1998 Ford F150 Stereo Wiring Diagram
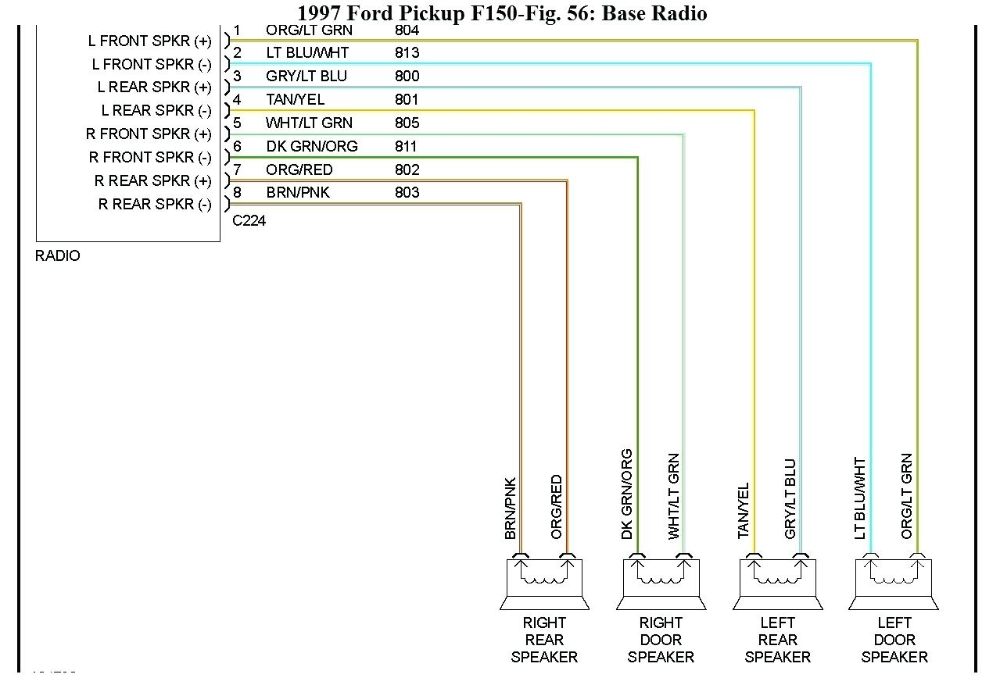
Alright, let's dive into the stereo wiring diagram for a 1998 Ford F-150. This isn't just a bunch of lines and colors; it's a roadmap to your truck's audio system. Whether you're replacing a blown speaker, upgrading to a modern head unit, or just trying to diagnose a buzzing sound, understanding this diagram is crucial.
Purpose of the Diagram
The primary purpose of this wiring diagram is to provide a visual representation of how all the components of your F-150's stereo system are connected. Think of it as the blueprints for your audio setup. It's useful for:
- Repairs: Identifying faulty wiring or components, such as a damaged speaker wire or a short in the power supply.
- Upgrades: Planning and executing upgrades like installing a new head unit, amplifier, or subwoofer. This helps you understand which wires to tap into and where to run new wires.
- Troubleshooting: Diagnosing audio problems, like no sound from a speaker, a constant static noise, or the head unit not turning on.
- Learning: Gaining a deeper understanding of how car audio systems function.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Before we jump into the symbols, let's identify the key components you'll find on a typical 1998 F-150 stereo wiring diagram. Keep in mind that different trim levels might have slightly different configurations, particularly with the addition of premium sound systems.
- Head Unit (Radio): This is the central control unit for your stereo, handling functions like AM/FM radio, cassette/CD playback (if equipped), and often pre-amplification.
- Speakers: Typically, you'll find speakers in the front doors and possibly in the rear of the cab.
- Wiring Harness: The bundle of wires that connects the head unit to the speakers, power source, and other components. This is where the wiring diagram really shines, showing you exactly which wire does what.
- Power Source: The 12V DC power from the vehicle's battery. This is essential for powering the head unit and amplifier (if present).
- Ground: The return path for the electrical current. A good, clean ground connection is vital for proper operation.
- Antenna: Receives radio signals for AM/FM reception.
- Amplifier (Optional): Some F-150s, especially those with upgraded sound systems, may have a separate amplifier located under the seat or behind a trim panel.
