1994 Chevy Truck Wiring Diagram Free
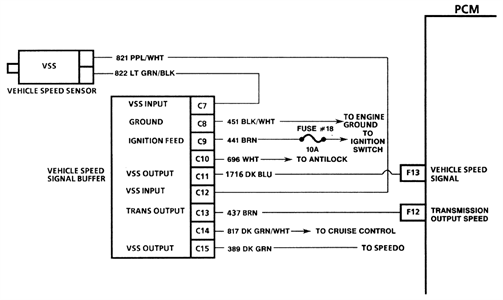
For the seasoned DIY mechanic or the aspiring automotive enthusiast, understanding your vehicle's wiring is paramount. This article focuses on the 1994 Chevy Truck Wiring Diagram – a crucial resource for anyone tackling electrical repairs, modifications, or simply wanting a deeper understanding of their truck. We'll delve into the purpose of the diagram, its key components, the symbology used, and how to use it for real-world troubleshooting. Plus, we'll emphasize safety precautions when working with electrical systems. And the best part? We have the diagram ready for you to download.
Purpose of the 1994 Chevy Truck Wiring Diagram
The primary purpose of a wiring diagram is to provide a visual roadmap of your vehicle's electrical system. It shows how various electrical components are interconnected, allowing you to trace circuits, identify faulty components, and understand the flow of electricity. Specifically, the 1994 Chevy Truck Wiring Diagram is invaluable for:
- Troubleshooting electrical problems: Pinpointing shorts, opens, or incorrect wiring.
- Performing electrical repairs: Replacing damaged wires, connectors, or components with confidence.
- Installing aftermarket accessories: Safely and correctly wiring in new stereos, lights, or other electrical devices.
- Understanding your vehicle's electrical system: Gaining a comprehensive understanding of how different systems interact.
- Modifying electrical circuits: Making custom modifications, such as adding relays or switches, while maintaining safety and functionality.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the Wiring Diagram
The 1994 Chevy Truck Wiring Diagram isn't a single document, but rather a collection of diagrams covering various systems. These diagrams are typically broken down by specific circuits or subsystems. Some common sections include:
- Starting and Charging System: Covers the battery, alternator, starter motor, and related wiring.
- Ignition System: Details the distributor, ignition coil, spark plugs, and associated circuits.
- Fuel System: Illustrates the fuel pump, fuel injectors, sensors, and wiring related to fuel delivery.
- Lighting System: Includes headlights, taillights, turn signals, brake lights, and interior lighting circuits.
- Instrument Panel: Shows the wiring for gauges, indicators, and warning lights.
- Air Conditioning and Heating System: Covers the compressor, blower motor, sensors, and control circuits.
- Body Electrical: Includes power windows, door locks, and other body-related electrical systems.
Key specs often included are voltage ratings (typically 12V DC), wire gauge sizes (AWG - American Wire Gauge), and amperage ratings for fuses and circuit breakers.
Understanding Wiring Diagram Symbols
A wiring diagram uses a standardized set of symbols to represent electrical components and connections. Understanding these symbols is crucial for interpreting the diagram correctly.
- Lines: Solid lines represent wires. Dashed lines might indicate shielded wires or ground connections. The thickness of the line often indicates the wire gauge – thicker lines represent thicker wires.
- Colors: Wires are color-coded to help identify them in the vehicle. The diagram will usually have a legend explaining the color codes. Common colors include Red (power), Black (ground), Yellow (ignition), and Blue (lighting).
- Ground Symbols: Various symbols represent ground connections. The most common is a series of downward-pointing lines, resembling an inverted Christmas tree.
- Component Symbols: Specific symbols represent various electrical components:
- Resistor: A zigzag line.
- Capacitor: Two parallel lines.
- Diode: A triangle pointing to a line.
- Relay: A coil and a switch.
- Fuse: A squiggly line inside a rectangle.
- Switch: A line that can be open or closed.
- Connectors: Represented by circles or squares where wires connect. Connector numbers are often indicated for easy identification.
How It Works: Circuit Tracing
Using the wiring diagram to trace a circuit involves following the lines from the power source (usually the battery) through the various components to the ground. Let's say you're troubleshooting a non-functional headlight. You would:
- Locate the headlight circuit on the wiring diagram.
- Start at the power source (battery or ignition switch).
- Follow the wire through the fuse, switch, headlight relay (if equipped), and finally to the headlight itself.
- Check for breaks in the wire, faulty connections, or a blown fuse along the way.
- Verify the ground connection for the headlight. A poor ground can prevent the headlight from working.
Voltage drop testing is a valuable technique for diagnosing circuit problems. It involves measuring the voltage drop across each component in the circuit. A higher-than-expected voltage drop indicates a resistance, potentially caused by corrosion or a loose connection.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some practical troubleshooting tips when using the 1994 Chevy Truck Wiring Diagram:
- Start with the basics: Check the battery voltage, fuses, and grounds before diving into complex diagnostics.
- Use a multimeter: A multimeter is your best friend for electrical troubleshooting. Use it to check voltage, continuity, and resistance.
- Isolate the problem: If a circuit isn't working, try to isolate the faulty component by disconnecting sections of the circuit.
- Refer to the diagram frequently: The diagram is your guide. Don't try to guess – use the diagram to trace the circuit and identify potential problems.
- Check for common issues: Corroded connectors, broken wires, and faulty grounds are common causes of electrical problems.
- Understand common failure points: Certain components, such as relays and switches, are more prone to failure than others.
Safety Precautions
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Always observe the following safety precautions:
- Disconnect the battery: Before working on any electrical circuit, disconnect the negative battery cable to prevent accidental shocks or shorts.
- Use insulated tools: Use tools with insulated handles to protect yourself from electric shock.
- Avoid working in wet conditions: Water conducts electricity, so avoid working on electrical systems in wet or damp environments.
- Be careful around the airbag system: The airbag system is a delicate and potentially dangerous component. Consult a professional if you need to work near the airbag module. Disconnecting the battery is essential before working on the airbag system.
- Fuses and Circuit Breakers: Always replace fuses with the correct amperage rating. Using a higher-rated fuse can damage the circuit and potentially cause a fire. Never bypass a fuse.
- High Energy Components: Be extremely cautious around the ignition system, specifically the ignition coil and distributor. These components can produce high voltage that can cause a severe shock.
By understanding the purpose, key components, and symbology of the 1994 Chevy Truck Wiring Diagram, you'll be well-equipped to tackle a wide range of electrical repairs and modifications. Remember to prioritize safety and take your time. With the right tools and a little patience, you can confidently diagnose and resolve electrical issues on your trusty Chevy truck. And to help you get started, we have the complete wiring diagram file ready for you to download. Happy wrenching!
