1994 Jeep Wrangler 2.5 Fuel Injectors Wiring Diagram
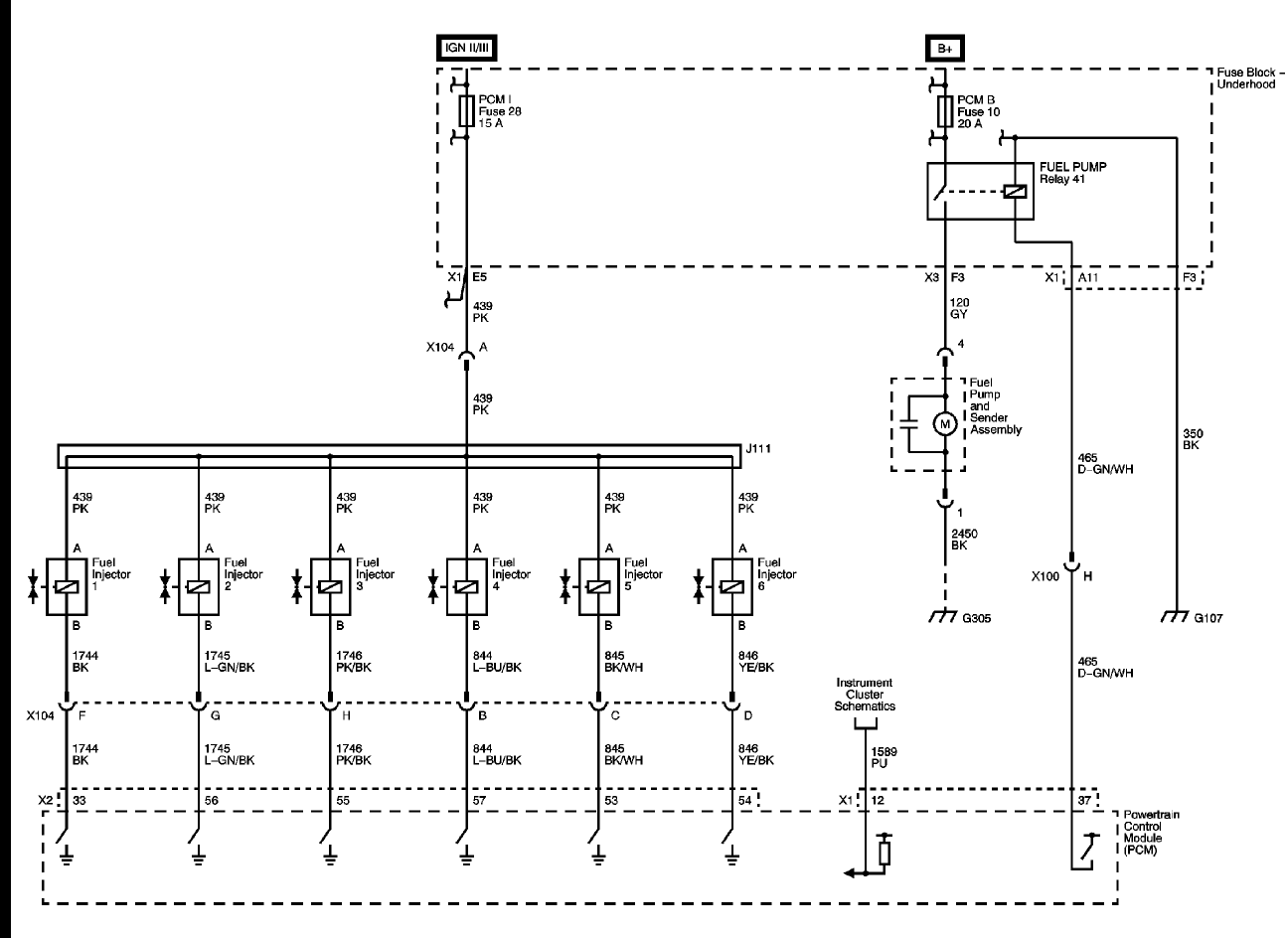
Let's dive into the fuel injector wiring diagram for the 1994 Jeep Wrangler 2.5L engine. This diagram is your roadmap to understanding how the fuel injectors are controlled, diagnosing issues, and even performing some modifications, if that's your thing. Think of it as the circulatory system map for your Jeep's fueling system.
Purpose of Understanding the Fuel Injector Wiring Diagram
Why bother learning this? Well, a solid understanding of the fuel injector wiring diagram is indispensable for several reasons:
- Troubleshooting: When your Jeep runs rough, misfires, or refuses to start, problems with the fuel injectors or their wiring are prime suspects. The diagram allows you to pinpoint breaks, shorts, or other electrical issues in the circuit.
- Repairing: Instead of blindly replacing parts, the diagram helps you identify the faulty component, saving you time and money. You can use it to trace wires, test connectors, and verify that signals are reaching the injectors correctly.
- Modification: Planning to upgrade your fuel injectors for improved performance? Knowing the wiring is crucial for ensuring a seamless and correct installation. It also helps when installing piggyback ECUs or other fuel management devices.
- Learning: Even if you're not currently facing any problems, familiarizing yourself with the diagram builds a foundational understanding of your Jeep's engine management system.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Before we jump into the diagram, let's get familiar with the key components involved:
- Fuel Injectors: These are electromechanical devices that spray fuel into the intake manifold. Each injector has a nozzle and a solenoid valve controlled by the PCM. The 1994 2.5L Wrangler uses throttle body injection (TBI), so there are typically only one or two injectors.
- Powertrain Control Module (PCM): This is the "brain" of the engine. It receives signals from various sensors and controls the fuel injectors by grounding the circuit.
- Injector Connectors: These connect the wiring harness to the fuel injectors. They can sometimes become corroded or damaged, leading to intermittent or complete failure.
