2002 Chevy Trailblazer 4.2 Serpentine Belt Diagram
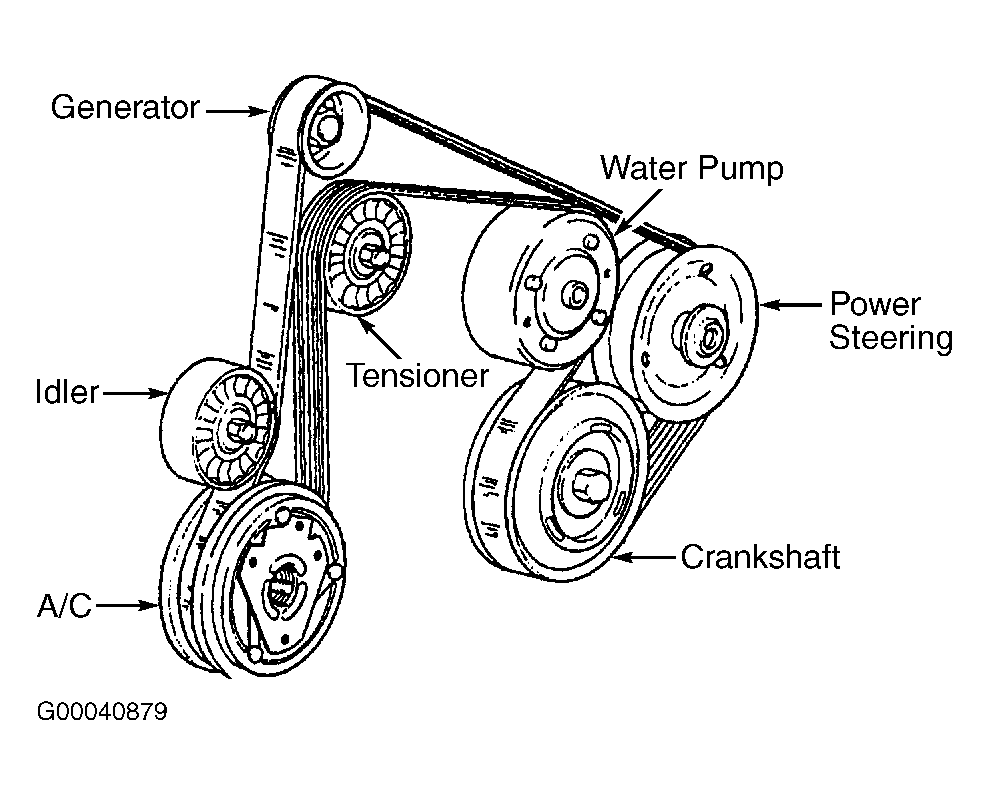
Alright, let's dive into the serpentine belt system of the 2002 Chevy Trailblazer with the 4.2L inline-six engine. Understanding this system is crucial for several reasons. Whether you're tackling routine maintenance, diagnosing a squealing noise, or even planning an accessory upgrade, knowing the belt's routing and function is paramount. This isn't just about slapping a new belt on; it's about ensuring proper tension, preventing component damage, and keeping your Trailblazer running smoothly.
Purpose: Why This Diagram Matters
A serpentine belt diagram isn't just a pretty picture; it's a vital tool for several tasks:
- Replacement and Installation: The most obvious use. When replacing a worn or damaged serpentine belt, the diagram ensures you route the new belt correctly. An incorrectly routed belt will lead to system failure, component damage, and potentially strand you.
- Troubleshooting: A squealing or slipping belt can often be traced back to improper tension or a misaligned pulley. The diagram helps you identify each component and its role, allowing you to pinpoint the source of the problem.
- Accessory Diagnosis: If your AC isn't blowing cold, your power steering is stiff, or your battery isn't charging, the serpentine belt is a prime suspect. The diagram clarifies which accessories are driven by the belt, streamlining your troubleshooting efforts.
- Preventative Maintenance: Regular inspection of the belt and its components can prevent catastrophic failures. The diagram helps you visually inspect each pulley and accessory for wear and tear.
- Modification and Upgrades: Planning to install an aftermarket supercharger or a high-output alternator? You'll need to understand the existing belt routing to ensure proper integration.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2002 Trailblazer 4.2L uses a single, multi-ribbed serpentine belt to drive several crucial engine accessories. Here’s a breakdown of the key components and some typical specifications:
- Serpentine Belt: This is the star of the show. Made of reinforced rubber, it's designed to transmit power from the crankshaft pulley to the various accessories. A typical belt for this application is approximately 90-95 inches long, but always verify the exact length for your specific model year and options. Look for markings like "K6" or "K7" followed by a length measurement.
- Crankshaft Pulley (Harmonic Balancer): Located at the bottom of the engine, this pulley is directly connected to the crankshaft and provides the driving force for the entire serpentine system. It also acts as a dampener to absorb vibrations from the engine.
