2002 Nissan Altima Fuse Box Diagram
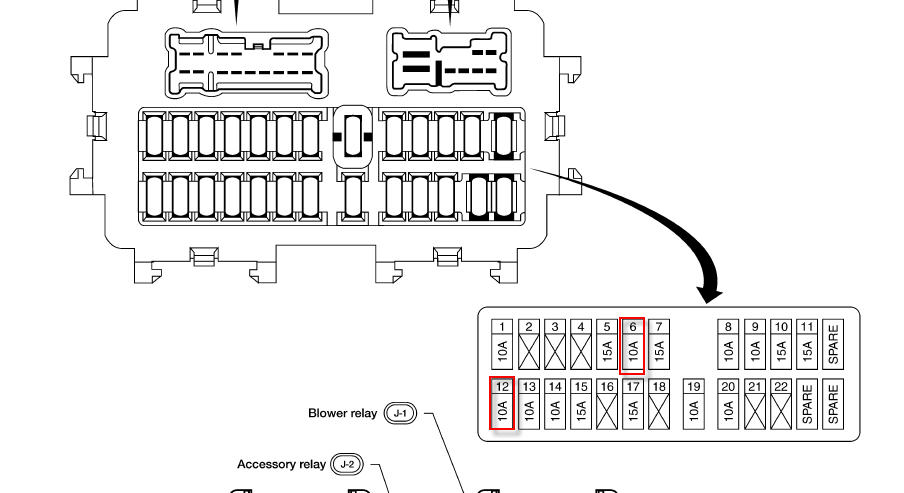
Alright, let's dive into the 2002 Nissan Altima fuse box diagram. This isn't just a pretty picture; it's your roadmap to understanding and troubleshooting the electrical system of your Altima. Whether you're chasing down a dead cigarette lighter, planning an aftermarket accessory installation, or just trying to understand how your car ticks, this diagram is invaluable. We've got the full diagram available for download (link at the end), but let's walk through it so you know what you're looking at.
Purpose of the Fuse Box Diagram
Why bother with a fuse box diagram? Simple: it's the key to diagnosing and fixing electrical problems in your Altima. Think of it like this: the fuse box is the central distribution point for electricity in your car. Fuses are designed to be the weak link in the circuit. When a circuit draws excessive current (usually due to a short circuit or an overloaded component), the fuse blows, protecting the more expensive and critical components like the ECU (Engine Control Unit) or the power windows motor. Without a diagram, you're just guessing which fuse controls what, leading to wasted time and potentially damaging your car.
Beyond repairs, the diagram is essential for adding aftermarket accessories. Want to install a new stereo, fog lights, or a remote starter? You'll need to know which circuits can handle the extra load and where to tap into the electrical system safely. The fuse box diagram provides this information, preventing you from overloading a circuit and causing a fire or damaging your car's electronics.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the Fuse Box
The 2002 Altima has primarily two fuse box locations: one inside the cabin (usually under the dashboard on the driver's side) and one in the engine compartment. The engine compartment fuse box tends to handle circuits for critical engine management components, lighting, and other high-current devices. The interior fuse box handles things like the radio, interior lights, and power accessories.
Here are some key components you'll find in the fuse box:
- Fuses: These are the protective devices. They're rated in amperes (amps or A), which indicates how much current they can handle before blowing. Common fuse ratings in your Altima might be 5A, 7.5A, 10A, 15A, 20A, 25A, and 30A.
- Relays: Relays are electrically operated switches. They allow a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit. For example, the headlight relay uses a small current from the headlight switch to control the larger current needed to power the headlights.
- Circuit Breakers: Some circuits, particularly those controlling power windows or seats, might use circuit breakers instead of fuses. Circuit breakers automatically reset after a short time, but they'll continue to trip if the fault persists.
- Fuse Puller: A small plastic tool (often included in the fuse box itself) used to safely remove fuses.
Understanding the Symbols and Diagram
The fuse box diagram isn't just a list of fuse numbers; it's a schematic. Here's how to decipher it:
- Lines: Lines represent the electrical circuits. Thicker lines usually indicate circuits carrying more current.
- Colors: Wire colors are often indicated on the diagram, typically using abbreviations (e.g., BL for Blue, R for Red, BK for Black). Knowing the wire color can help you trace the circuit in the car.
- Icons: Icons represent the components protected by each fuse. These icons can vary, but common ones include:
- A headlight icon for headlight circuits.
- A radio icon for the radio circuit.
- A cigarette lighter icon for the cigarette lighter circuit (or power outlet).
- A fan icon for the blower motor circuit.
- Fuse Number and Amperage: Each fuse is labeled with a number and its amperage rating (e.g., Fuse #12, 15A). This is crucial for replacing a blown fuse with the correct type.
The diagram will usually be separated into sections for the interior and engine bay fuse boxes, or it might be presented as separate diagrams altogether. Make sure you're looking at the correct diagram for the fuse box you're working on.
How It Works: A Simplified Explanation
The electrical system of your car works by creating closed circuits. Electricity flows from the battery, through a switch (like the headlight switch), through the component (like the headlight bulb), and back to the battery. The fuse is placed in this circuit as a safety measure. If, for some reason, the current in the circuit exceeds the fuse's rating, the fuse's internal element melts (blowing the fuse), breaking the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity. This prevents overheating, fires, and damage to the components in the circuit.
Think of the fuse as a gatekeeper. It only allows a certain amount of current to pass through. If too much current tries to flow, the gate slams shut, protecting the rest of the system.
Real-World Use and Basic Troubleshooting
Let's say your cigarette lighter isn't working. Here's how you can use the fuse box diagram to troubleshoot:
- Consult the Diagram: Find the fuse box diagram for your 2002 Altima (remember, we have it for you to download).
- Locate the Cigarette Lighter Fuse: Look for the icon that resembles a cigarette lighter. Note the fuse number and amperage rating.
- Inspect the Fuse: Use the fuse puller to remove the fuse. Hold it up to the light and examine the internal element. If the element is broken or melted, the fuse is blown.
- Replace the Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the same amperage rating. Never use a fuse with a higher amperage rating, as this could overload the circuit and cause damage.
- Test the Circuit: Turn on the ignition and test the cigarette lighter. If it still doesn't work, there may be another problem, such as a faulty cigarette lighter socket or a wiring issue.
If a fuse blows repeatedly, it indicates a more serious problem. There's likely a short circuit or an overload in the circuit. You'll need to investigate further to find the cause of the excessive current draw. This might involve tracing wires, inspecting components, and using a multimeter to measure voltage and resistance.
Safety Precautions
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Here are some important safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery. This will prevent accidental shocks or short circuits.
- Use the Correct Fuse: Always replace a blown fuse with a fuse of the same amperage rating. Using a higher amperage fuse can bypass the circuit's protection and lead to damage or fire.
- Avoid Water: Never work on electrical components in wet conditions. Water is a conductor of electricity and can increase the risk of electric shock.
- Be Careful with Relays: Relays can get hot, especially when they're operating. Avoid touching them directly, especially after the car has been running for a while.
- High Current Circuits: Pay extra attention to circuits associated with the alternator, starter motor, and other high-current devices. These circuits can deliver a powerful shock.
Certain components near the fuse box carry high voltage and amperage. The main power distribution block, for example, is directly connected to the battery and can deliver a substantial shock even with the car turned off. Exercise extreme caution when working in this area.
Remember, if you're not comfortable working on electrical systems, it's always best to consult a qualified mechanic.
We have the complete 2002 Nissan Altima fuse box diagram available for download. Knowing how to interpret this diagram will save you time, money, and potential headaches down the road. Good luck!
