2 Speed Wiper Motor Wiring Diagram
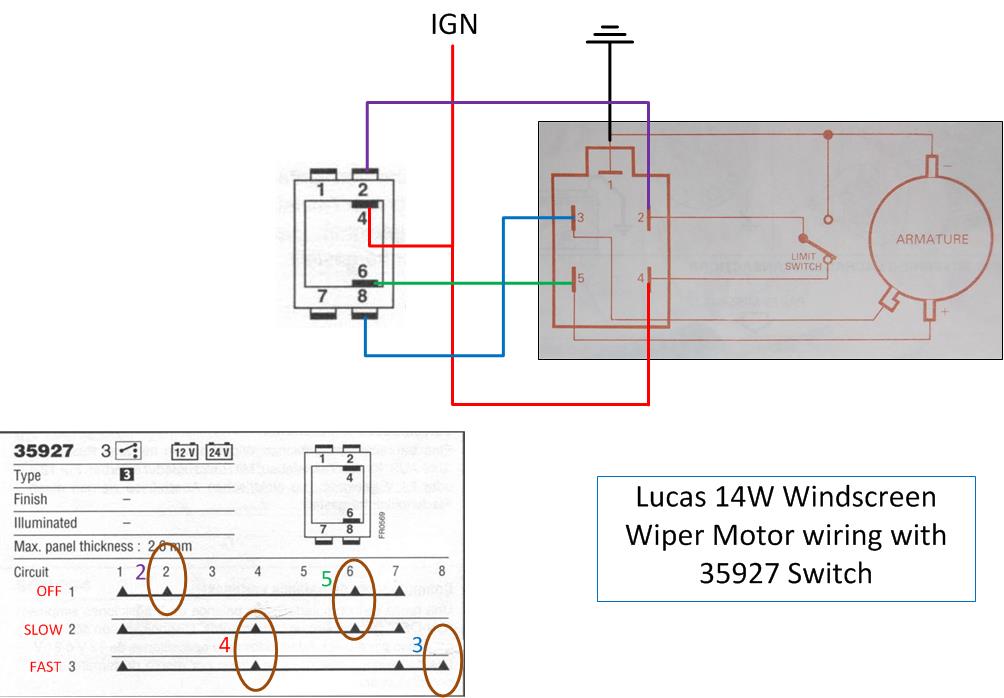
Alright, let's dive into the wonderful world of 2-speed wiper motor wiring diagrams. Whether you're tackling a repair, performing a custom modification, or simply trying to understand your car's electrical system better, a solid understanding of this circuit is invaluable. We're going to break down the diagram, explain the components, and give you some real-world troubleshooting tips. Think of me as your experienced guide to this often-overlooked part of your vehicle.
Purpose of Understanding the 2-Speed Wiper Motor Diagram
Why bother with a wiper motor diagram? There are several compelling reasons:
- Repair and Diagnosis: If your wipers are acting up – maybe they're stuck, only work on one speed, or won't turn off – the diagram is your roadmap to finding the fault. It allows you to systematically check wiring, connections, and component functionality.
- Customization and Upgrades: Thinking about installing an aftermarket wiper motor, or integrating a new control switch? The diagram shows you how the original system is wired, allowing for seamless integration (or knowing what you're about to change!).
- Electrical System Understanding: The wiper motor circuit is a relatively simple electrical system that demonstrates basic automotive electrical principles like relays, switches, and power distribution. It's a great learning tool.
- Preventative Maintenance: Understanding the wiring can help you spot potential problems before they become major headaches. For example, noticing frayed wires or corroded connectors early on can prevent a complete system failure.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Before we get into the diagram itself, let's define the key components we'll encounter. These are the usual suspects in a typical 2-speed wiper system:
- Wiper Motor: The heart of the system, converting electrical energy into mechanical motion to move the wiper arms. Usually a DC permanent magnet motor.
- Wiper Switch: Located on the steering column or dashboard, this allows the driver to select the desired wiper speed (Low, High, Off, and sometimes Intermittent).
- Wiper Motor Gearbox/Linkage: This reduces the motor's speed and converts the rotary motion into the back-and-forth movement of the wiper arms across the windshield. Usually includes a crank arm and a series of connecting rods.
- Relay(s): Often used to control the high-speed circuit, reducing the load on the wiper switch. A relay is an electrically operated switch; a small current in the relay coil controls a much larger current in the main circuit.
- Fuse: A safety device that protects the circuit from overcurrent conditions. When too much current flows, the fuse element melts, breaking the circuit.
- Ground Connection: A vital part of any electrical circuit, providing a return path for the current to the vehicle's chassis (which is connected to the negative terminal of the battery).
- Wiring Harness: A bundle of wires that connects all the components together. The wires are typically color-coded for easy identification.
Symbols in the Diagram
Understanding the symbols used in the wiring diagram is critical. Here's a breakdown of common symbols you'll encounter:
- Solid Lines: Represent wires. Thicker lines often indicate wires that carry higher current.
