2006 Dodge Ram 1500 Fuse Box Diagram
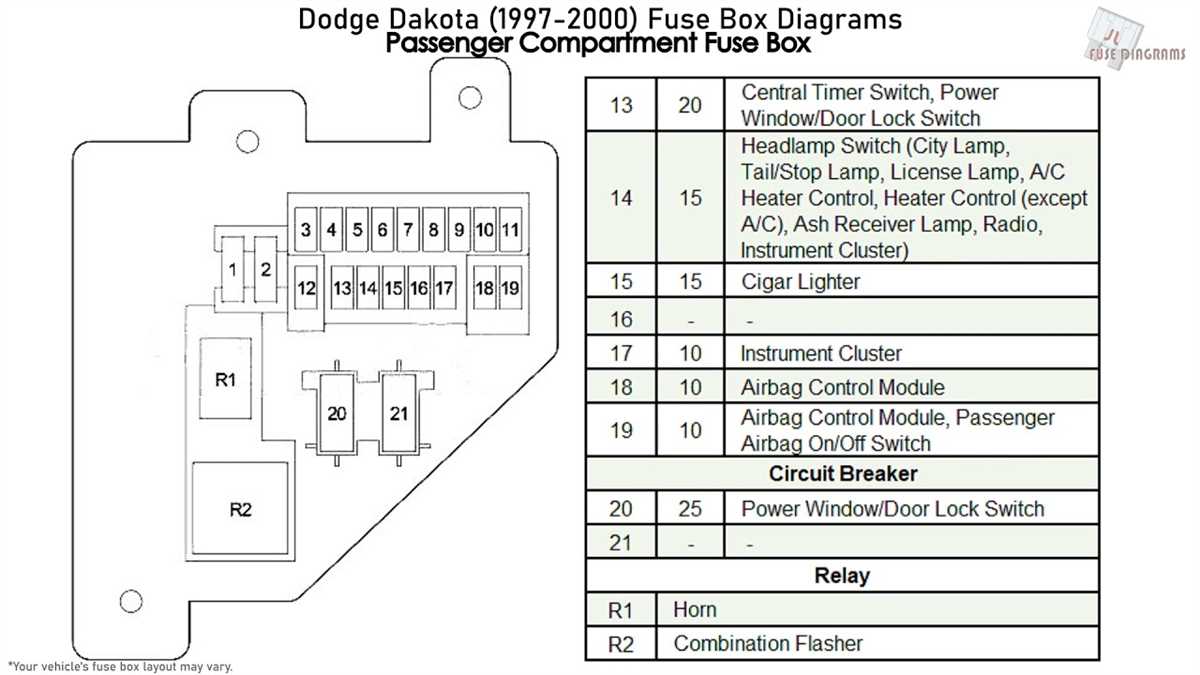
Alright, let's dive into the 2006 Dodge Ram 1500 fuse box diagram. Understanding this diagram is crucial for anyone tackling electrical repairs, adding aftermarket accessories, or simply wanting a deeper understanding of their truck's electrical system. Whether you're troubleshooting a faulty trailer light or installing a new stereo, knowing where to find the right fuse and what it protects can save you time, money, and a whole lot of frustration.
Purpose of the Fuse Box Diagram
The fuse box diagram is essentially a roadmap to your truck's electrical system. It identifies the location of each fuse and relay, and more importantly, what circuit each protects. This is vital for several reasons:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Issues: When a circuit fails (e.g., your headlights stop working), the diagram helps you quickly locate the relevant fuse for inspection.
- Installing Aftermarket Accessories: Adding new components like lights, stereos, or winches requires tapping into the truck's electrical system. The diagram helps you identify safe and appropriate circuits to use, preventing overload and potential damage.
- Preventing Further Damage: Identifying a blown fuse quickly and replacing it with the correct amperage rating can prevent more serious electrical problems from developing. Using the wrong fuse can lead to overheating, short circuits, and even fires.
- General Maintenance and Knowledge: Even if you're not experiencing problems, understanding the fuse box layout provides valuable insight into your truck's electrical architecture.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the 2006 Dodge Ram 1500 Fuse Box
The 2006 Dodge Ram 1500 typically has two main fuse box locations:
- The Power Distribution Center (PDC): Located under the hood, usually near the battery. This box houses fuses and relays for high-current circuits like the starter motor, alternator, headlights, and other essential vehicle functions.
- The Interior Fuse Box: Located inside the cab, often on the driver's side, typically behind a panel on the dashboard or side of the footwell. This box handles lower-current circuits like interior lights, the radio, power windows, and the cigarette lighter (power outlet).
The fuse box diagram is usually found inside the fuse box cover itself. It’s often a printed label or a plastic insert. If it's missing, you can typically find it in your owner's manual or, as we'll discuss later, download a copy.
