1999 Silverado Stereo Wiring Diagram
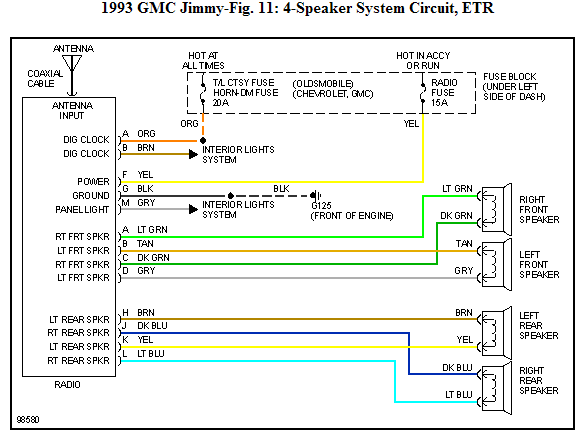
Welcome, fellow gearhead! You're here because you're wrestling with the stereo system in your 1999 Silverado, or perhaps you're just the type who likes to understand how things work. Either way, this deep dive into the 1999 Silverado stereo wiring diagram will equip you with the knowledge to troubleshoot issues, plan upgrades, or simply gain a better appreciation for the electronics humming beneath your dashboard. We're aiming to empower you with a clear understanding, so let's get started.
Purpose: Why Bother With a Wiring Diagram?
Let's be honest, staring at a spaghetti bowl of wires isn't anyone's idea of a good time. However, having a solid understanding of your Silverado's stereo wiring is absolutely crucial for several reasons:
- Troubleshooting Problems: When your speakers cut out, your head unit won't power on, or you're experiencing strange electrical glitches, the wiring diagram is your roadmap to finding the fault. It pinpoints the exact wires involved and their connections.
- Planning Upgrades: Thinking of installing a new head unit, amplifier, or speakers? You need to know which wires do what to ensure a proper and safe installation. Mismatched connections can damage your new equipment or, worse, your vehicle's electrical system.
- Learning and Modification: For those who enjoy tinkering and customizing, understanding the wiring diagram unlocks a world of possibilities. You can tap into existing circuits, add new features, and tailor your audio system to your specific needs.
- Correcting Previous Work: Maybe a previous owner attempted a modification and left a mess of cut and spliced wires. A wiring diagram lets you unravel the chaos and restore the system to its original, functional state.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the 1999 Silverado Stereo System
Before we dive into the diagram itself, let's establish the core components and their basic functions within the 1999 Silverado stereo system:
- Head Unit (Radio): The brain of the operation. It receives radio signals, plays CDs (if equipped), processes audio signals, and distributes them to the speakers. The '99 Silverado typically came with a standard Delco AM/FM radio with optional CD player.
- Speakers: These convert electrical audio signals into sound waves. Silverados typically have speakers in the front doors and sometimes in the rear of the cab, depending on the cab configuration (regular, extended, or crew cab).
- Wiring Harness: This is the bundle of wires that connects all the components together. It's usually a single large connector at the back of the head unit and individual connectors at the speakers.
- Antenna: Receives radio signals and sends them to the head unit.
- Power Supply: The stereo system receives power from the vehicle's battery. This usually involves both a constant 12V supply (for memory) and a switched 12V supply (that turns on with the ignition).
- Ground: Provides a return path for the electrical current. A good, solid ground connection is crucial for proper operation.
Decoding the Diagram: Symbols, Lines, and Colors
A wiring diagram isn't just a random collection of lines and colors; it's a standardized language. Here's a breakdown of what the common symbols represent:
- Solid Lines: These represent wires. The thickness of the line usually doesn't indicate the wire gauge (wire thickness), but rather is used for visual clarity.
- Dashed Lines: These can represent shielded wires or wires that are routed through a specific harness or loom.
- Circles: These often represent connectors or splices where wires are joined together.
- Squares or Rectangles: These typically represent components like the head unit, speakers, or other modules.
- Color Codes: This is absolutely vital. Each wire is identified by a color code (e.g., RED, BLK, YEL, GRN). These codes are usually abbreviated (e.g., RD, BK, Y, GN). Matching the color codes on the diagram to the actual wires in your vehicle is essential for correct identification. You’ll often see dual color codes like “RD/WH” which means Red with a White stripe.
