2005 Nissan Xterra Fuse Box Diagram
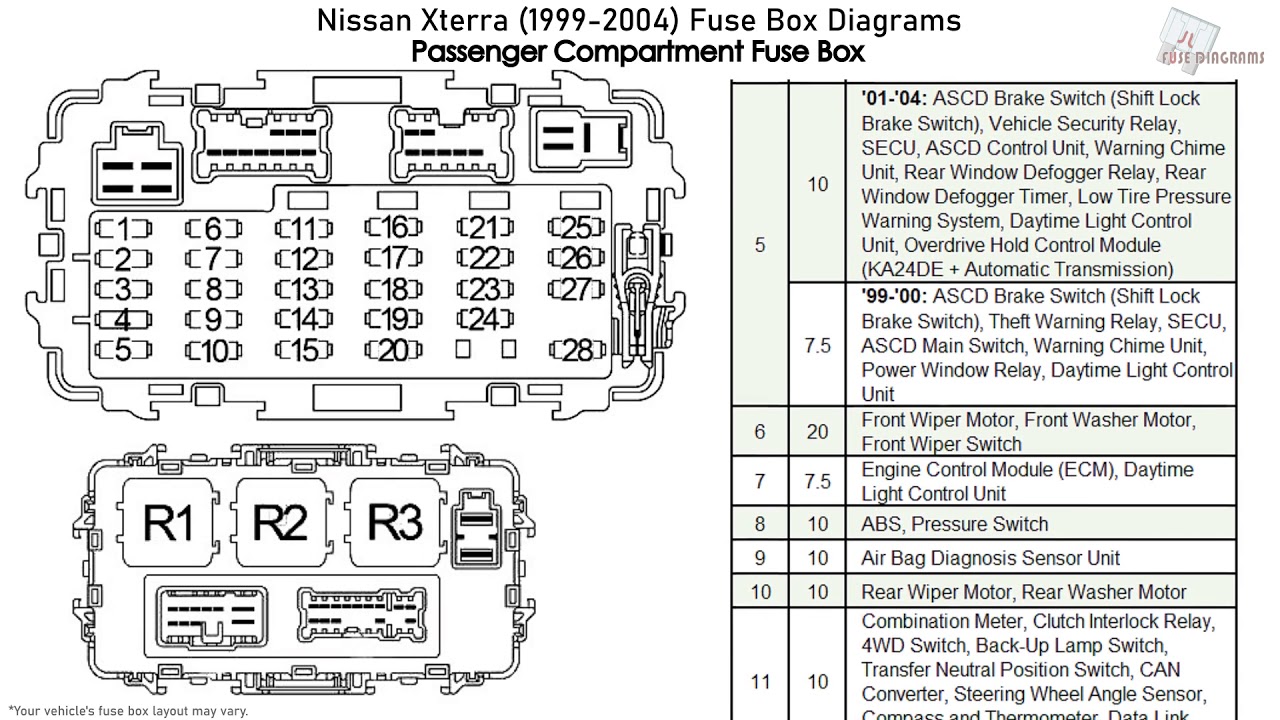
Let's dive into the often-overlooked but crucially important world of the 2005 Nissan Xterra fuse box diagram. Whether you're diagnosing electrical gremlins, planning an aftermarket accessory installation, or simply trying to understand your vehicle's electrical system better, having a solid understanding of this diagram is essential. This isn't just a picture; it's a roadmap to your Xterra's electrical health.
Purpose of the Fuse Box Diagram
The fuse box diagram serves several vital purposes:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Problems: When a circuit stops working – a light goes out, the radio dies, or the power windows cease to function – the fuse box is often the first place to look. The diagram allows you to quickly identify the fuse associated with the faulty circuit.
- Installing Aftermarket Accessories: Adding things like aftermarket lights, a subwoofer, or a dashcam requires tapping into the vehicle's electrical system. Understanding the fuse box layout is crucial for selecting the right circuit and safely connecting your new accessory, avoiding overloading circuits.
- Preventing Electrical Fires: Fuses are designed to protect your vehicle from electrical fires by breaking the circuit when the current exceeds a safe level. A blown fuse is a symptom, and the diagram helps you identify the cause of the overload, preventing potential hazards.
- General Vehicle Understanding: Even if you're not experiencing problems, studying the fuse box diagram gives you a better understanding of how your Xterra's electrical systems are organized and protected.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2005 Nissan Xterra typically has two primary fuse box locations:
- Interior Fuse Box: Located inside the cabin, usually under the dashboard on the driver's side. This box primarily handles circuits for interior accessories, lights, and control modules.
