2006 Buick Lacrosse 3.8 Belt Diagram
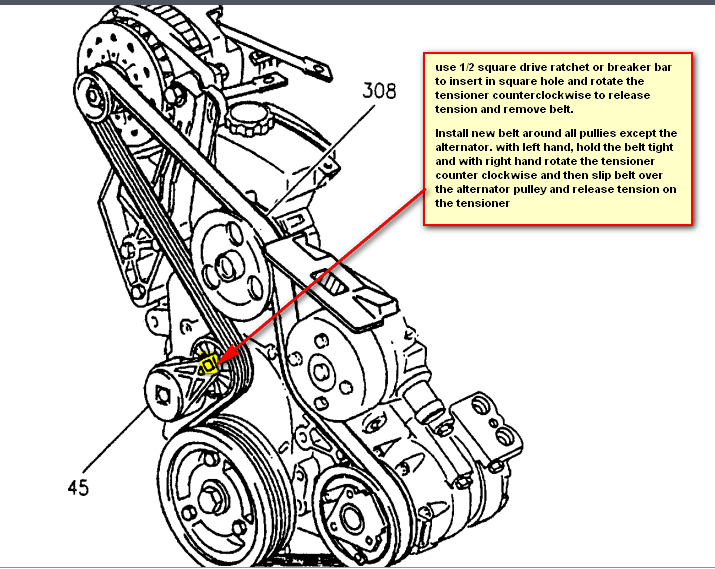
The serpentine belt on your 2006 Buick Lacrosse with the 3.8L V6 engine is a critical component responsible for powering several essential systems. Understanding its routing and condition is crucial for preventative maintenance and quick repairs. This article provides a detailed breakdown of the 2006 Buick Lacrosse 3.8L serpentine belt diagram, covering everything from its purpose and components to troubleshooting and safety tips.
Purpose of the Serpentine Belt Diagram
The serpentine belt diagram is your roadmap for understanding how the belt is routed around the various pulleys in your engine bay. It's absolutely vital for several reasons:
- Repair and Replacement: When replacing a worn or broken belt, the diagram shows the correct path to ensure proper function and avoid damage to the belt or other components. Incorrect routing can lead to belt slippage, reduced performance of driven accessories, and even premature belt failure.
- Troubleshooting: A squealing or chirping belt often indicates a problem, such as a misaligned pulley, a worn tensioner, or a failing accessory. The diagram helps you identify these components and their relationship to the belt.
- General Maintenance: Regularly inspecting the belt's condition and ensuring proper tension is crucial. The diagram assists you in locating the tensioner and understanding how it works.
- Learning: Understanding the serpentine belt system helps you grasp the overall workings of your engine and its auxiliary components.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Before diving into the diagram, let's outline the key components of the serpentine belt system in your 2006 Buick Lacrosse 3.8L:
- Serpentine Belt: A single, long belt made of reinforced rubber that drives multiple engine accessories. The 'serpentine' name comes from its winding path around various pulleys.
- Crankshaft Pulley (Harmonic Balancer): Connected directly to the engine's crankshaft, this pulley drives the serpentine belt. It also dampens torsional vibrations from the engine.
- Alternator Pulley: The alternator converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy, charging the battery and powering electrical systems.
- Power Steering Pump Pulley: The power steering pump provides hydraulic pressure to assist steering.
- Air Conditioning (A/C) Compressor Pulley: The A/C compressor circulates refrigerant in the air conditioning system.
- Water Pump Pulley: The water pump circulates coolant throughout the engine to prevent overheating.
- Tensioner Pulley: A spring-loaded pulley that maintains proper tension on the serpentine belt. This is critical for preventing slippage and ensuring the proper operation of all accessories. The tensioner arm pivots, and the tensioner assembly includes a pulley.
- Idler Pulley(s): Smooth pulleys that guide the belt and provide additional wrap around other pulleys to increase grip and prevent slippage. Not all engines have idler pulleys.
