2005 Chevy Colorado Fuse Box Diagram
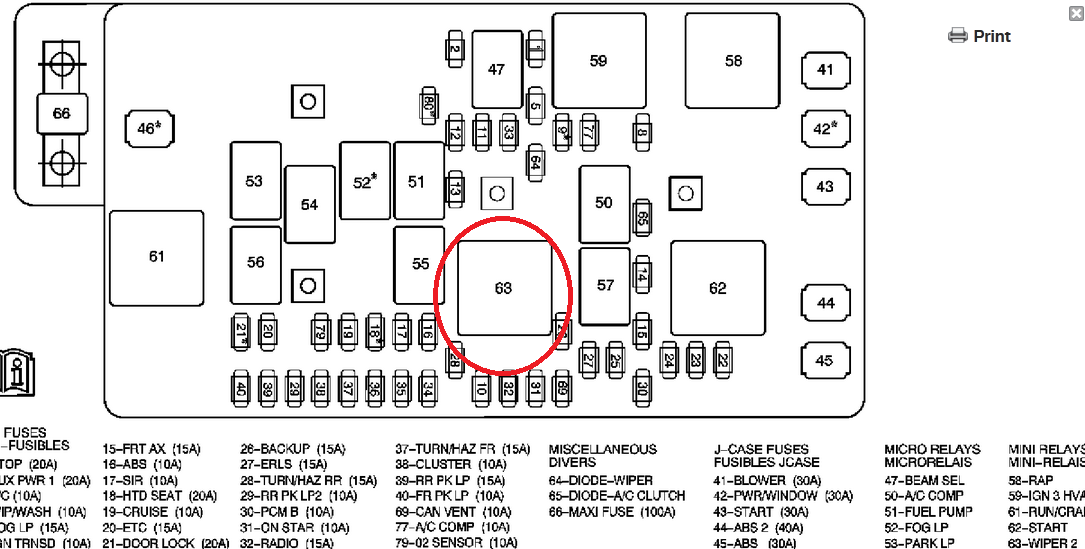
The 2005 Chevy Colorado fuse box diagram is your crucial roadmap to understanding and maintaining the electrical system of your truck. Whether you're tackling a blown fuse, adding aftermarket accessories, or simply trying to diagnose an electrical issue, having a solid grasp of this diagram is essential. This guide will break down the intricacies of the 2005 Colorado fuse box, empowering you to confidently troubleshoot and repair electrical problems.
Purpose of the Fuse Box Diagram
Why is this diagram so important? Well, think of it as the electrical system's instruction manual. Its primary purposes include:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Issues: Quickly identify the fuse or relay responsible for a malfunctioning component. Instead of blindly testing every fuse, the diagram points you directly to the suspect.
- Replacing Blown Fuses: Knowing the amperage rating and function of each fuse is crucial for proper replacement. Using the wrong fuse can lead to further damage or even a fire.
- Adding Aftermarket Accessories: When installing new lights, stereos, or other electrical add-ons, you need to tap into the existing wiring safely. The diagram helps you locate appropriate circuits and ensure proper fuse protection for your new device.
- Understanding Vehicle Systems: Gaining a deeper understanding of how the various electrical systems are interconnected can be invaluable for preventative maintenance and overall vehicle knowledge.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2005 Chevy Colorado typically has two fuse box locations:
- Under-Hood Fuse Box: Located in the engine compartment, this box houses larger fuses and relays that protect critical components like the engine control module (ECM), starter, alternator, and lighting circuits.
- Interior Fuse Box: Usually found on the driver's side, either under the dashboard or on the side of the dash (accessed when the door is open). This box covers interior circuits such as power windows, door locks, radio, and instrument panel.
Important Specs:
- Voltage: The Colorado operates on a 12-volt DC electrical system.
- Fuse Types: The 2005 Colorado uses various fuse types, including blade-type fuses (ATO, ATC) of varying sizes (mini, standard). The specific sizes may vary by location.
