2004 Silverado 1500 Chevy 04 Silverado Dash Cluster Wiring Diagram
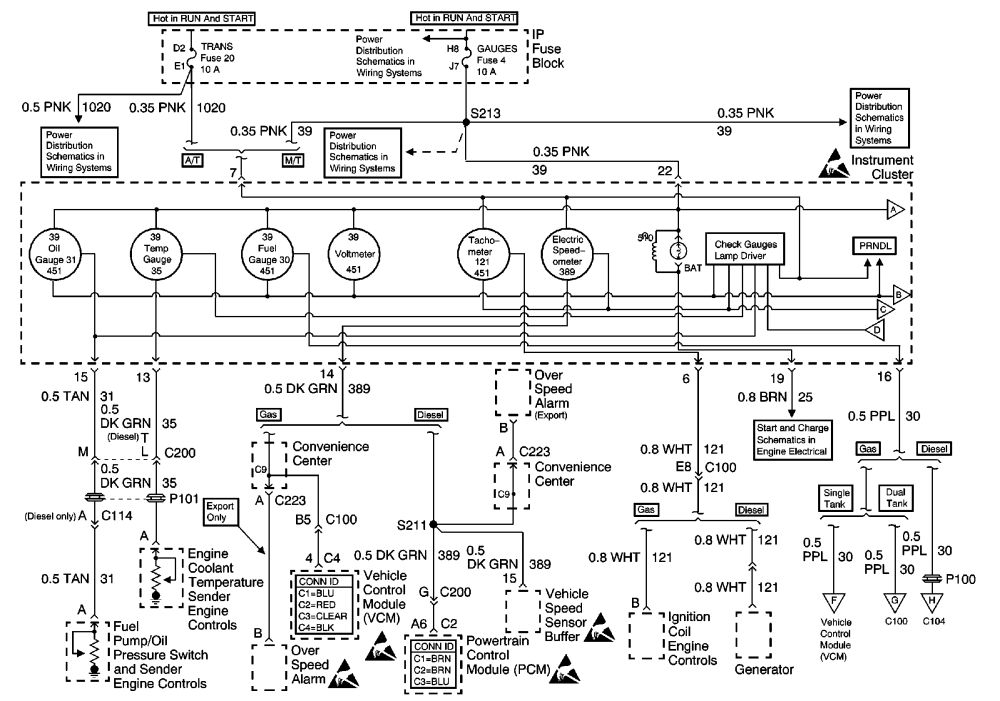
Understanding the 2004 Silverado 1500's dash cluster wiring is crucial for various reasons, whether you're tackling a repair, customizing your truck with aftermarket gauges, or simply expanding your automotive knowledge. This document serves as your guide to interpreting the wiring diagram, offering insights into its intricacies and practical applications.
Purpose of Understanding the Wiring Diagram
The wiring diagram is your roadmap to the electrical system within the instrument cluster, often called the dash cluster. Here's why it's essential:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Problems: Identifying faulty wiring, shorts, or open circuits is impossible without a clear diagram. A malfunctioning gauge or indicator light can often be traced back to a wiring issue.
- Gauge Customization and Upgrades: If you plan to install aftermarket gauges (e.g., boost gauge, wideband O2 sensor), you'll need to tap into existing circuits. The diagram shows you where to safely and correctly connect these.
- Repairing a Damaged Cluster: If your cluster is damaged (e.g., due to water intrusion), the wiring diagram helps you understand how to repair or replace damaged components and wiring harnesses.
- Understanding Vehicle Systems: Even if you're not actively working on the cluster, studying the diagram provides a deeper understanding of how the vehicle's electrical system communicates information to the driver.
Key Specifications and Main Parts of the 2004 Silverado 1500 Dash Cluster
Before diving into the diagram, it's helpful to familiarize yourself with the key components within the 2004 Silverado 1500's instrument cluster and their basic functions:
- Gauges: These display vital vehicle information. The most common include:
- Speedometer: Displays vehicle speed.
- Tachometer: Displays engine speed (RPM).
- Fuel Gauge: Displays the amount of fuel remaining.
- Coolant Temperature Gauge: Displays engine coolant temperature.
- Oil Pressure Gauge: Displays engine oil pressure (if equipped; some models have an idiot light instead).
- Voltmeter: Displays the battery voltage.
- Indicator Lights: These illuminate to indicate various vehicle conditions or warnings. Examples include:
- Check Engine Light (MIL): Indicates an engine malfunction.
- ABS Light: Indicates a problem with the Anti-lock Braking System.
- Brake Light: Indicates the parking brake is engaged or a brake system issue.
- Airbag Light: Indicates a problem with the airbag system.
- Turn Signal Indicators: Indicate when the turn signals are active.
- Display Screen (if equipped): Some models feature a digital display that shows information such as mileage, trip data, and warning messages.
- Connectors: These are the physical plugs that connect the cluster to the vehicle's wiring harness. They carry power, ground, and signal information to and from the cluster. Understanding the pinout of these connectors is critical.
