1997 Dodge Ram 2500 Fuse Box Diagram
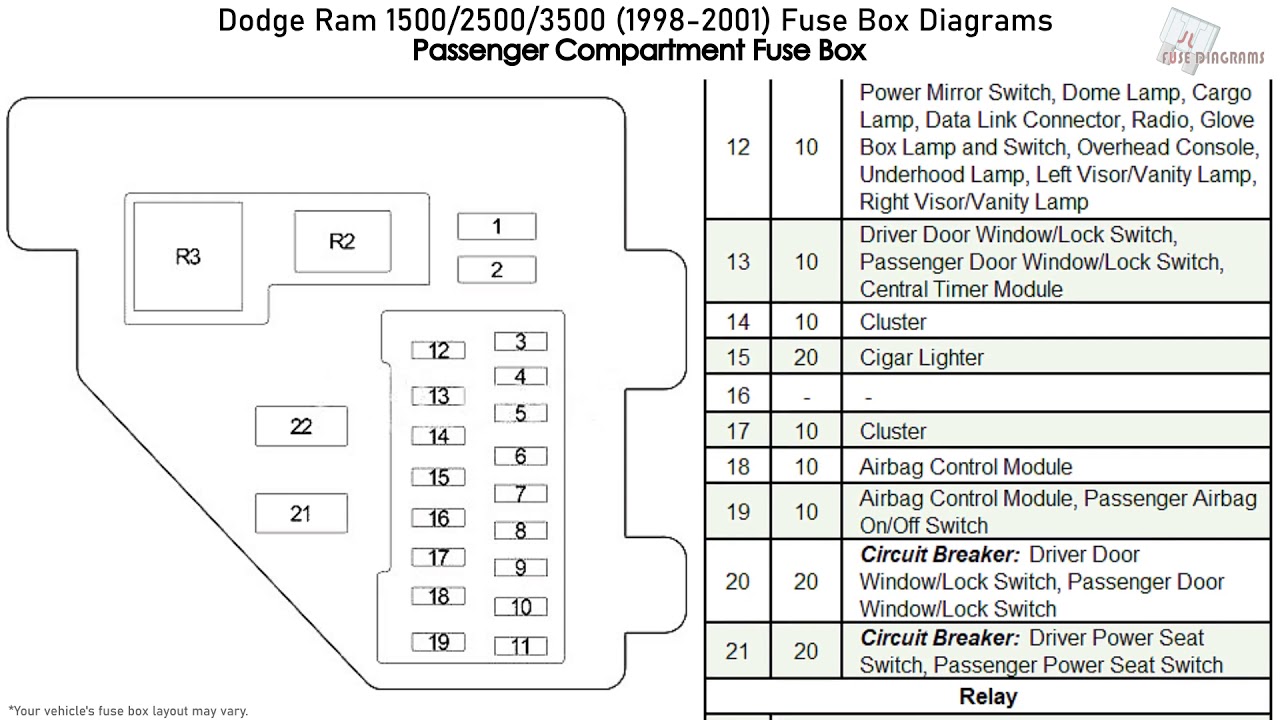
Alright, let's dive into the fuse box diagram for your 1997 Dodge Ram 2500. This document is your best friend when it comes to diagnosing electrical issues, adding aftermarket accessories, or just understanding how the electrical system in your truck is wired. Forget guessing – this diagram is your roadmap.
Purpose of the Fuse Box Diagram
Why is a fuse box diagram so important? Simple: it provides a visual and textual representation of the electrical protection system within your Ram 2500. Without it, troubleshooting a blown fuse or planning a new electrical modification can be a frustrating and potentially damaging endeavor. Think of it as the electrical equivalent of a map for a road trip. You wouldn't attempt to drive cross-country without a map (or GPS), would you? The diagram serves several key purposes:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Faults: When something electrical stops working, the first thing you should check is the fuses. The diagram allows you to quickly identify the fuse associated with the affected circuit.
- Identifying Fuse Ratings: The diagram, often in conjunction with markings on the fuse box itself, specifies the ampere (A) rating of each fuse. Using the correct amperage is critical; using a fuse with a higher rating can bypass the circuit protection and lead to component damage or even a fire.
- Planning Electrical Modifications: Adding a new radio, lights, or any other electrical accessory requires tapping into the existing electrical system. The diagram helps you locate suitable power sources and ensure you're using appropriately fused circuits.
- Learning the Electrical System: For those who are curious about how their vehicle works, the fuse box diagram provides a glimpse into the overall electrical architecture of the Ram 2500.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Your 1997 Dodge Ram 2500 likely has at least two fuse locations: one in the interior (usually under the dashboard or on the side of the dash) and another in the engine compartment (typically near the battery). We'll focus primarily on the interior fuse box, as it tends to house a wider range of circuits. Key components to be aware of include:
- Fuse Box Housing: The physical enclosure that holds all the fuses and relays. It's usually made of plastic and has a cover that can be removed for access.