- Wire Gauge: The diagram may or may not explicitly state the wire gauge (e.g., 16 AWG, 18 AWG). However, knowing the wire gauge is crucial when replacing or extending wires. Using a wire gauge that is too thin can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards.
- Ground Symbol: This symbol (often resembling a triangle with horizontal lines) indicates a connection to the vehicle's chassis, providing a return path for the electrical current.
Color codes are crucial. Common colors include:
- Red (RD): Typically a constant 12V power source.
- Yellow (YEL): Often a switched 12V power source (ignition controlled).
- Black (BLK): Ground.
- White (WHT): Often used for speaker wires or illumination.
- Green (GRN): Can be used for various functions, including speaker wires.
- Blue (BLU): Often used for remote turn-on for amplifiers.
How It Works: Tracing the Signal Path
Now, let's trace the flow of electricity and audio signals through the system. Imagine starting with the head unit. The head unit receives power from the battery (constant 12V) and the ignition switch (switched 12V). When the ignition is turned on, the head unit powers up. It then processes audio signals from the radio tuner, CD player, or auxiliary input (if equipped).
These processed audio signals are then sent to the speakers via the wiring harness. Each speaker has two wires: a positive (+) wire and a negative (-) wire. The positive wire carries the audio signal, while the negative wire provides the return path to the head unit (or, in some cases, to a common ground point). The head unit amplifies the audio signal before sending it to the speakers, which vibrate to produce sound.
If you're adding an aftermarket amplifier, the signal flow changes slightly. The head unit's preamp outputs (low-level audio signals) are connected to the amplifier's inputs. The amplifier then boosts the signal and sends it to the speakers. This setup provides much greater power and control over the audio system.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Let's put this knowledge into practice with some common troubleshooting scenarios:
- No Power to Head Unit: Check the fuses first! There's usually a fuse for the radio in the fuse box (often located under the dashboard or in the engine compartment). If the fuse is blown, replace it with one of the same amperage. If it blows again immediately, there's a short circuit somewhere in the wiring. Use the diagram to trace the power wires (red and yellow) and look for any damaged or pinched wires. Also, verify the ground connection is solid.
- One Speaker Not Working: Check the speaker connections. Make sure the wires are securely attached to the speaker terminals and to the head unit (or amplifier). Use a multimeter to check for continuity in the speaker wire. If the wire is broken, replace it. You can also swap the speaker with another one to see if the problem is with the speaker itself.
- Distorted Sound: This could be a sign of a blown speaker, a loose connection, or a problem with the head unit or amplifier. Check the speaker for any signs of damage. Try adjusting the volume and tone controls on the head unit to see if that makes a difference.
- Dim or Flickering Display: Check the illumination wire (often orange or white/blue). This wire dims the display when the headlights are turned on. Make sure the connection is secure and that the dimmer switch is functioning correctly.
Safety First: Handle with Care
Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous. Here are some crucial safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative terminal of the battery before working on any electrical components. This prevents accidental shorts and potential electrical shocks.
- Work in a Well-Lit Area: Good lighting is essential for seeing what you're doing and avoiding mistakes.
- Use Proper Tools: Invest in quality wire strippers, crimpers, and a multimeter. Using the wrong tools can damage wires and components.
- Avoid Working with Live Wires: Never work on live wires unless absolutely necessary, and even then, take extreme caution.
- Be Aware of Airbag Systems: Some wiring harnesses may be located near airbag sensors or modules. Disconnecting or tampering with these systems can cause the airbags to deploy, which can be extremely dangerous. Consult a qualified technician if you're unsure about anything.
- Fuses are Important!: Never replace a fuse with one of higher amperage. This bypasses the safety mechanism and can lead to serious damage or fire.
Remember, when in doubt, consult a qualified automotive electrician. Some repairs are best left to the professionals.
You now have a strong foundation for understanding the 1999 Silverado stereo wiring diagram. Armed with this knowledge, you can confidently tackle troubleshooting, upgrades, and modifications to your audio system. Good luck, and happy listening!
We have the full, high-resolution wiring diagram file ready for you to download. This detailed diagram will provide the visual clarity you need to navigate your Silverado's stereo system with confidence.