- Printed Circuit Board (PCB): The PCB is the heart of the cluster, containing the electronic components and wiring traces that connect everything together.
Understanding Wiring Diagram Symbols
Wiring diagrams use standardized symbols to represent components and connections. Here's a breakdown of common symbols you'll encounter:
- Lines: Represent wires. Thicker lines may indicate wires carrying higher current.
- Colors: Each wire is assigned a color code (e.g., RED, BLK, BRN). These colors are usually abbreviated on the diagram. Color coding helps you trace wires in the vehicle.
- Circles: Can represent various components, depending on what's inside (resistor, capacitor, etc.)
- Ground Symbol: A symbol (often resembling a downward-pointing triangle) indicates a ground connection.
- Connector Symbols: Rectangular boxes with pins represent electrical connectors. The pin numbers are usually labeled.
- Splice Symbols: Indicate where multiple wires are joined together.
- Component Symbols: Vary depending on the component (e.g., a resistor symbol looks like a zigzag line, a capacitor symbol looks like two parallel lines). Refer to a key on the diagram for a complete list.
Key Abbreviations: Be familiar with common abbreviations such as:
- GND: Ground
- IGN: Ignition
- PCM: Powertrain Control Module (Engine Computer)
- BCM: Body Control Module
- DLC: Data Link Connector (OBDII port)
How the 2004 Silverado Dash Cluster Wiring Works
The instrument cluster receives information from various sensors and modules throughout the vehicle. This information is transmitted via electrical signals through the wiring harness. For example:
- Speedometer: Receives a signal from the vehicle speed sensor (VSS), typically located on the transmission. The signal is a series of pulses that correspond to the vehicle's speed. The cluster interprets these pulses and displays the speed on the speedometer.
- Tachometer: Receives a signal from the PCM, which monitors engine RPM. The PCM sends a pulsed signal to the tachometer, indicating engine speed.
- Fuel Gauge: Receives a signal from the fuel level sensor in the fuel tank. The sensor's resistance changes with the fuel level, sending a corresponding voltage signal to the gauge.
- Indicator Lights: Are typically activated by the PCM or BCM based on sensor inputs or diagnostic codes. For example, if the PCM detects an engine misfire, it will illuminate the Check Engine Light.
The dash cluster itself contains a microprocessor that processes the incoming signals and controls the gauges, indicator lights, and display screen. The wiring diagram illustrates how these signals are routed and connected within the cluster.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some basic troubleshooting tips using the wiring diagram:
- Gauge Malfunctions: If a gauge is not working, first check its power and ground connections using the diagram. Use a multimeter to verify that power and ground are present at the appropriate pins on the cluster connector. If power and ground are good, the problem may be with the gauge itself or the signal wire from the sensor.
- Indicator Light Problems: If an indicator light is not illuminating (or is illuminated constantly), check the wiring and the bulb. Use the diagram to identify the correct wire for the light. Then, use a multimeter to check for voltage at the bulb socket when the light should be on.
- Connector Issues: Carefully inspect the connectors for corrosion or damaged pins. Clean any corrosion with electrical contact cleaner. If a pin is bent or broken, you may need to replace the connector.
- Continuity Testing: Use a multimeter to test the continuity of wires. This will confirm if a wire is broken or shorted to ground. Refer to the wiring diagram to determine the correct points to test between.
Example: Let's say your fuel gauge is reading empty even though you know the tank is full. Using the wiring diagram, you'd first identify the fuel gauge's power, ground, and signal wires. Then, you'd check for power and ground at the cluster connector. If those are good, you'd check the signal wire for continuity to the fuel level sensor. If the wire is intact, you'd suspect a faulty fuel level sensor or a problem within the cluster itself.
Safety Precautions
Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous. Observe the following safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on the electrical system. This prevents accidental shorts and potential damage to the vehicle's electronics.
- Avoid Working on the Airbag System Unless Qualified: The airbag system is a highly sensitive and potentially dangerous component. Improper handling can cause the airbags to deploy, resulting in serious injury. If you suspect a problem with the airbag system, consult a qualified technician.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools designed for automotive electrical work. This will help prevent shorts and electrical shock.
- Be Careful with Wires: Avoid cutting or splicing wires unless you are absolutely sure of what you are doing. Consult the wiring diagram before making any modifications.
- Protect the PCM/BCM: These are sensitive electronic components. Static electricity can damage them. Ground yourself before touching the PCM or BCM.
By understanding the 2004 Silverado 1500 dash cluster wiring diagram and following these guidelines, you can confidently troubleshoot electrical problems, customize your truck, and deepen your understanding of automotive electrical systems. Remember, if you're unsure about anything, it's always best to consult a qualified mechanic.
We have the 2004 Silverado 1500 Dash Cluster Wiring Diagram available for download. It is a valuable resource that will allow you to repair, customize, and maintain your Chevy Silverado. With the download, you will be able to get a high quality image and print out the diagram in a larger format.
