2005 Infiniti Fx35 Fuse Box Diagram
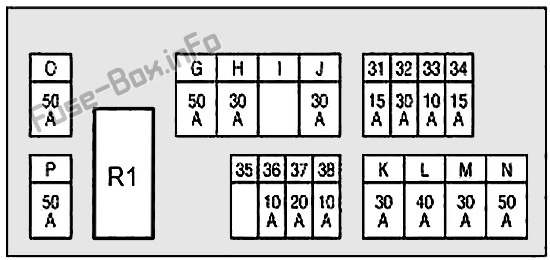
Alright, let's dive into the fuse box diagram for your 2005 Infiniti FX35. This isn't just a piece of paper; it's your roadmap to understanding and troubleshooting the electrical system in your vehicle. Whether you're tackling a blown fuse, adding aftermarket accessories, or just trying to understand how your FX35 ticks, knowing your way around the fuse box is crucial.
Why Bother with the Fuse Box Diagram?
Knowing your fuse box diagram isn't just for professional mechanics. It's a huge asset for any car owner, particularly if you like to tinker or want to avoid expensive shop visits. Here's why it matters:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Issues: Quickly identify and replace blown fuses without guesswork. This can save you time and money compared to diagnosing the problem at a shop.
- Adding Aftermarket Accessories: Want to install a new stereo, lights, or a dashcam? Knowing which fuses to tap into, or where to install an inline fuse, is essential for protecting your vehicle's electrical system.
- Understanding Your Vehicle: The diagram provides a window into the FX35's electrical architecture. You'll gain a better understanding of how different systems are powered and protected.
- Preventing Further Damage: Incorrectly replacing a fuse with a higher amperage fuse can lead to serious electrical damage, even fire. The diagram helps you avoid these costly mistakes.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the 2005 FX35 Fuse Boxes
The 2005 Infiniti FX35 has multiple fuse boxes, not just one. Understanding their locations and functions is the first step:
- Interior Fuse Box (Driver's Side): Located under the dashboard on the driver's side. This is typically where you'll find fuses for interior lights, power windows, the audio system, and other convenience features. This is the main fuse box we'll concentrate on.
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box: Situated in the engine bay, near the battery. This houses fuses and relays for critical engine components like the fuel pump, ignition system, and engine control unit (ECU), also referred to as the powertrain control module (PCM).
- Intelligent Power Distribution Module (IPDM): The IPDM is also found in the engine compartment. It's an electronic module that controls various electrical components and houses some fuses and relays. It is more sophisticated than the standard fuse box, offering some electronic control over circuits.
Key Components within the Fuse Boxes:
- Fuses: These are the sacrificial links in the electrical system, designed to blow and break the circuit when there's an overcurrent. They're rated in amps (A). The diagram shows their amperage rating and the circuit they protect.
- Relays: Electrically operated switches that allow a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit. For example, a low-current switch on your dashboard can activate a relay that supplies power to your headlights.
- Connectors: These are the points where wires connect to the fuse box and to other components. They're typically color-coded and keyed to prevent incorrect connections.
Understanding the Symbols on the Diagram
The fuse box diagram isn't just a bunch of lines and numbers; it uses a standardized set of symbols. Here's a breakdown of what you'll typically find:
- Lines: Represent electrical wires or circuits. The thickness of the line might indicate the wire gauge (diameter).
- Boxes: Represent fuses or relays. Numbers inside the boxes indicate the fuse or relay number within the fuse box.
- Numbers and Letters: These are crucial for identifying the specific fuse or relay and its amperage rating. For example, "15A" indicates a 15-amp fuse.
- Abbreviations: You'll see abbreviations for different circuits and components, such as "ECU" (Engine Control Unit), "IGN" (Ignition), "ACC" (Accessory), "HTR" (Heater), "PWR WDW" (Power Window) and many others.
- Color Coding (on some diagrams): Some diagrams use color coding to further differentiate circuits. For example, red might represent a constant power supply, while blue might represent a circuit that's only active when the ignition is on. Unfortunately, most OEM diagrams are black and white.
Important Diagram Conventions: The diagram will usually have a legend or key that explains all the symbols and abbreviations used. Refer to it frequently.
How It Works: The Fuse Box in Action
The fuse box acts as the central distribution point for electrical power throughout your FX35. It receives power from the battery and then distributes it to various circuits through fuses and relays.
Here's a simplified explanation:
- Power from the battery enters the fuse box.
- The power is routed to different circuits, each protected by a fuse.
- When a component needs power (e.g., headlights), the switch for that component completes the circuit.
- If there's a surge of current (e.g., a short circuit), the fuse in that circuit blows, breaking the circuit and preventing damage to the component and wiring.
Relays amplify signals. A low-current signal from a switch activates the relay, which then allows a high-current circuit to flow to the component (e.g., the starter motor). Without a relay, the switch would have to handle the full current draw of the component, which could damage the switch.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's how you can use the fuse box diagram to troubleshoot common electrical issues:
- Identify the Problem: Determine which component isn't working (e.g., the cigarette lighter, a headlight, the power windows).
- Consult the Diagram: Find the fuse that corresponds to the affected component on the fuse box diagram. Note the fuse number and amperage rating.
- Inspect the Fuse: Locate the fuse in the fuse box and visually inspect it. A blown fuse will have a broken filament inside.
- Replace the Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the same amperage rating. Never use a higher amperage fuse.
- Test the Circuit: After replacing the fuse, test the component to see if it's working. If the fuse blows again immediately, there's a short circuit in the wiring or component. This requires further diagnosis.
- Using a Multimeter: A multimeter can be used to test for voltage at the fuse terminals to confirm power is present. It can also be used to check for continuity across a fuse to see if it's blown. Set the multimeter to the appropriate voltage range and carefully probe the fuse terminals.
Example: Let's say your cigarette lighter isn't working. You consult the diagram and find that fuse #12 (15A) protects the cigarette lighter circuit. You check fuse #12 in the interior fuse box, and it's blown. You replace it with a new 15A fuse, and the cigarette lighter now works. Problem solved!
Safety: Proceed with Caution!
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Here are some crucial safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on the fuse box, disconnect the negative (-) battery cable. This prevents accidental short circuits.
- Use the Right Tools: Use insulated tools to avoid shocks.
- Never Bypass a Fuse: Don't use a wire or metal object to bypass a fuse. This can cause a fire.
- Identify High-Risk Components: Be particularly careful when working around the engine compartment fuse box, which contains fuses and relays for critical engine components. Mistakes here can lead to serious engine damage. The fuel pump relay, for example, is crucial for fuel delivery.
- Work in a Well-Lit Area: Ensure you have adequate lighting to clearly see the fuse box and the diagram.
Risk Alert: Some circuits, like those powering the airbags or ABS system, require specialized knowledge and tools. If you're not comfortable working on these systems, it's best to leave it to a professional. Incorrect handling of these systems can have serious consequences.
We have a downloadable copy of the 2005 Infiniti FX35 fuse box diagram available for you. Feel free to download it and keep it handy for future reference. Good luck with your electrical troubleshooting and modifications!
