2003 Dodge Ram 1500 5.7 Hemi Spark Plug Wire Diagram
The 2003 Dodge Ram 1500 with the 5.7L Hemi engine is a classic workhorse. Whether you're performing routine maintenance, tackling a misfire, or just trying to understand your truck better, having access to and understanding the spark plug wire diagram is invaluable. This document serves as a roadmap for your ignition system. This article will break down the intricacies of the 2003 Dodge Ram 1500 5.7L Hemi spark plug wire diagram, enabling you to confidently diagnose and repair ignition-related issues.
Purpose of the Spark Plug Wire Diagram
A spark plug wire diagram is a visual representation of the wiring layout for the ignition system. It illustrates the precise connections between the ignition coil(s), distributor (if applicable), and the spark plugs. Understanding this diagram is crucial for several reasons:
- Troubleshooting Misfires: Identifying which cylinder is misfiring and tracing its corresponding spark plug wire back to the coil allows for targeted diagnostics.
- Performing Tune-Ups: Ensuring correct spark plug wire routing and secure connections during spark plug replacement is vital for optimal engine performance.
- Diagnosing Ignition System Problems: If your engine is experiencing issues like hard starts, rough idling, or lack of power, the diagram helps pinpoint potential wiring faults, shorts, or open circuits.
- Modifications and Upgrades: When installing aftermarket ignition components, such as performance coils or spark plug wires, the diagram provides a reference for proper installation.
- General Understanding: Even if you don’t plan on wrenching yourself, understanding the diagram helps you communicate effectively with your mechanic.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the 2003 Ram 1500 5.7L Hemi Ignition System
Before diving into the diagram, let's outline the core components of the ignition system in the 2003 Ram 1500 with the 5.7L Hemi:
Main Components:
- Ignition Coils: The Hemi engine uses a coil-on-plug (COP) ignition system. This means each spark plug has its own dedicated ignition coil. Each coil transforms the 12V from the battery to the high voltage (typically 20,000 - 30,000 volts) required to create a spark.
- Spark Plugs: These devices are threaded into the cylinder head. The high-voltage electricity jumps across the spark plug gap, igniting the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber. The 2003 Ram 1500 5.7L Hemi typically requires specific spark plugs (Champion RC12MCC4 or equivalent) with the correct heat range and gap.
- Spark Plug Wires (Boots): Although it's a coil-on-plug system *there are still short spark plug boots* which connect the bottom of the coil to the spark plug. These are often overlooked when talking about the ignition system, but are critical in delivering the high voltage pulse.
- Engine Control Unit (ECU): The ECU controls the ignition timing and firing order, determining when each spark plug fires. The ECU receives signals from various sensors (crankshaft position sensor, camshaft position sensor, etc.) to optimize ignition timing for different driving conditions.
- Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP): This sensor monitors the position of the crankshaft, providing the ECU with information needed to determine when to fire the spark plugs.
- Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP): This sensor provides information about the camshaft position, which is crucial for proper fuel injection and ignition timing.
Key Specs:
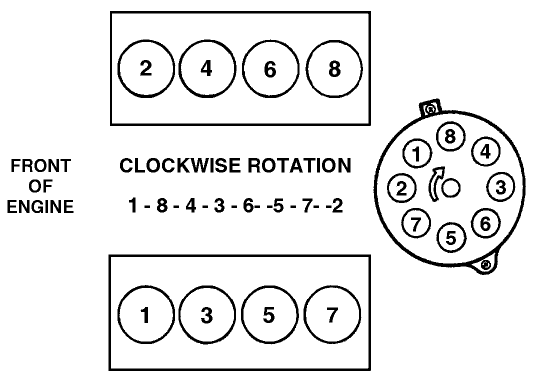
- Firing Order: 1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2 (essential for proper wire routing)
- Spark Plug Gap: Typically 0.043 - 0.048 inches (consult your owner's manual or a reliable repair manual for the exact specification).