Key specifications, while not explicitly on the diagram, are still good to know. Typically, speaker impedance in these systems is 4 ohms. The power handling capacity of the head unit is usually around 4x15-25 watts RMS (Root Mean Square – a more accurate measure of continuous power). Knowing these values is crucial when upgrading speakers or adding an amplifier.
Symbols – Deciphering the Diagram
Understanding the symbols is paramount to reading the wiring diagram effectively. Here's a breakdown of common symbols you'll encounter:
- Solid Lines: Represent wires. The thickness of the line usually doesn't indicate wire gauge, but it's more for visual clarity.
- Dashed Lines: Sometimes indicate shielded wires or less critical connections. They might also represent wires that are optional depending on the specific vehicle configuration.
- Colors: Each wire is represented by a specific color or a color combination (e.g., Red/White). This is critical for identifying the correct wire in the harness. The diagram legend will tell you what each color signifies (e.g., Red = +12V Constant, Black = Ground, etc.).
- Circles with Numbers: Often represent connector pins. The number indicates the pin number within that connector. This is very useful when troubleshooting specific connections.
- Ground Symbol: Looks like an upside-down triangle or a series of horizontal lines getting shorter. It indicates a connection to the vehicle's chassis, providing a ground path.
- Speaker Symbol: A circle with a cone shape inside, representing the speaker. "+" and "-" symbols next to it indicate polarity.
- Fuse Symbol: A squiggly line inside a rectangle. Indicates a fuse that protects the circuit from overcurrent.
- Connector Symbol: Varies, but generally looks like a rectangle or oval with lines connecting to it, representing a wiring harness connector.
Note: The wiring diagram also often uses abbreviations for colors like BK (Black), RD (Red), WH (White), GN (Green), BU (Blue), YL (Yellow), etc. Make sure you check the legend!
How It Works
The system works by taking power from the vehicle's battery (usually through a fused connection) to the head unit. The head unit then processes audio signals from various sources (radio, CD, etc.) and sends them to the speakers. The speakers convert the electrical signals into sound waves.
A simplified signal path looks like this:
- Battery (+12V) -> Fuse -> Head Unit (Power)
- Battery (Ground) -> Head Unit (Ground)
- Antenna -> Head Unit (Radio Signal)
- Head Unit (Audio Output) -> Speakers
- Speakers (Ground) -> Vehicle Chassis (Through Wiring)
If an amplifier is present, the head unit sends a low-level signal to the amplifier, which then boosts the signal before sending it to the speakers. The amplifier also requires a separate power and ground connection.
Real-World Use – Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some basic troubleshooting tips using the wiring diagram:
- No Power to Head Unit: Use the diagram to trace the power wire from the battery (via the fuse) to the head unit. Check the fuse first! Use a multimeter to verify that you have 12V at the head unit's power wire. Also, check the ground connection.
- No Sound from a Speaker: Check the speaker wiring connection at both the head unit (or amplifier, if present) and the speaker itself. Use a multimeter to test the speaker wire for continuity. Also, test the speaker itself for continuity (a reading of a few ohms is typical).
- Static or Noise: Could be a grounding issue. Check all ground connections for corrosion or looseness. Also, make sure the antenna connection is secure.
- Speaker Not Working After Head Unit Upgrade: Double-check that you've wired the speakers correctly according to the new head unit's wiring diagram. Pay close attention to polarity (+ and -).
When troubleshooting, always
disconnect the negative battery terminalto prevent accidental shorts and damage to the electrical system.
Safety – Highlight Risky Components
Working with car electrical systems can be dangerous if you're not careful. Here are some key safety points:
- Airbags: Some wiring harnesses may run near airbag sensors. Never cut or tamper with any wires near airbags without knowing exactly what you're doing. Accidental airbag deployment can cause serious injury.
- Power Wires: Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on any electrical components. This will prevent accidental shorts and potential electrical fires.
- Fuses: Never replace a blown fuse with one of a higher amperage rating. This can overload the circuit and cause a fire. Use the correct amperage fuse as specified in your owner's manual or on the fuse box cover.
- Soldering: When soldering wires, use proper ventilation and avoid inhaling fumes.
Keep in mind that automotive electrical systems can be complex. If you're not comfortable working with electricity, it's always best to consult a qualified professional.
We have the full 1998 Ford F-150 stereo wiring diagram available for download. It provides a much clearer and more detailed view of the system than what we can describe here. This file is invaluable for anyone working on their truck's audio system.
