or other conductive material. This eliminates the circuit protection and can lead to a fire.
- Use the Correct Tools: Use insulated tools designed for electrical work.
- Be Careful with the Airbag System: The airbag system is highly sensitive and can be accidentally deployed if mishandled. Refer to your car's service manual for specific instructions on disabling the airbag system before working near it. Airbag fuses and wiring are often highlighted in the fuse diagram.
- High-Current Fuses and Relays: Be particularly careful when working with high-current fuses and relays, such as those for the starter motor or alternator. These circuits can carry a significant amount of current and pose a greater risk of electrical shock.
Remember, if you're uncomfortable working on your car's electrical system, it's always best to consult a qualified mechanic. Electrical problems can be complex and potentially dangerous.
We have the complete and accurate fuse box diagram for your 2004 Nissan Sentra available for download. This diagram will be a valuable resource for your electrical troubleshooting and repair projects.
