1996 Dodge Ram 2500 Fuse Box Diagram
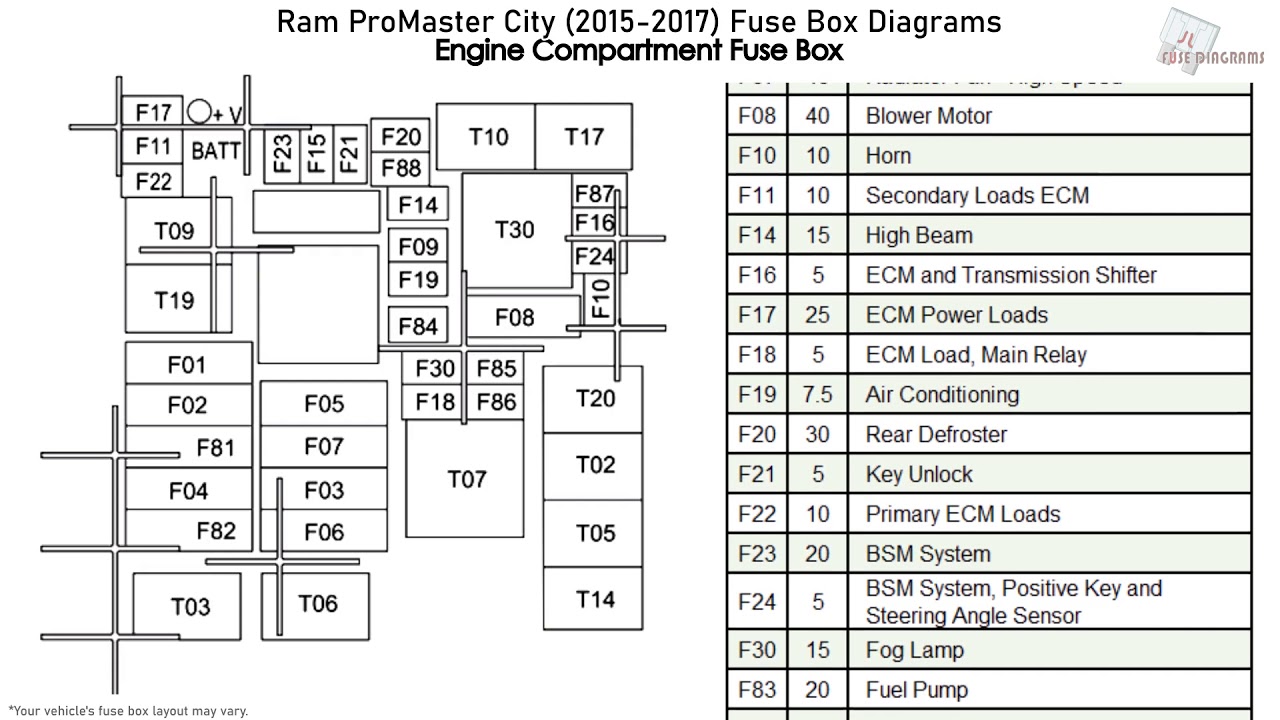
Alright, let's dive into the 1996 Dodge Ram 2500 fuse box diagram. Whether you're chasing down an electrical gremlin, planning an aftermarket upgrade, or simply want a better understanding of your truck's inner workings, this diagram is your indispensable guide. It's more than just a pretty picture; it's a roadmap to your Ram's electrical system.
Purpose of the Fuse Box Diagram
The fuse box diagram serves several critical purposes:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Problems: When a circuit malfunctions – a headlight stops working, the radio cuts out, or the power windows refuse to budge – the fuse box is usually the first place to check. The diagram allows you to quickly identify the fuse associated with the problematic circuit.
- Replacing Blown Fuses: A blown fuse indicates an overcurrent situation. Replacing it with the correct amperage fuse, as indicated by the diagram, is often the solution. However, always investigate the root cause of the blown fuse to prevent recurrence.
- Installing Aftermarket Accessories: Adding accessories like auxiliary lights, a new stereo system, or a trailer brake controller requires tapping into the truck's electrical system. The fuse box diagram shows you available circuits and the appropriate fuse sizes to use, ensuring your new components are safely powered.
- Understanding Your Vehicle's Electrical System: Beyond repairs, the diagram offers a deeper understanding of how the different electrical components are connected and protected. This knowledge empowers you to perform more advanced diagnostics and modifications.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the Fuse Box
The 1996 Dodge Ram 2500 typically has two main fuse boxes:
- Interior Fuse Box: Located, usually, under the dashboard on the driver's side. This fuse box houses fuses for interior components like lights, radio, power windows, and other comfort and convenience features.