- Wiring Harness: This is the network of wires that connects all the electrical components of the engine.
- Fuel Pump Relay: This relay provides power to the fuel pump, ensuring fuel is available to the injectors.
- Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP): This sensor provides information to the PCM about the engine's RPM and crankshaft position, crucial for timing the fuel injection.
- Oxygen Sensor: While not directly in the injector circuit, it provides feedback to the PCM about the air/fuel ratio, influencing injector pulse width.
- Battery: Provides the initial 12V power.
- Fuse box: Protects the circuits from overcurrent.
Symbols in the Wiring Diagram
Understanding the symbols is crucial to interpreting the diagram. Here's a breakdown of common elements:
- Lines: Solid lines represent wires. Dashed lines might indicate shielded wires or grounds. Line thickness generally doesn't indicate wire gauge, but rather emphasizes a key connection.
- Colors: Each wire is color-coded (e.g., RED, BLK, GRN). The diagram key will specify what each color represents in terms of circuit function.
- Connectors: Represented by a circle or square with lines entering and exiting. They indicate points where the wiring harness can be disconnected. Numbers near the connector indicate pin numbers.
- Ground Symbols: Look for symbols that resemble an upside-down Christmas tree or a series of descending horizontal lines. These indicate where the circuit is grounded to the vehicle's chassis.
- Component Symbols: Fuel injectors are often represented by a rectangle or a solenoid symbol. Relays are typically shown as a coil and a switch.
- Fuses: Fuses are drawn as a jagged line inside a rectangle.
- Splices: A dot where lines intersect indicates a splice where wires are joined together.
A typical fuel injector circuit will show 12V power coming from the ignition switch, through a fuse, and then to one side of the injector. The other side of the injector connects back to the PCM. The PCM controls the injector by grounding this circuit, completing the circuit and activating the injector.
How It Works
The fuel injection system works in a closed-loop feedback system. Here's a simplified explanation:
- Sensor Input: Sensors like the CKP sensor, oxygen sensor, and throttle position sensor (TPS) send data to the PCM.
- PCM Processing: The PCM analyzes this data to determine the optimal air/fuel mixture.
- Injector Control: The PCM sends a signal to the fuel injectors to open and spray fuel into the intake manifold. The pulse width (the length of time the injector stays open) determines the amount of fuel injected.
- Feedback Loop: The oxygen sensor measures the exhaust gases and sends feedback to the PCM, which adjusts the injector pulse width to maintain the ideal air/fuel ratio.
In the 1994 2.5L Wrangler TBI system, the PCM triggers the fuel injector(s) by switching its ground on and off. When the PCM grounds the injector circuit, the solenoid inside the injector energizes, opening the nozzle and allowing fuel to spray. The longer the PCM grounds the circuit (longer pulse width), the more fuel is injected.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some common problems you can diagnose with the help of the wiring diagram:
- No Fuel Injection: If the engine cranks but doesn't start, check the fuel pump relay and fuse. If those are good, use a multimeter to test for voltage at the injector connector. If there's no voltage, trace the wiring back to the power source using the diagram. If there's voltage, the problem is likely with the injector itself or the PCM's ability to ground the circuit.
- Rough Idle or Misfires: A faulty fuel injector can cause a rough idle or misfires. Use a noid light to check if the injector is receiving a signal from the PCM. If the noid light flashes, the PCM is sending the signal, but the injector may be clogged or faulty. If the noid light doesn't flash, the problem is with the wiring or the PCM. You can also use a multimeter to check the resistance of the injector. A drastically different resistance compared to the other injector (or a known good value) indicates a problem.
- Check Engine Light (CEL): If the CEL is illuminated with codes related to the fuel injectors (e.g., P0201, P0202), use the diagram to trace the wiring and check for shorts, opens, or loose connections.
Example Troubleshooting Scenario: You have a P0201 code (Injector Circuit Malfunction - Cylinder 1). The wiring diagram shows that the injector for cylinder 1 receives power from a specific fuse and is grounded by the PCM on a particular pin. First, check the fuse. If it's blown, replace it and see if the problem returns. If the fuse is good, use a multimeter to check for voltage at the injector connector. If there's no voltage, use the diagram to trace the wire back to the fuse box, looking for breaks or shorts. If there's voltage, check the continuity of the wire between the injector connector and the PCM pin indicated in the diagram. A lack of continuity indicates a broken wire. Finally, with the engine running (carefully!), use a noid light to verify the PCM is pulsing the injector. If not, the PCM itself might be faulty (but test thoroughly first!).
Safety Considerations
Working on the fuel injection system involves handling gasoline, which is highly flammable. Take the following precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery cable before working on any electrical components.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: Gasoline fumes can be harmful.
- Avoid Sparks: Be careful not to create any sparks, especially near fuel lines or the fuel tank.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools and wear safety glasses.
- Depressurize the Fuel System: Before disconnecting any fuel lines, depressurize the fuel system by relieving the pressure at the Schrader valve on the fuel rail (if equipped). Be prepared for some fuel to spray out.
- Be Aware of High Voltage: While the fuel injectors themselves operate on 12V, the ignition system (which works in tandem with the injectors) involves significantly higher voltages. Be careful when working near the ignition coil or distributor.
Conclusion
Understanding the 1994 Jeep Wrangler 2.5L fuel injector wiring diagram is a powerful tool for diagnosing and repairing fuel-related problems. By familiarizing yourself with the components, symbols, and troubleshooting techniques outlined above, you can save time and money and keep your Jeep running smoothly.
We have the complete 1994 Jeep Wrangler 2.5L fuel injector wiring diagram available for download. This detailed diagram will provide you with the specific wire colors, connector locations, and circuit paths you need for accurate diagnosis and repair.
