2005 Dodge Ram 1500 5.7 Hemi Exhaust System Diagram
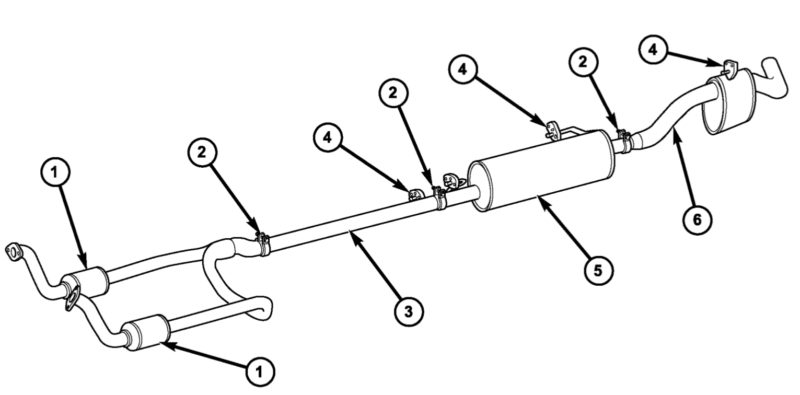
Okay, so you're tackling the exhaust system on your 2005 Dodge Ram 1500 with the 5.7L Hemi? Smart move. Understanding this system is crucial whether you're chasing down a pesky exhaust leak, planning an upgrade, or just want to grasp how your truck breathes. This breakdown, with a downloadable diagram at the end, will arm you with the knowledge you need. Let's dive in.
Why This Diagram Matters
Why bother with an exhaust system diagram? Simple: it's your roadmap. Trying to work on the exhaust without understanding its layout is like navigating a city without a map. You might get there eventually, but you'll waste a lot of time and potentially make costly mistakes. This diagram is essential for:
- Repairing Exhaust Leaks: Locating the source of that irritating rumble or hissing sound.
- Planning Upgrades: Deciding which components to replace for improved performance or sound.
- Diagnosing Performance Issues: Understanding how a clogged or damaged exhaust can impact your engine's efficiency.
- General Maintenance: Ensuring all components are properly connected and in good working order.
- Learning: Gaining a deeper understanding of your vehicle's mechanics.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the 2005 Ram 1500 Hemi Exhaust
The 2005 Dodge Ram 1500 5.7L Hemi exhaust system is a fairly straightforward design, but understanding its key components and their specifications is critical:
- Exhaust Manifolds (or Headers): These bolt directly to the engine cylinder heads and collect exhaust gases from each cylinder. They are typically made of cast iron, but aftermarket headers are often made of stainless steel for improved flow and durability. Note: The Hemi's exhaust manifolds are known for their relatively restrictive design, making them a popular upgrade target.
- Catalytic Converters: These vital emissions control devices use catalysts (platinum, palladium, and rhodium) to convert harmful pollutants like hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and nitrogen (N2). The 2005 Ram 1500 Hemi typically has two catalytic converters, one for each exhaust bank (left and right).
- Oxygen Sensors (O2 Sensors): These sensors monitor the oxygen content in the exhaust stream. There are usually two sets of O2 sensors: upstream sensors (before the catalytic converters) and downstream sensors (after the catalytic converters). The upstream sensors provide feedback to the engine control unit (ECU) to optimize the air-fuel mixture, while the downstream sensors monitor the efficiency of the catalytic converters.
- Muffler: This reduces the noise produced by the exhaust gases. Mufflers come in various designs (chambered, baffled, straight-through) each with different sound characteristics.
- Tailpipe: This is the final section of the exhaust system that directs the exhaust gases away from the vehicle.
- Pipes and Connections: These connect all the components together. They are typically made of steel and are connected using flanges, clamps, or welds.
- Hangers and Mounts: These support the exhaust system and prevent it from vibrating excessively or contacting other parts of the vehicle.
- Exhaust Flanges: These are bolted connections that allow for the easy removal and replacement of exhaust components.
Typical Pipe Diameter: The stock exhaust pipe diameter is usually around 2.5 inches. Many aftermarket systems increase this diameter to 3 inches or larger for improved exhaust flow.