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box: Found in the engine bay, often near the battery. This box houses fuses and relays for critical engine components, headlights, and other heavy-duty electrical loads.
Key components within each fuse box include:
- Fuses: These are the sacrificial elements that protect circuits from overcurrent. They come in various Ampere (A) ratings, each designed to handle a specific amount of current. Common fuse types include blade fuses (ATO/ATC), mini-blade fuses, and occasionally cartridge fuses for higher-current applications.
- Relays: Relays are electromechanical switches that allow a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit. They are used for components that draw significant power, such as headlights, the fuel pump, and the starter motor.
- Circuit Breakers: Some circuits use circuit breakers instead of fuses. Circuit breakers automatically interrupt the flow of current when an overload occurs, and can be reset manually or automatically once the overload is removed.
- Fuse Puller: A small plastic tool usually located within the fuse box that helps to safely remove fuses without damaging them.
Symbols – Understanding the Diagram
A good fuse box diagram isn't just a picture; it's a coded message. Understanding the symbols is key to decoding it.
- Lines: Solid lines usually indicate a direct connection. Dashed lines might indicate a shared connection or a grounding point.
- Colors: Wire colors are often indicated next to the fuse or relay designation. Knowing the wire color can help you trace the circuit if needed.
- Icons:
- Lightbulb: Represents lights (headlights, taillights, interior lights).
- Speaker: Indicates the audio system.
- Fan: Represents a motor, often related to the climate control system.
- Steering Wheel: Often represents systems related to steering, like power steering.
- Engine Block: Represents engine management systems.
- Numbers and Letters: Each fuse and relay will be labeled with a number or alphanumeric code (e.g., "F12," "ECCS"). This code corresponds to a description in the diagram's legend.
A typical diagram will include a legend or key that explains what each symbol and abbreviation represents. Always refer to the legend!
How It Works
Let’s consider a simple example: the headlights. The circuit typically works like this:
- You turn on the headlight switch inside the cabin.
- This sends a signal to a relay located in the engine compartment fuse box.
- The relay, powered by the battery, closes the circuit, allowing high-current electricity to flow to the headlights.
- A fuse (e.g., a 15A fuse) protects the headlight circuit from overcurrent. If too much current flows (due to a short circuit, for example), the fuse will blow, interrupting the flow of electricity and preventing damage to the wiring and headlights.
The fuse box diagram shows you the location of the headlight fuse and relay, as well as their corresponding ratings and the wiring associated with the circuit. Understanding this flow is crucial for diagnosing problems.
Real-World Use – Basic Troubleshooting
Here's a basic troubleshooting scenario:
Problem: Your Xterra's radio isn't working.
- Consult the Diagram: Find the fuse box diagram (usually in your owner's manual or online – or the one you can download from us).
- Locate the Radio Fuse: Identify the fuse labeled for the radio. It might be labeled "Radio," "Audio," or something similar.
- Inspect the Fuse: Use the fuse puller to remove the fuse. Visually inspect it. If the small wire inside the fuse is broken or the fuse is blackened, it's blown.
- Replace the Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the same amperage rating. Never use a fuse with a higher rating! This could bypass the protection and lead to a fire.
- Test: Turn on the radio. If it works, the problem is solved. If the fuse blows again immediately, there's a short circuit in the radio circuit that needs further investigation.
Safety
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Here are some safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Whenever possible, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery before working on the electrical system. This reduces the risk of accidental shorts and electric shock.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools designed for electrical work.
- Never Bypass Fuses: Never replace a fuse with a higher amperage fuse or a piece of wire. This can overload the circuit and cause a fire.
- Identify High-Risk Components: The starter motor circuit and the alternator circuit carry very high current. Exercise extreme caution when working on these circuits.
- Don't Work in Wet Conditions: Avoid working on the electrical system in wet or damp conditions.
Always consult a qualified mechanic if you are unsure about any aspect of electrical troubleshooting or repair. Electrical problems can be complex and potentially dangerous, and it's better to be safe than sorry.
Downloading the Diagram
To help you further, we have a high-resolution, printable version of the 2005 Nissan Xterra fuse box diagram available for download. This diagram will be invaluable for any electrical work you plan to undertake. Download it and keep it handy for future reference!
