2002 Nissan Sentra Fuse Box Diagram
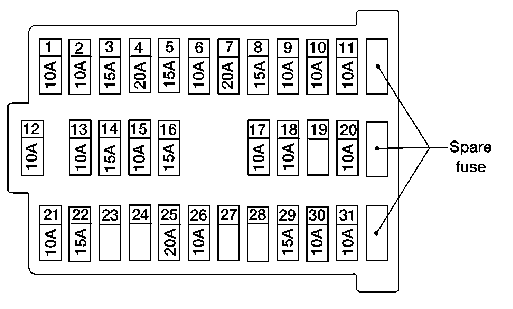
Alright, let's dive into the 2002 Nissan Sentra fuse box diagram. Whether you're chasing down an electrical gremlin, planning a modification, or simply trying to better understand your car's electrical system, having a clear understanding of the fuse box layout is absolutely essential. This isn't just about replacing a blown fuse; it's about understanding the interconnectedness of your car's systems.
Purpose: Why Bother with the Fuse Box Diagram?
Why should you care about a seemingly mundane diagram? Here's the breakdown:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Issues: The most common reason. A non-functional radio, a faulty turn signal, or a dead cigarette lighter often point to a blown fuse. The diagram helps you quickly identify the culprit instead of blindly pulling fuses.
- Performing Electrical Modifications: Adding aftermarket accessories (like a new sound system, auxiliary lights, or a dashcam) requires tapping into the car's electrical system. You need to know which circuits can handle the extra load and where to safely connect your new device.
- Understanding Your Car's Electrical System: The diagram provides a visual representation of how different components are powered and protected. This knowledge is invaluable for advanced diagnostics and repairs.
- Preventing Fires and Further Damage: Replacing a blown fuse with one of a higher amperage rating is a recipe for disaster. The diagram helps ensure you're using the correct fuse for each circuit, preventing potential electrical fires and damage to sensitive components.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the 2002 Sentra Fuse Boxes
The 2002 Nissan Sentra typically has two main fuse boxes:
- Interior Fuse Box: Located inside the cabin, usually under the dashboard on the driver's side. This fuse box primarily protects circuits related to interior components like the radio, lights, power windows, and various control modules.
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box: Found under the hood, near the battery. This fuse box houses fuses and relays for engine-related components like the fuel pump, ignition system, headlights, and cooling fan.
Within each fuse box, you'll find:
- Fuses: These are the sacrificial links in the electrical chain. They contain a thin wire that melts and breaks the circuit when an overcurrent condition occurs, preventing damage to other components. Fuses are rated in amperes (amps or A), which indicates the amount of current they can handle before blowing.
- Relays: Electrically operated switches that allow a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit. Relays are used to switch on and off things like headlights, fuel pumps, and starter motors.
- Circuit Breakers: Similar to fuses, but they can be reset after tripping. Circuit breakers are typically used for circuits that are prone to temporary overloads.
- Connectors and Wiring: These are the physical connections and wires that carry electricity to and from the fuses, relays, and other components.
Decoding the Diagram: Symbols, Lines, and Colors
Understanding the fuse box diagram requires deciphering its symbols and conventions. Here's a breakdown:
- Fuse Symbols: Fuses are typically represented by a rectangle with a squiggly line inside or a simple line with a break in the middle.
- Relay Symbols: Relays are usually depicted as a coil (representing the electromagnet) and a switch (representing the contacts).
- Line Thickness: The thickness of the lines in the diagram can sometimes indicate the wire gauge (thickness) and, therefore, the current-carrying capacity. Thicker lines generally represent wires that can handle higher currents.
- Colors: Wiring colors are crucial for identifying specific circuits. The diagram will often include a color code legend, indicating which color corresponds to which circuit (e.g., Blue/Red stripe for the fuel pump relay control circuit). Using the correct wire is essential for troubleshooting and adding accessories.
- Abbreviations: Expect to see abbreviations like "IGN" for ignition, "ACC" for accessory, "BATT" for battery, and "GND" for ground.
- Numerical Values: Each fuse location is usually labeled with a number and its amperage rating (e.g., "Fuse #12, 15A").
Pay close attention to the legend on the diagram. This is the key to understanding the specific symbols and abbreviations used for your 2002 Sentra.
How It Works: A Simplified Explanation
The fuse box is essentially a central distribution point for electrical power. The battery provides the electrical energy, and the fuse box distributes this energy to various components through individual circuits. Each circuit is protected by a fuse that's designed to blow if the current exceeds a safe level.
When you turn on a switch (e.g., headlights), you're completing a circuit that allows electricity to flow from the battery, through the fuse, to the headlights, and back to the battery (completing the loop). If there's a short circuit (e.g., a wire chafing against the chassis), the current will surge dramatically, causing the fuse to blow and interrupt the circuit, preventing further damage.
Relays act as intermediaries, allowing low-current circuits (like the signal from a headlight switch) to control high-current circuits (like the headlights themselves). This prevents the switch from being overloaded and simplifies the wiring.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's how you can use the fuse box diagram to troubleshoot common electrical problems:
- Identify the Problem: What's not working? (e.g., cigarette lighter, radio, headlights).
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse associated with the malfunctioning component.
- Inspect the Fuse: Visually check the fuse. A blown fuse will have a broken filament. You can also use a multimeter set to continuity mode to test the fuse. A working fuse will show continuity (a beep or a reading of 0 ohms).
- Replace the Fuse: Use a fuse with the exact same amperage rating. Never use a fuse with a higher amperage rating.
- Test the Component: After replacing the fuse, test the component to see if it's working.
- If the Fuse Blows Again: If the new fuse blows immediately, there's likely a short circuit in the wiring or a problem with the component itself. Further investigation is required. This is where a wiring diagram (more detailed than the fuse box diagram) becomes invaluable.
Pro Tip: Keep a spare set of fuses of various amperage ratings in your glove compartment. You never know when you'll need them.
Safety First: Handling Risky Components
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Always observe these safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent accidental shorts and shocks.
This is crucial!
- Use Insulated Tools: Use tools with insulated handles to prevent electrical shock.
- Never Work in Wet Conditions: Water is a conductor of electricity, so avoid working on electrical systems in wet environments.
- Be Careful with High-Voltage Circuits: Some circuits, like those related to the ignition system, can carry high voltages even with the battery disconnected. Exercise extreme caution.
- Don't Tamper with Airbag Circuits: Airbag systems are extremely sensitive and can deploy unexpectedly if tampered with. If you need to work near airbag components, consult a qualified technician.
- Consult a Professional: If you're uncomfortable working with electrical systems, consult a qualified mechanic. It's better to be safe than sorry.
Specifically, be cautious around the main power distribution cables connected to the battery and alternator. These can deliver a significant shock. Also, be aware that some capacitors within the vehicle's electronic modules can store a charge even after the battery has been disconnected. Allow time for these capacitors to discharge before working on those modules.
Remember, electrical problems can sometimes be complex. If you're not sure what you're doing, it's always best to seek professional help. A little knowledge can be dangerous, and an incorrect diagnosis can lead to further damage or even injury.
By understanding the 2002 Nissan Sentra fuse box diagram, you can confidently tackle basic electrical troubleshooting and repairs. Stay safe, use the right tools, and don't hesitate to consult a professional when needed.
We have the complete 2002 Nissan Sentra Fuse Box Diagram available for download. It's a high-resolution PDF, perfect for printing and keeping in your car. It includes both the interior and engine compartment fuse box layouts, as well as a detailed legend explaining all the symbols and abbreviations. Having this diagram on hand can save you a lot of time and frustration when troubleshooting electrical issues or planning modifications.