Understanding the Symbols in the Diagram
A good exhaust system diagram uses symbols and conventions to represent different components and features. Here’s a breakdown of what you might encounter:
- Solid Lines: Represent the exhaust pipes themselves. Their thickness often indicates the pipe diameter.
- Dashed Lines: Might represent heat shields or other non-structural components.
- Boxes or Rectangles: Usually represent the catalytic converters and muffler.
- Circles or Ovals: Can denote O2 sensor locations or flange connections.
- Arrows: Show the direction of exhaust gas flow.
- Numbers or Letters: Refer to specific part numbers or annotations that are explained in a legend or table accompanying the diagram.
- Colors: While less common in basic diagrams, some might use colors to differentiate materials (e.g., stainless steel vs. aluminized steel).
Interpreting the Diagram: Pay attention to the orientation of the components. The diagram should show the exhaust system as it's installed on the vehicle. Note the placement of the O2 sensors, especially the upstream and downstream sensor locations, as these are critical for proper engine operation.
How the Exhaust System Works on the Hemi
The exhaust system's primary function is to remove spent gases from the engine after the combustion process. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
- Exhaust Stroke: As the piston moves upward during the exhaust stroke, the exhaust valve opens, and the burnt gases are forced out of the cylinder.
- Exhaust Manifold Collection: The exhaust gases enter the exhaust manifold, which collects them from all cylinders on that bank of the engine.
- Catalytic Conversion: The exhaust gases then flow through the catalytic converter(s), where harmful pollutants are converted into less harmful substances. The O2 sensors play a crucial role by monitoring the exhaust gas composition and providing feedback to the engine control unit (ECU) to optimize the catalytic converter's efficiency.
- Muffling: The exhaust gases then pass through the muffler, which reduces the noise levels.
- Exhaust to Atmosphere: Finally, the exhaust gases are expelled through the tailpipe into the atmosphere.
The Hemi engine's exhaust system is designed to balance performance, emissions, and noise levels. However, the stock system can be restrictive, limiting the engine's potential power output. This is why many owners choose to upgrade their exhaust systems with aftermarket components.
Real-World Use and Basic Troubleshooting
Let’s look at some practical scenarios where knowing your exhaust system comes in handy:
- Exhaust Leak Diagnosis: Listen carefully for hissing or rumbling sounds, especially when the engine is cold. Check all connections (flanges, clamps) for signs of leaks (soot, rust). Using the diagram, you can systematically inspect each section of the exhaust. A common spot for leaks is at the exhaust manifold gasket.
- O2 Sensor Replacement: If you're getting an O2 sensor error code, the diagram helps you locate the specific sensor you need to replace. Important: Use the correct type of O2 sensor for your vehicle.
- Catalytic Converter Problems: A failing catalytic converter can cause a reduction in power, poor fuel economy, and a sulfurous smell. The diagram will help you identify the location of the converter and plan for its replacement.
- Muffler Damage: Check the muffler for rust, dents, or holes. A damaged muffler will be louder than normal and may affect exhaust flow.
Troubleshooting Tip: A vacuum leak *can* sometimes mimic exhaust problems, so ensure you've ruled that out. Also, a loose heat shield can rattle and sound like an exhaust leak.
Safety Considerations
Working on the exhaust system can be dangerous if you don't take proper precautions:
- Hot Surfaces: The exhaust system gets extremely hot. Never work on the exhaust system when the engine is hot. Allow it to cool completely before starting any work.
- Jack Stands: Always use jack stands to support the vehicle when working underneath it. Never rely solely on a jack.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris.
- Gloves: Wear gloves to protect your hands from cuts and burns.
- Welding (If Applicable): If you're doing any welding, take all necessary safety precautions, including wearing a welding helmet and gloves.
- O2 Sensors and Electrical Connections: Disconnect the battery before working on any electrical components, including O2 sensors.
- Rust and Corrosion: Exhaust components are prone to rust and corrosion, which can make them difficult to remove. Use penetrating oil to loosen rusted bolts and nuts.
Remember: If you're not comfortable working on the exhaust system yourself, it's best to take your vehicle to a qualified mechanic.
We have the detailed exhaust system diagram for your 2005 Dodge Ram 1500 5.7L Hemi ready for you. It provides a visual representation of everything we've discussed, making it easier to understand the system and perform repairs or upgrades. You can download it [HERE - Placeholder for Download Link]. Good luck with your project!