- Fuses: These are the sacrificial components designed to protect electrical circuits from overcurrent. They come in various amperage ratings, indicated by numbers printed on the fuse itself (e.g., 10A, 20A, 30A). Common types for this era are blade-type fuses (ATO/ATC).
- Relays: Electromagnetic switches that control high-current circuits using a low-current signal. Relays are often used for headlights, fuel pump, and other power-hungry devices.
- Wiring Harness Connectors: These connect the fuse box to the rest of the vehicle's electrical system. They can be a source of problems if they become corroded or loose.
- Grounding Points: Critical for completing electrical circuits. The fuse box will have dedicated grounding points, which should be clean and secure.
Symbols, Lines, Colors, and Icons
Understanding the symbols and conventions used in the fuse box diagram is crucial for accurate interpretation. Here's a breakdown of common elements:
- Fuses: Represented by a zig-zag line or a rectangle with a diagonal line through it. The amperage rating is usually indicated nearby.
- Relays: Typically shown as a rectangle with a coil symbol inside, along with contact points that switch the circuit on or off.
- Wires: Represented by solid lines. Wire colors are often indicated by abbreviations (e.g., BLK for black, RED for red, GRN for green, WHT for white, BLU for blue, YEL for yellow). Sometimes, stripes are indicated, like "WHT/BLK" for a white wire with a black stripe.
- Ground: Shown as a series of downward-pointing lines connected to a horizontal line (like an upside-down Christmas tree). This indicates a connection to the vehicle's chassis, which serves as the ground.
- Component Symbols: The diagram will use various symbols to represent electrical components like headlights, turn signals, the radio, etc. A legend or key will usually be provided to explain these symbols.
- Dotted Lines: May indicate a shielded or protected wire run, or a connection that is not directly part of the fuse box circuit.
How It Works: The Fuse Box as a Central Hub
The fuse box acts as a central distribution and protection point for the electrical system. Power from the battery flows into the fuse box, and from there, it's distributed to various circuits throughout the vehicle. Each circuit is protected by a fuse of the appropriate amperage rating. Here's the basic flow:
- Power Input: The main power supply from the battery enters the fuse box.
- Circuit Distribution: The power is distributed to individual circuits, each dedicated to a specific component or system (e.g., headlights, wipers, radio).
- Fuse Protection: Each circuit passes through a fuse. If the current in the circuit exceeds the fuse's rating (due to a short circuit or overload), the fuse's internal filament melts, breaking the circuit and preventing damage to the component.
- Relay Control (if applicable): For high-current circuits, a relay is used. A low-current signal from a switch (e.g., the headlight switch) activates the relay, which then allows the high current to flow to the component.
- Grounding: Each circuit requires a complete path back to the battery. This is achieved through grounding wires that connect the component to the vehicle's chassis.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Okay, let's get practical. Here’s how you can use the fuse box diagram to troubleshoot common electrical problems:
- Identify the Problem: Determine which electrical component is not working (e.g., the cigarette lighter, a specific headlight).
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse associated with the malfunctioning component in the fuse box diagram.
- Inspect the Fuse: Remove the fuse and visually inspect it. Look for a broken filament inside the fuse. If the filament is broken, the fuse is blown. A multimeter can also be used to test the fuse for continuity. A good fuse will show continuity (close to 0 ohms).
- Replace the Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the exact same amperage rating. Never use a fuse with a higher rating.
- Test the Component: Turn on the component and see if it now works. If it does, great! The problem was a blown fuse.
- If the Fuse Blows Again: If the new fuse blows immediately or shortly after being replaced, there's likely a short circuit in the wiring or a faulty component. This requires further investigation, possibly using a multimeter to check for shorts to ground.
Safety: Highlight Risky Components
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Always observe these safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on the fuse box or any electrical component, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery. This prevents accidental short circuits and electric shocks.
- Use the Correct Fuse Rating: Never replace a fuse with one of a higher amperage rating. This can bypass the circuit protection and lead to overheating, component damage, or even a fire.
- Avoid Working in Wet Conditions: Water is a conductor of electricity. Never work on the electrical system in wet conditions.
- Be Aware of High-Current Circuits: Some circuits, like the starter motor and alternator, carry very high currents. Exercise extreme caution when working with these circuits.
- Consult a Professional: If you're not comfortable working with electrical systems, or if you encounter a complex problem, consult a qualified mechanic. Electrical problems can be tricky to diagnose and repair, and improper repairs can be dangerous.
Keep in mind that specific fuse assignments can vary slightly depending on the exact trim level and options of your 1997 Dodge Ram 2500. However, this guide provides a solid foundation for understanding and troubleshooting your truck's electrical system.
Now that you have a solid understanding of the fuse box diagram, you're better equipped to tackle electrical repairs and modifications on your 1997 Dodge Ram 2500. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult a professional if you're unsure about any aspect of the electrical system.
We have a downloadable PDF file containing the 1997 Dodge Ram 2500 Fuse Box Diagram. You can [Link to download] it here.