- Coil Type: Coil-on-Plug (COP)
Understanding the Spark Plug Wire Diagram Symbols
Spark plug wire diagrams use standardized symbols to represent electrical components and wiring. Here's a breakdown of common symbols you might encounter:
- Solid Lines: Represent electrical wires.
- Dotted Lines: May represent shielded wires or grounding connections.
- Coil Symbol: A coil symbol represents each ignition coil. In a COP system, there will be eight separate coil symbols.
- Spark Plug Symbol: Represented by a distinctive shape, often resembling a resistor with a gap.
- Connector Symbol: Indicates a point where wires connect.
- Ground Symbol: Indicates a connection to the vehicle's chassis ground.
- Wire Colors: Wires are typically color-coded (e.g., red, black, blue, green). The diagram will include a legend indicating the color of each wire. Pay close attention to these!
- Numbers: Numbers near the wires or components often indicate the cylinder number or the pin number on a connector.
How It Works: The Hemi Ignition System
The Hemi ignition system is a sophisticated system that delivers a powerful spark to each cylinder with precision. Here's a simplified overview of how it works:
- The ECU receives signals from the crankshaft position sensor (CKP) and camshaft position sensor (CMP), determining the exact position of the engine's crankshaft and camshaft.
- Based on this information, the ECU calculates the optimal ignition timing.
- The ECU sends a signal to each individual ignition coil.
- Each ignition coil amplifies the voltage to create a high-voltage spark.
- The high-voltage spark travels through the spark plug boot to the spark plug.
- The spark jumps the gap on the spark plug, igniting the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber.
Because each cylinder has its own coil, this coil-on-plug design allows for very precise timing and a strong spark. There are no spark plug wires running from a single distributor, as in older designs, just the coil-on-plug and boot.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Using the spark plug wire diagram, you can troubleshoot common ignition problems:
- Misfire Diagnosis: If your truck is experiencing a misfire (indicated by a rough idle, shaking, or a check engine light), start by retrieving the diagnostic trouble code (DTC) using an OBD-II scanner. The code will identify the cylinder that is misfiring (e.g., P0301 - Cylinder 1 Misfire). Once you know the misfiring cylinder, use the diagram to locate the corresponding coil and spark plug. Inspect the spark plug boot for damage (cracks, tears, or corrosion). Replace the boot if necessary. Swap the coil with one from a known-good cylinder to see if the misfire moves. If it does, the coil is faulty.
- Checking Connections: Use the diagram to trace the wiring from the coil to the ECU. Check for loose or corroded connectors. Clean the connectors with electrical contact cleaner.
- Testing Coil Resistance: Use a multimeter to test the resistance of each ignition coil. Compare the readings to the manufacturer's specifications.
- Visually Inspecting Spark Plugs: Remove the spark plugs and inspect them for signs of wear, damage, or fouling (carbon buildup, oil contamination). Replace the spark plugs if necessary.
Safety Precautions
Working with the ignition system involves high voltage, so safety is paramount.
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery cable before working on the ignition system. This prevents accidental shocks and damage to electronic components.
- Use Insulated Tools: Use insulated pliers and screwdrivers to avoid electrical shock.
- Avoid Working in Wet Conditions: Never work on the ignition system in wet or damp conditions.
- Be Cautious Around the Coils: Even with the battery disconnected, the ignition coils can retain a residual charge. Avoid touching the terminals directly. Let them discharge before handling.
- Don't Test Spark Plugs While Installed: It's highly dangerous to hold a spark plug against the engine block to test for spark while it's connected to the coil. This can result in a severe electrical shock.
Always consult a qualified mechanic if you are unsure about any aspect of the ignition system. Improperly working on the ignition system can damage the vehicle and cause injury.
We have the 2003 Dodge Ram 1500 5.7L Hemi Spark Plug Wire Diagram available for download. This diagram will serve as a valuable resource as you navigate the complexities of your truck's ignition system. Good luck!
