2 Door Power Window Wiring Diagram
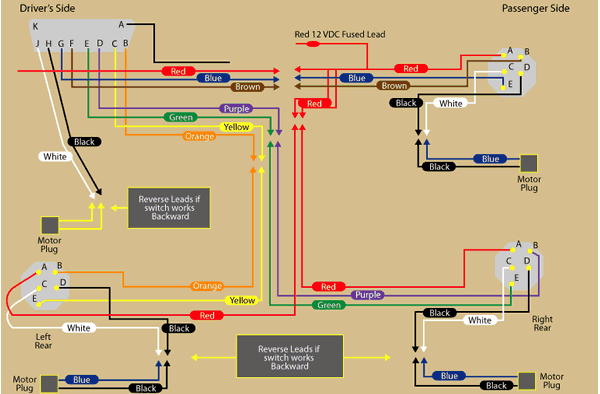
So, you're looking to understand the wiring for a 2-door power window system? Excellent choice! Whether you're troubleshooting a faulty window, upgrading to power windows, or just want to deepen your automotive electrical knowledge, understanding the wiring diagram is crucial. This article will walk you through everything you need to know, from the purpose and key components to troubleshooting and safety precautions. We've even got a downloadable diagram ready for you at the end.
Why Bother with the Wiring Diagram?
A power window wiring diagram is more than just a schematic; it's a roadmap to the entire system. Its purpose is multifaceted:
- Repair and Diagnosis: Pinpointing shorts, opens, or faulty components becomes significantly easier. Instead of blindly probing wires, you can trace the circuit and identify the issue quickly.
- Upgrades and Modifications: Adding aftermarket components like alarms or remote window control requires understanding how the existing system is wired. A diagram allows you to integrate new parts seamlessly.
- Learning and Understanding: For DIY mechanics, studying a wiring diagram is a fantastic way to grasp the fundamental principles of automotive electrical systems. It's like dissecting a machine, piece by piece.
- Preventative Maintenance: Periodically checking the wiring against the diagram can help identify potential problems before they lead to complete failure. Loose connections, corroded wires, and other issues can be spotted early.
Key Specs and Main Parts of a 2-Door Power Window System
A typical 2-door power window system consists of several key components, each playing a vital role:
- Power Window Motor: The heart of the system. This DC motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, driving the window regulator. Two motors are used in a 2 door system.
- Window Regulator: This mechanical assembly converts the motor's rotational motion into the linear motion needed to raise and lower the window glass.
- Power Window Switch(es): These switches, located on the door panels, control the flow of current to the motor, dictating the window's direction of movement (up or down). Usually a master switch on the driver's side controls both windows and a secondary switch on the passenger side controls its own.
- Relays: Often, relays are used to handle the high current needed by the window motors. A relay is an electrically operated switch that allows a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit.
- Circuit Breaker or Fuse: These are essential safety devices that protect the wiring from overload. If the current exceeds a certain limit, the breaker trips or the fuse blows, interrupting the circuit.
- Wiring Harness: A bundle of wires connecting all the components. The wiring harness is carefully routed and secured to prevent damage.
- Ground Connection: A solid ground connection is critical for proper operation. A poor ground can cause all sorts of weird electrical issues.
Typical Voltage: Most automotive electrical systems operate at 12V DC. This is the standard voltage you'll be dealing with when working on a power window system.
Wire Gauge: The gauge (thickness) of the wires is important. Power window motors draw a significant amount of current, so appropriately sized wires are necessary to prevent overheating and voltage drop. Typically, you'll find 14-16 gauge wire used for the main power and ground circuits.
Decoding the Symbols: A Guide to Understanding the Diagram
Understanding the symbols used in a wiring diagram is paramount. Here's a breakdown of the common symbols you'll encounter:
- Lines: Represent wires. A solid line indicates a direct connection. A dashed line might represent a shielded wire or a connection that is not always present (e.g., an optional feature).
- Colors: Each wire is typically identified by its color. Common colors include red (power), black (ground), blue, green, yellow, and white. Color codes vary between manufacturers, so always refer to the specific diagram for your vehicle.
- Circles: Often represent connectors or terminals.