- Alternator Pulley: Driven by the serpentine belt, the alternator generates electrical power to recharge the battery and supply electricity to the vehicle's systems.
- Power Steering Pump Pulley: This pulley drives the power steering pump, providing hydraulic assistance for steering.
- Air Conditioning Compressor Pulley: Engaged by the AC compressor clutch, this pulley drives the compressor, which circulates refrigerant to cool the cabin.
- Water Pump Pulley: The water pump circulates coolant through the engine to prevent overheating. Its pulley is driven by the serpentine belt.
- Tensioner Pulley: This spring-loaded pulley maintains proper tension on the serpentine belt, preventing slippage and ensuring efficient power transfer. This is a critical component. A failing tensioner can lead to belt squeal and premature belt wear.
- Idler Pulley(s): One or more smooth pulleys that help guide the serpentine belt and maintain proper wrap around the other pulleys.
Symbols: Understanding the Diagram
Serpentine belt diagrams use specific symbols to represent components and belt routing. Here's a guide:
- Solid Lines: Indicate the path of the front (ribbed) side of the serpentine belt. This is the side that makes contact with the pulleys.
- Dotted Lines: Often used (though not always) to represent the path of the back (smooth) side of the belt. Sometimes, a different color may indicate the back side.
- Arrows: Show the direction of belt travel around each pulley. This is crucial for ensuring proper routing.
- Pulley Symbols: Typically represented as circles. Smaller circles often denote idler pulleys. Larger circles usually represent accessory pulleys. The diagram may label them with abbreviations like "ALT" for alternator, "P/S" for power steering, "A/C" for air conditioning, "WP" for water pump, and "CRANK" for crankshaft.
- Tensioner Symbol: Usually depicted with an arrow indicating the direction of tensioner movement.
How It Works
The serpentine belt system on the 2002 Trailblazer 4.2L is designed for efficient power transfer. The crankshaft pulley, driven by the engine, spins the serpentine belt. This belt, in turn, drives all the engine accessories listed above. The tensioner pulley automatically adjusts to maintain the correct belt tension as the belt stretches or components heat up. The idler pulleys ensure the belt wraps sufficiently around each pulley for optimal grip and power transfer. A properly functioning system is essential for reliable vehicle operation.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some common issues you might encounter and how the serpentine belt diagram can help:
- Squealing Belt:
- Possible Causes: Loose belt, worn belt, glazed belt, misaligned pulley, failing tensioner.
- Troubleshooting with Diagram: Use the diagram to check belt routing and ensure the belt is properly seated on all pulleys. Inspect the tensioner pulley for smooth movement and proper spring tension. A worn tensioner can cause intermittent squealing. Look for signs of belt damage (cracks, fraying, glazing).
- Belt Slippage:
- Possible Causes: Loose belt, worn belt, oil contamination, damaged pulley.
- Troubleshooting with Diagram: Verify the belt routing. Check for oil leaks near the pulleys that could be contaminating the belt. Inspect pulleys for damage or excessive wear.
- Accessory Failure (e.g., No Power Steering):
- Possible Causes: Broken or slipped belt, failed power steering pump.
- Troubleshooting with Diagram: Confirm the belt is intact and properly routed around the power steering pump pulley. If the belt is fine, the power steering pump itself may be faulty.
- Overheating:
- Possible Causes: Slipping or broken belt preventing the water pump from circulating coolant effectively.
- Troubleshooting with Diagram: Confirm the belt is intact and properly routed around the water pump pulley.
Safety: Highlight Risky Components
Working on the serpentine belt system involves several safety considerations:
- Engine Off: Always ensure the engine is off and the ignition key is removed before working on the serpentine belt system.
- Hot Engine: Allow the engine to cool completely before touching any components. Exhaust manifolds and other engine parts can be extremely hot.
- Moving Parts: Keep hands, clothing, and tools clear of the serpentine belt and pulleys when the engine is running. The rotating belt can cause serious injury.
- Tensioner Spring: The tensioner pulley is spring-loaded and can snap back forcefully when released. Use the correct tool to relieve tension safely. Refer to your vehicle's repair manual for specific instructions. Incorrectly releasing the tensioner can cause injury.
- Battery Disconnect: While not always strictly necessary, disconnecting the negative battery cable provides an extra margin of safety, especially if you're unfamiliar with the system.
Understanding the 2002 Chevy Trailblazer 4.2L serpentine belt system is a valuable skill for any DIY mechanic. Using the diagram as a guide, you can confidently tackle belt replacements, troubleshoot common issues, and maintain your vehicle's performance.
We have a high-resolution, printable PDF of the 2002 Chevy Trailblazer 4.2L Serpentine Belt Diagram available for download. This diagram provides a clear and detailed visual reference for your projects, making the process even easier.