The belt itself is typically a multi-ribbed belt, also known as a V-ribbed belt or poly-V belt. The number of ribs and the belt length are specific to your 2006 Lacrosse 3.8L. Refer to the parts catalog or the old belt itself for the correct replacement part number. Using the wrong size belt can lead to serious problems.
Symbols in the Serpentine Belt Diagram
The serpentine belt diagram uses standard symbols to represent the various components and the belt routing:
- Solid Lines: Represent the path of the *outside* of the serpentine belt.
- Dashed Lines: Usually indicate the *inside* (grooved side) of the serpentine belt, which engages with the grooved pulleys.
- Circles: Represent pulleys. The diagram will often label each circle with an abbreviation for the component it drives (e.g., ALT for Alternator, P/S for Power Steering, A/C for Air Conditioning, WP for Water Pump, CRANK for Crankshaft).
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of rotation for each pulley. This is helpful in understanding how the belt transmits power.
- Spring Symbol: Often shown near the tensioner pulley to represent the spring-loaded mechanism that maintains belt tension.
Some diagrams may use different colors to highlight specific sections of the belt or to distinguish between different components. Always refer to the diagram's key or legend for a complete explanation of the symbols used.
How It Works
The serpentine belt system is a simple but effective mechanism. The crankshaft pulley, driven by the engine, is the driving force. The serpentine belt wraps around this pulley and transfers rotational force to all the other accessory pulleys. The tensioner pulley maintains constant tension on the belt, ensuring sufficient grip to prevent slippage. Without adequate tension, the accessories will not operate properly, leading to dim headlights (alternator), hard steering (power steering pump), and poor cooling (water pump) or lack of AC function (A/C compressor).
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some common problems associated with the serpentine belt and how the diagram can help you diagnose them:
- Squealing/Chirping: This is often caused by a loose belt, a worn belt, or a misaligned pulley. The diagram helps you inspect the belt's routing and identify the tensioner for adjustment or replacement. Also, misaligned pulleys can be identified by carefully looking at the belt's path along its entire route when the engine is running. Use the diagram to note each pulley and its driven component.
- Belt Slippage: Slippage can occur due to a worn belt, a faulty tensioner, or oil contamination on the belt. The diagram helps you visually inspect the belt for cracks, fraying, or oil residue.
- Accessory Failure: If an accessory, such as the alternator or power steering pump, is not functioning correctly, the problem could be a broken or slipping serpentine belt. The diagram helps you trace the belt's path to that specific accessory to check for damage.
- Visible Cracks or Wear: Regular inspection (every 6 months or so) using the diagram as a reference for the belt's path can help spot cracks, fraying, or glazing. These signs indicate the belt needs replacement.
To diagnose a noise, you can use a mechanics stethoscope to pinpoint the source of the sound. Be extremely careful when working around a running engine.
Safety Precautions
Working around a running engine and its moving parts can be dangerous. Here are some safety precautions to keep in mind:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before starting any work on the serpentine belt system, disconnect the negative battery terminal to prevent accidental starting of the engine.
- Keep Hands and Clothing Clear: Never put your hands or clothing near the serpentine belt or pulleys while the engine is running. These parts can cause serious injury.
- Use Proper Tools: Use the correct tools for the job, such as a serpentine belt tool for removing and installing the belt. This reduces the risk of injury and damage to the components.
- Wear Safety Glasses: Protect your eyes from debris.
- Hot Components: Be aware that the engine and exhaust system can be extremely hot, even after the engine has been turned off for a while. Allow the engine to cool down before working on it.
The tensioner pulley is spring loaded and can snap back suddenly when released. Use caution when releasing the tension on the belt.
We have the 2006 Buick Lacrosse 3.8L Serpentine Belt Diagram available as a downloadable file. This detailed diagram will give you the confidence to tackle your serpentine belt maintenance and repairs safely and effectively.