- Dashed Lines: Sometimes indicate connections within a component (e.g., inside the wiper motor itself) or represent a less critical connection or a shield.
- Color Codes: Wires are usually color-coded (e.g., Red = Power, Black = Ground, Blue = Low Speed, etc.). A legend on the diagram will explain the color scheme. Always refer to the legend for accuracy.
- Circles/Dots: Indicate connection points where wires are joined together.
- Rectangles with Wires: Represent connectors, where wires are plugged into components or other parts of the wiring harness.
- Relay Symbol: A coil symbol connected to a switch symbol. The coil represents the relay's electromagnet, and the switch represents the contacts that open and close when the coil is energized.
- Fuse Symbol: A wavy line or a rectangle with a "fuse" label.
- Ground Symbol: A series of descending horizontal lines, often resembling an upside-down tree.
- Switch Symbol: Various representations depending on the type of switch (e.g., single-pole, double-throw). The diagram will show the switch positions (Off, Low, High).
How the 2-Speed Wiper System Works
Let's break down how the 2-speed wiper system generally functions:
- Power Supply: The circuit receives power from the vehicle's battery, usually through the ignition switch.
- Low-Speed Operation: When the wiper switch is set to the "Low" position, power is routed through a specific wire to the wiper motor. This supplies the motor with a certain voltage, causing it to operate at a slower speed. Often, the low speed runs power through an internal resistor in the motor to reduce voltage and RPM.
- High-Speed Operation: When the wiper switch is set to "High," power is routed through a different wire, typically directly to the motor, bypassing any resistors or other speed-reducing components. This results in the motor receiving full voltage and operating at its maximum speed. In many designs, the high-speed circuit uses a relay to handle the higher current draw. The wiper switch activates the relay, which then closes the circuit to the motor.
- Park Position: Most wiper systems have a "park" feature that automatically stops the wipers in a defined position (usually at the bottom of the windshield) when the switch is turned off. This is achieved through a special contact within the wiper motor gearbox that continues to supply power to the motor until it reaches the park position. Even when the main switch is off, this park circuit remains active until the wipers reach the bottom of the windshield.
- Ground Path: A crucial part of the circuit, the ground wire completes the electrical loop, allowing current to flow and the motor to operate. A poor ground connection is a common cause of wiper problems.
Real-World Use and Basic Troubleshooting
Okay, your wipers aren't working. Let's troubleshoot. Here's a simplified approach, using the wiring diagram:
- No Wipers at All:
- Check the Fuse: The first and easiest step. Replace if blown. A constantly blown fuse indicates a short circuit.
- Check the Ground: A bad ground can cause all sorts of issues. Clean and tighten the ground connection near the wiper motor.
- Test the Wiper Switch: Use a multimeter to check if the switch is sending power to the motor in both Low and High positions.
- Test the Motor Directly: Disconnect the wiring harness from the wiper motor and apply 12V directly to the motor terminals (following the wiring diagram). If the motor runs, the problem is in the wiring or switch. If it doesn't run, the motor is likely faulty.
- Wipers Only Work on One Speed:
- Check the Wiring: Inspect the wires and connectors for damage or corrosion, focusing on the circuit for the speed that isn't working.
- Test the Wiper Switch: As above, use a multimeter to check for proper voltage output in both switch positions.
- Check the Relay (if applicable): If the high speed isn't working, test the relay. You can usually hear it click when activated. If not, it may be faulty.
- Wipers Don't Park Correctly:
- Check the Park Switch/Contact: This is usually located inside the wiper motor gearbox. It may be dirty or worn. Sometimes, cleaning the contacts can resolve the issue.
- Wiring to the Park Switch: Ensure the wiring to the park switch is intact and properly connected.
Safety Considerations
Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous. Keep these safety tips in mind:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative terminal of the battery before working on the electrical system to prevent shorts and electrical shocks.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools to avoid electrical shock.
- Be Careful with Wiring: Wires can become brittle over time and crack, exposing bare conductors. Handle wires carefully and replace damaged wires.
- Understand the Diagram: Don't guess! Take the time to study the wiring diagram and understand the circuit before you start working.
- Fuses are Critical: Never bypass a fuse with a wire or other conductive material. This can cause a fire. Always use the correct amperage fuse.
- High Current: The wiper motor can draw a significant amount of current, especially when stalled. Avoid touching exposed terminals while the motor is operating.
Remember that diagnosing electrical problems can sometimes be challenging. If you're not comfortable working on the electrical system, it's best to consult a qualified mechanic.
Now that you have a basic grasp of the 2-speed wiper motor wiring diagram, you’re better equipped to diagnose and fix common problems. Take your time, be methodical, and be safe! Good luck!
By the way, we have a detailed 2-speed wiper motor wiring diagram file available for download. It includes detailed color codes and specific component locations for common vehicles. Feel free to download it and use it as a reference for your projects.