- Relays: Electromechanical switches that use a small electrical current to control a larger current. Relays are used for components like the fuel pump, headlights, and horn.
Understanding Fuse Box Diagram Symbols
The fuse box diagram isn't just a jumble of lines and numbers; it's a standardized representation of the electrical circuits. Deciphering the symbols is key to understanding its layout.
- Lines: Represent the electrical wiring connecting the fuses and relays to the various components. The thickness of the line doesn't necessarily indicate wire gauge; it's simply a visual aid.
- Numbers: Correspond to the fuse or relay location within the fuse box. The diagram will list these numbers alongside a description of the circuit it protects.
- Amperage Ratings: Each fuse has an amperage rating (e.g., 10A, 15A, 20A) printed on it. This indicates the maximum current the fuse can handle before blowing. Always replace a blown fuse with one of the same amperage rating.
- Color Coding: Fuses are often color-coded to indicate their amperage rating. While this is a helpful guide, always double-check the printed amperage on the fuse itself. Common color codes include:
- Yellow: 20A
- Blue: 15A
- Red: 10A
- Brown: 7.5A
- Icons: Represent the component the fuse protects. Common icons include headlights, windshield wipers, radio, power windows, etc. If the icon isn't immediately clear, refer to the legend on the diagram.
How It Works: The Electrical Circuit
To effectively use the fuse box diagram, it's helpful to understand the basic principles of an electrical circuit.
- Power Source: The battery provides the electrical power.
- Wiring: Wires carry the electricity from the battery to the components.
- Fuse: The fuse acts as a safety device. It's a thin wire designed to melt and break the circuit if the current exceeds its amperage rating, preventing damage to the component and the wiring.
- Switch: A switch controls the flow of electricity to the component.
- Component: The device that uses the electricity (e.g., a light bulb, motor).
- Ground: The circuit is completed by returning the electricity to the battery through a ground connection.
When a circuit experiences an overload (too much current), the fuse blows, interrupting the flow of electricity and protecting the system. The fuse box diagram tells you exactly which fuse protects which circuit.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's how you can use the fuse box diagram to troubleshoot common electrical problems:
- Identify the Problem: Determine which component isn't working (e.g., the radio, headlights).
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse or relay associated with that component in the fuse box diagram.
- Inspect the Fuse: Remove the fuse and visually inspect it. A blown fuse will have a broken filament inside. You can also use a multimeter to test for continuity (electrical flow) across the fuse terminals. A good fuse will show continuity; a blown fuse will not.
- Replace the Fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage rating.
- Test the Component: See if the component now works. If it does, the problem was likely just a blown fuse.
- If the Fuse Blows Again: If the new fuse blows immediately, there's a larger problem. This indicates a short circuit or an excessive current draw in the circuit. Further diagnosis is required, potentially involving checking the wiring and the component itself. It's best to consult a qualified mechanic in this case.
Safety Precautions
Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous. Take these precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on the fuse box, disconnect the negative (-) battery terminal to prevent accidental short circuits.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools designed for automotive electrical work.
- Never Bypass a Fuse: Never use a wire or other conductive material to bypass a fuse. This can cause a fire and severely damage the electrical system.
- Be Cautious Around Relays: Relays can handle high voltages and currents. Handle them with care.
- High-Current Circuits: Be especially careful when working with circuits that handle high currents, such as the starter and alternator circuits. These circuits can deliver a powerful shock.
Note: The starter and alternator circuits, often protected by high-amperage fuses or fusible links, can deliver a significant electrical shock if mishandled. Exercise extreme caution around these components.
Conclusion
The 2005 Chevy Colorado fuse box diagram is an invaluable tool for any DIY mechanic or car enthusiast. By understanding the diagram's layout, symbols, and function, you can confidently troubleshoot and repair electrical problems, saving time and money. Remember to prioritize safety and consult a qualified mechanic if you're unsure about any procedure.
We have access to the complete 2005 Chevy Colorado fuse box diagram. You can download the file for detailed reference and printing.