- Squares or Rectangles: Represent components like switches, relays, and motors. Inside the square, you'll often find a symbol representing the specific component (e.g., a coil symbol for a relay).
- Ground Symbol: This symbol (usually three horizontal lines getting progressively shorter) indicates a connection to the vehicle's chassis ground.
- Fuse/Circuit Breaker Symbol: A fuse is typically represented by a wavy line inside a rectangle or a 'U' shape. A circuit breaker might be shown as a switch symbol with a wavy line.
Line Thickness: Sometimes, the thickness of a line indicates the gauge of the wire. Thicker lines represent wires that can carry more current.
How It Works: A Step-by-Step Explanation
Let's break down how a 2-door power window system typically functions:
- Power Supply: The system receives power from the vehicle's battery, typically through a fuse or circuit breaker. This protects the system from overcurrent situations.
- Switch Activation: When you press the power window switch, you're essentially completing a circuit. The switch directs current to the appropriate terminals of the power window motor.
- Motor Operation: Depending on which direction you push the switch (up or down), the polarity of the voltage applied to the motor is reversed. This causes the motor to rotate in the corresponding direction.
- Regulator Movement: The motor's rotation drives the window regulator, which converts the rotary motion into linear motion, raising or lowering the window glass.
- Grounding: The circuit is completed through a solid ground connection to the vehicle's chassis.
- Relay Usage (Optional): Some systems use relays to handle the high current drawn by the motors. The switch controls a low-current circuit that activates the relay, which in turn controls the high-current circuit to the motor. This protects the switch from damage caused by high current.
Polarity Reversal: Key to understanding the operation of a power window motor is the concept of polarity reversal. Changing the direction of the current flow through the motor changes the direction of its rotation.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some common problems and how to troubleshoot them using the wiring diagram:
- Window Doesn't Move:
- Check the Fuse/Circuit Breaker: This is the first step. If it's blown or tripped, replace it with the correct amperage rating. A repeatedly blowing fuse indicates a short circuit.
- Test the Switch: Use a multimeter to check for continuity through the switch when it's activated. If there's no continuity, the switch is likely faulty.
- Check the Motor: Apply 12V directly to the motor terminals (observe polarity). If the motor doesn't run, it's likely bad.
- Inspect Wiring: Look for broken, corroded, or loose wires, especially around connectors and hinges. Use the wiring diagram to trace the circuit.
- Verify Ground: Ensure a solid ground connection. Clean any corrosion and tighten the ground terminal.
- Window Moves Slowly:
- Check Voltage Drop: Use a multimeter to measure the voltage at the motor terminals while the window is operating. Excessive voltage drop indicates resistance in the circuit, possibly due to corroded connections or undersized wiring.
- Inspect Regulator: A worn or binding regulator can cause the motor to work harder, slowing down the window.
- One Window Works, the Other Doesn't:
- Isolate the Problem: The wiring diagram will help you isolate the problem to a specific circuit for the non-functioning window. Check the switch, motor, and wiring for that circuit.
Safety First: Handling High-Current Components
Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous if proper precautions aren't taken:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative terminal of the battery before working on any electrical system. This prevents accidental shorts and electrocution.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools specifically designed for automotive electrical work.
- Avoid Working in Wet Conditions: Water and electricity are a dangerous combination.
- Inspect Wiring Carefully: Look for damaged insulation or exposed wires. Replace any damaged wiring immediately.
- Don't Exceed Fuse Ratings: Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating than specified can damage the wiring and create a fire hazard.
- Be Aware of High-Current Circuits: Power window motors draw a significant amount of current. Be careful when working around these circuits.
Warning: Automotive batteries contain sulfuric acid, which can cause severe burns. Handle batteries with care and wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and eye protection.
We hope this guide has provided you with a solid understanding of 2-door power window wiring diagrams. Armed with this knowledge, you'll be better equipped to diagnose, repair, and upgrade your power window system.
You can download a sample 2-door power window wiring diagram here: Download Wiring Diagram. Remember to always consult the specific wiring diagram for your vehicle model, as wiring configurations can vary significantly between manufacturers and models.
