2001 Dodge Ram 1500 Evap System Diagram
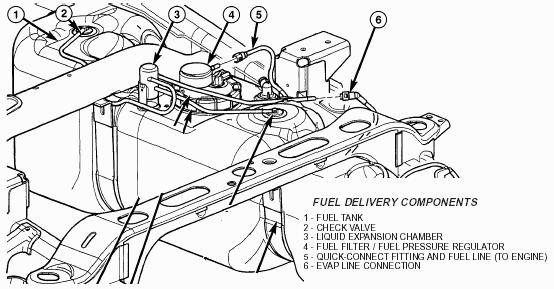
Let's dive deep into the EVAP system diagram for your 2001 Dodge Ram 1500. Understanding this system is crucial for diagnosing and repairing fuel vapor leaks, improving fuel efficiency, and keeping your truck running smoothly. Whether you're tackling a pesky check engine light or just want to expand your automotive knowledge, this guide will break down the EVAP system's intricacies.
Why This Diagram Matters
Having a solid understanding of the EVAP (Evaporative Emission Control) system diagram is invaluable for a few key reasons:
- Troubleshooting: When your check engine light illuminates, and the code points to an EVAP system issue (like P0440, P0441, P0442, P0455, etc.), the diagram becomes your roadmap. It helps you trace the system, locate potential problem areas, and test components methodically.
- Repairing: Replacing a faulty purge valve or vapor canister without knowing where it's located can be a time-consuming and frustrating process. The diagram provides the precise location of each component.
- Understanding: Gaining a deeper understanding of how your vehicle manages fuel vapors not only empowers you to handle repairs but also makes you a more informed vehicle owner.
- Modification Considerations: If you are planning on modifying the vehicle, you will need to ensure that you do not violate any emission laws and fully understand how the EVAP system works with other systems.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2001 Dodge Ram 1500's EVAP system is a pretty standard example of the era's technology. The aim is simple: prevent fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere.
Main Components:
- Fuel Tank: This is where it all starts. Fuel vapors are naturally produced within the tank.
- Fuel Cap: A seemingly simple component, but a properly sealing fuel cap is crucial. A loose or damaged cap is a common cause of EVAP system leaks.
- Vapor Canister: The heart of the system. This canister, typically filled with activated charcoal, stores fuel vapors from the fuel tank.
- Purge Valve (Solenoid): This electrically controlled valve allows the engine to draw stored fuel vapors from the vapor canister into the intake manifold to be burned. It's controlled by the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
- Vent Valve (Solenoid): The vent valve controls airflow into the vapor canister. It usually resides close to the canister. It is normally open allowing air into the canister as fuel is drawn out. When the system is being tested the vent valve is closed to seal the system to test for leaks.
- Leak Detection Pump (LDP): While not present on all 2001 Dodge Ram 1500 models, especially earlier ones, some configurations may incorporate an LDP to actively test the system for leaks. The PCM will instruct the pump to apply a vacuum or pressure to the EVAP system and then monitor the pressure sensor for any loss of pressure.
- Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor (FTPS): This sensor measures the pressure within the fuel tank. The PCM uses this data to monitor the EVAP system and diagnose potential problems.
- Hoses and Tubing: A network of hoses and tubing connects all the components. These are prone to cracking and leaks over time.
Key Specifications:
- System Type: Negative Pressure (Vacuum)
- Control Method: PCM (Powertrain Control Module)
- Purge Valve Duty Cycle: Variable, controlled by PCM based on engine load and other parameters. The PCM opens and closes the valve rapidly to control the amount of vapor entering the engine.
- Typical Vacuum During Testing: 5-10 inches of water column
Understanding the Symbols
The EVAP system diagram uses a variety of symbols to represent different components and connections. While the specific legend may vary slightly depending on the source, here's a general guide:
- Solid Lines: Typically indicate hard fuel lines or vacuum lines.