- Power Distribution Center (PDC): Found under the hood, often near the battery. The PDC contains fuses and relays for high-current circuits such as the engine control module (ECM), headlights, starter motor, and other vital engine and drivetrain systems. The PDC is often called a fuse box, however, technically the PDC houses fuses and relays. Relays are electromechanical switches that control high-current circuits with a low-current signal.
The diagram itself is generally a printed sheet, often found inside the fuse box cover or in the owner's manual. It will show the location of each fuse and relay, along with a brief description of the circuit it protects and the correct amperage rating. Keep in mind that diagrams can sometimes vary slightly depending on the specific trim level and options of your Ram.
Decoding the Symbols: Lines, Colors, and Icons
Understanding the symbols on the fuse box diagram is crucial for accurate interpretation.
- Lines: Lines represent electrical connections or circuits. A solid line indicates a direct connection, while a dashed line might indicate a connection through a switch or relay.
- Colors: Wire colors are often indicated on the diagram, either as a color abbreviation (e.g., "RED" for red, "BLK" for black, "BLU" for blue) or as a color code. These colors correspond to the actual wire colors in your truck's wiring harness. Knowing the wire color can be incredibly helpful when tracing circuits.
- Icons: Various icons are used to represent different electrical components. Common icons include:
- Fuse: A small rectangle with a squiggly line inside.
- Relay: A square or rectangle with a coil symbol inside.
- Switch: A symbol representing a mechanical switch.
- Ground: The ground symbol, indicating the connection to the vehicle's chassis for grounding.
- Light Bulb: Indicates headlights, taillights or interior lights.
The diagram will also provide an amperage rating for each fuse. This rating is crucial! Using a fuse with a higher amperage than specified can overload the circuit and potentially cause a fire. Never, under any circumstance, use a fuse with a higher amperage rating than what is specified in the fuse box diagram.
The diagram sometimes presents the fuses in an organized order and it also can be out of order. Take the time to go through the entire diagram to find the fuse that you are searching for.
How It Works: A Basic Electrical Circuit
To truly understand the fuse box diagram, it's helpful to grasp the basics of an electrical circuit. A circuit consists of a power source (the battery), a conductor (wires), a load (the device being powered, like a headlight), and a path back to the battery (ground). The fuse is placed in the circuit to protect it from overcurrents.
When too much current flows through the circuit – perhaps due to a short circuit or a malfunctioning component – the fuse's internal element melts, breaking the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity. This prevents damage to other components and reduces the risk of fire. Think of a fuse as a safety valve for your electrical system.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's a simple troubleshooting scenario:
- Symptom: Your Ram's interior lights are not working.
- Diagnosis: Consult the fuse box diagram to identify the fuse responsible for the interior lights (usually labeled as "Interior Lamps" or similar).
- Inspection: Locate the identified fuse in the fuse box and visually inspect it. If the fuse element is broken or blackened, it's blown.
- Replacement: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the exact same amperage rating.
- Testing: Turn on the interior lights to see if the problem is resolved.
If the new fuse blows immediately, there's likely a short circuit in the wiring or a problem with one of the interior light fixtures. Further investigation is needed.
When troubleshooting, always use a multimeter to verify the presence of voltage and continuity. This will help you isolate the problem area more effectively.
Safety: Handle with Care!
Working with electrical systems involves inherent risks. Take these precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the negative battery terminal. This prevents accidental shorts and potential electrical shocks.
- Avoid Water: Never work on electrical systems in wet conditions. Water is an excellent conductor of electricity and can create a dangerous shock hazard.
- High-Current Circuits: Be extremely careful when working with high-current circuits in the PDC, such as those for the starter motor or alternator. These circuits can deliver a powerful electrical shock.
- Proper Tools: Use insulated tools specifically designed for electrical work.
- Don't Overfuse: Never replace a fuse with one of a higher amperage rating. This can bypass the circuit protection and lead to a fire.
The ECM (Engine Control Module) circuits within the PDC should be approached with caution. Mishandling these circuits can damage the ECM, which is an expensive component to replace.
Important Reminder: If you are not comfortable working with electrical systems, consult a qualified mechanic. Electrical problems can be complex and dangerous.
Having a reliable fuse box diagram is the first step in understanding your Ram's electrical system. By understanding the diagram, you'll be able to quickly diagnose issues, modify the electrical system, and know where potential problems can occur.
You can download a printable version of the 1996 Dodge Ram 2500 fuse box diagram here: [LINK TO DOWNLOAD - Placeholder, insert actual link to a PDF diagram here]
