2005 Dodge Ram 1500 4.7 Belt Diagram
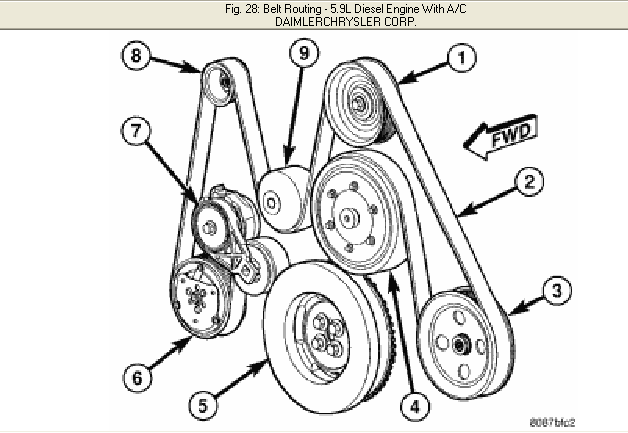
Hey there, fellow gearheads! Today, we're diving deep into the serpentine belt system of the 2005 Dodge Ram 1500 with the 4.7L engine. If you're planning on tackling some repairs, replacements, or just want to better understand how your truck's engine accessories are powered, having a clear understanding of the belt diagram is absolutely crucial.
Purpose of the Serpentine Belt Diagram
Why should you bother with this diagram? Well, imagine you're replacing a worn belt or trying to diagnose a squealing noise. Without a proper understanding of the belt routing, you're essentially flying blind. The diagram acts as a roadmap, showing you exactly how the belt should be installed and which components it drives. This is essential for:
- Accurate Belt Replacement: Incorrect routing can lead to premature wear, damage to accessories, and even complete engine failure.
- Troubleshooting: Knowing the belt path helps you identify potential problems like a seized pulley or misaligned component.
- General Maintenance: Familiarity with the system allows you to inspect for wear and tear and perform preventative maintenance.
- Understanding the System: A deeper understanding of how the belt drives the accessories (alternator, power steering pump, A/C compressor, water pump) allows you to work on other systems more effectively.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the 2005 Dodge Ram 1500 4.7L Serpentine Belt System
Before we get into the diagram itself, let's familiarize ourselves with the key components and some relevant specifications.
- Serpentine Belt: This is the heart of the system – a single, long belt that snakes around various pulleys to power engine accessories.
- Crankshaft Pulley (Harmonic Balancer): Bolted to the crankshaft, this pulley is the driving force of the entire system. It receives power directly from the engine.
- Alternator Pulley: The alternator generates electrical power for the truck's electrical system. The belt spins the alternator pulley to accomplish this.
- Power Steering Pump Pulley: This pulley drives the power steering pump, which provides hydraulic assistance for steering.
- Air Conditioning (A/C) Compressor Pulley: When the A/C is engaged, this pulley drives the compressor, which circulates refrigerant in the A/C system.
- Water Pump Pulley: The water pump circulates coolant throughout the engine to prevent overheating. The belt spins this pulley.
- Idler Pulley(s): These pulleys are smooth and don't drive any accessories. They are used to guide the belt, increase its wrap angle around other pulleys, and prevent slippage.
- Tensioner Pulley: This spring-loaded pulley maintains the proper tension on the serpentine belt. It's crucial for preventing belt slippage and premature wear. The tensioner is critical for belt life.
Important Specification: The correct belt length is critical. Using the wrong belt length will result in improper tension and can cause damage to the accessories or the belt itself. Refer to the owner's manual or a reliable parts catalog to determine the correct belt for your specific 2005 Dodge Ram 1500 4.7L.
Understanding the Serpentine Belt Diagram Symbols
The diagram itself isn't just a bunch of lines and circles. It uses specific symbols to represent each component and its relationship to the belt. Here's a breakdown of common symbols:
- Solid Line: Represents the path of the serpentine belt. The thickness of the line may indicate the side of the belt (ribbed or smooth) in contact with the pulley.
- Circle (Filled or Unfilled): Represents a pulley. Often the circle will have an abbreviation indicating what the pulley is.
- Filled Circle: A pulley which is driven.
- Unfilled Circle: An idler pulley.
- Arrows: Indicates the direction of rotation of each pulley. This is crucial for ensuring proper belt routing. Pay attention to the direction of rotation on the water pump specifically.
- Component Labels: Abbreviations like "ALT" (Alternator), "P/S" (Power Steering), "A/C" (Air Conditioning), "W/P" (Water Pump), "CRANK" (Crankshaft), and "IDL" (Idler) are used to identify each component.
- Tensioner Indicator: The tensioner pulley usually is symbolized to indicate the method by which tension is applied. Look for either a symbol of a spring, or a pivoting arm.
Pay close attention to the direction of the arrows on the diagram. Incorrect routing, especially reversing the direction of the water pump, can lead to catastrophic engine overheating.
How the Serpentine Belt System Works
The crankshaft pulley, driven directly by the engine, provides the rotational force that powers the entire serpentine belt system. As the crankshaft spins, it turns the serpentine belt, which in turn drives the various accessory pulleys. Each accessory – alternator, power steering pump, A/C compressor, and water pump – performs its specific function, contributing to the overall operation of the vehicle.
The tensioner pulley plays a vital role by maintaining the correct tension on the belt. This tension is crucial for preventing belt slippage, which can reduce the efficiency of the accessories and cause excessive belt wear. The tensioner is spring-loaded or hydraulically damped to accommodate slight variations in belt length and pulley alignment. Proper tension ensures that each accessory receives the necessary power to function correctly.
Real-World Use: Troubleshooting Tips
Okay, so you have the diagram and understand the basics. Let's talk about real-world troubleshooting.
- Squealing Noise: A squealing noise is often a sign of a slipping belt. This could be due to a worn belt, a loose tensioner, a seized pulley, or contamination (oil, coolant) on the belt.
- Visual Inspection: Carefully inspect the belt for cracks, fraying, missing ribs, or signs of wear. Also, check the pulleys for wobble, damage, or excessive play.
- Tensioner Check: The tensioner arm should move smoothly and maintain consistent tension on the belt. If the tensioner is loose or seized, it needs to be replaced.
- Pulley Inspection: Spin each pulley by hand to check for smooth rotation. A rough or noisy pulley indicates a failing bearing.
- Misalignment: Use a straightedge to check the alignment of the pulleys. Misalignment can cause premature belt wear and noise.
Safety Considerations
Working on the serpentine belt system can be dangerous if proper precautions are not taken.
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery cable before working on any electrical components, including the alternator.
- Hot Engine: Allow the engine to cool down completely before working on the serpentine belt system. The engine components can be extremely hot.
- Moving Parts: Never put your hands or tools near the serpentine belt while the engine is running. Serious injury can result.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris.
- Proper Tools: Use the correct tools for the job. For example, a serpentine belt tool is essential for releasing the tension on the tensioner pulley.
The crankshaft pulley (harmonic balancer) is a rotating mass and can cause serious injury if contacted while the engine is running. Exercise extreme caution when working near this component.
We have the full high-resolution diagram available for download. This will provide you with even greater detail and clarity as you work on your 2005 Dodge Ram 1500 4.7L. Good luck, and happy wrenching!