- Dashed Lines: Often represent electrical wiring or signal pathways.
- Arrows: Show the direction of airflow or fluid flow.
- Rectangles: Usually represent electrical components like solenoids (purge valve, vent valve).
- Circles: May indicate pressure sensors or other sensors.
- Color Coding: While not always present, some diagrams use color coding to distinguish between different types of lines (e.g., green for vacuum, blue for liquid fuel).
Pay close attention to the junctions (where lines connect). These are often potential leak points. Also, note the labels on each component. The diagram will usually have abbreviations, such as "PV" for purge valve, "VC" for vapor canister, and "FTPS" for fuel tank pressure sensor.
How the EVAP System Works
Here's a simplified explanation of how the EVAP system operates on your 2001 Dodge Ram 1500:
- Vapor Collection: As fuel evaporates in the tank, the vapors are routed to the vapor canister. The charcoal in the canister absorbs and stores these vapors.
- Purge Cycle: When the engine is running and conditions are right (e.g., engine is warm, vehicle is cruising), the PCM activates the purge valve.
- Vapor Combustion: The purge valve opens, allowing engine vacuum to draw air through the vent valve, through the vapor canister, and then into the intake manifold. This draws the stored fuel vapors from the canister and into the engine to be burned, preventing their release into the atmosphere.
- Leak Detection: The PCM constantly monitors the fuel tank pressure sensor. During certain driving conditions, the PCM will close the vent valve, sealing the EVAP system. It can then monitor the fuel tank pressure sensor and identify whether the pressure is staying constant, dropping slowly (indicating a small leak) or more rapidly (indicating a larger leak). In LDP equipped vehicles, the pump will be activated to either pressurize or pull vacuum, then the system is monitored for leakdown.
The entire process is controlled by the PCM, which takes into account engine load, speed, temperature, and other factors to optimize the purge rate and ensure proper operation.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some basic troubleshooting steps you can take based on common EVAP system issues:
- Check the Fuel Cap: This is the first and easiest step. Ensure the fuel cap is properly tightened and in good condition. Replace it if it's cracked or the seal is damaged.
- Inspect Hoses and Tubing: Visually inspect all the hoses and tubing for cracks, breaks, or loose connections. Pay attention to areas near the engine, where heat can cause hoses to deteriorate more quickly.
- Listen for Vacuum Leaks: With the engine running, listen for hissing sounds around the EVAP system components. This can indicate a vacuum leak.
- Check the Purge Valve: Disconnect the purge valve electrical connector. Using a multimeter, check for voltage at the connector when the engine is running. Also, check the valve for continuity to ground when the engine is off. Finally, ensure the valve closes completely when de-energized.
- Smoke Test: The best way to find EVAP leaks is to use a smoke machine. This introduces smoke into the system, making leaks easy to spot.
Safety Precautions
Working with the EVAP system involves dealing with fuel vapors, which are flammable. Always take the following precautions:
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: Avoid working in enclosed spaces where fuel vapors can accumulate.
- No Smoking or Open Flames: Keep all sources of ignition away from the work area.
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the negative battery terminal to prevent accidental shorts.
- Fuel Pressure: Be aware that the fuel tank might be pressurized. When opening fuel lines, do so slowly and be prepared for fuel to spill.
- Vapor Canister Location: In the Dodge Ram 1500, the location of the vapor canister can vary depending on the model year and configuration. Consult the diagram carefully to avoid damaging other components when accessing the canister.
The fuel tank and the fuel lines store fuel under pressure. Exercise extreme caution when working on these parts of the system. Always relieve the pressure before disconnecting any fuel lines.
By understanding the EVAP system diagram and following these guidelines, you can effectively diagnose and repair EVAP system issues on your 2001 Dodge Ram 1500.
We have the EVAP system diagram available as a downloadable file. This detailed diagram will provide a visual representation of the entire system, making it easier to locate components and trace lines.