Key Components:
- Fuses: Sacrificial devices designed to protect circuits from overcurrent. They contain a thin wire that melts and breaks the circuit when the current exceeds a safe level. Fuses are rated in amperes (amps), indicating the maximum current they can handle. Common fuse types include blade fuses (ATO/ATC), mini blade fuses, and cartridge fuses.
- Relays: Electrically operated switches that allow a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit. For example, the headlight switch uses a relay to control the high-current headlights, protecting the switch from burning out. Relays consist of a coil, a common contact, a normally open (NO) contact, and a normally closed (NC) contact.
- Circuit Breakers: Similar to fuses, but they can be reset after tripping. They are often used for circuits that experience temporary overloads.
Understanding the Symbols on the Fuse Box Diagram
Fuse box diagrams use a variety of symbols to represent different components and circuits. Here's a breakdown of some common symbols you'll encounter:
- Lines: Solid lines typically represent the positive (+) power feed, while dashed lines may indicate the ground (-) or a control signal. Line thickness can sometimes indicate the wire gauge (thicker lines = larger gauge wire = higher current capacity).
- Fuse Symbol: Usually depicted as a simple rectangle with a squiggle inside or a line broken in the middle. The amperage rating is usually printed next to the fuse symbol.
- Relay Symbol: A small square or rectangle with a coil symbol inside and lines indicating the switch contacts. The diagram will usually label the relay with its function (e.g., "Headlight Relay," "Fuel Pump Relay").
- Component Symbols: Symbols are used to represent the various components powered by the fuses, such as headlights (a circle with a filament symbol), the horn (a stylized horn shape), or the radio (a speaker symbol).
- Colors: While not always present on the diagram itself, wire colors are often associated with specific circuits. Knowing common Dodge wire color codes can be helpful for tracing circuits and diagnosing problems.
Important Note: The fuse box diagram is specific to your vehicle's year and trim level. Minor variations can exist, so always double-check that the diagram matches your actual fuse box layout.
How the Electrical System Works (Simplified)
Think of your truck's electrical system as a series of interconnected circuits. Each circuit starts at the battery, flows through a fuse, and then powers a specific component. The fuse acts as a safety valve, protecting the circuit from overcurrent. When a component is turned on, electricity flows through the circuit, powering the component. The electricity then returns to the battery through the ground (negative) circuit.
For example, consider the headlight circuit. When you turn on the headlights, the headlight switch sends a signal to a relay (typically). The relay then closes, allowing power to flow from the battery, through the headlight fuse, and to the headlights. If a short circuit occurs in the headlight wiring, the current will spike, causing the headlight fuse to blow and preventing further damage.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's how to use the fuse box diagram to troubleshoot a common electrical problem:
- Identify the Problem: What's not working? (e.g., the turn signals, the radio, the power windows).
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse box diagram (either in the fuse box cover, the owner's manual, or the downloadable resource we'll mention later).
- Find the Relevant Fuse: Use the diagram to identify the fuse that protects the circuit for the malfunctioning component. Pay close attention to the amperage rating.
- Inspect the Fuse: Carefully remove the fuse using a fuse puller (a small plastic tool designed for this purpose). Visually inspect the fuse. If the wire inside is broken or blackened, the fuse is blown.
- Replace the Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the same amperage rating. Never use a fuse with a higher amperage rating, as this could damage the circuit.
- Test the Circuit: Turn on the component to see if it now works. If the new fuse blows immediately, there's likely a short circuit in the wiring, and further diagnosis is required.
Pro Tip: Keep a spare set of fuses with different amperage ratings in your glove compartment. This can be a lifesaver when you're on the road.
Safety Considerations
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Always take the following precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical component, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent accidental shorts.
- Use Insulated Tools: Use tools with insulated handles to prevent electrical shock.
- Never Work on a Live Circuit: Unless absolutely necessary for diagnosis, avoid working on circuits with the power on.
- Identify High-Risk Components: Be particularly cautious when working with circuits involving the airbag system (SRS), the anti-lock braking system (ABS), and the fuel injection system. These systems can be sensitive and potentially dangerous if handled improperly. If unsure, consult a qualified mechanic.
- Don't Guess: If you're not comfortable working with electrical systems, seek professional assistance.
Important Warning: The airbag system is extremely sensitive. Improper handling can cause accidental deployment, resulting in serious injury. If you need to work near the airbag system, disconnect the battery and wait at least 10 minutes for the system to discharge before proceeding.
By understanding the 2006 Dodge Ram 1500 fuse box diagram and following these safety precautions, you can confidently tackle a wide range of electrical repairs and modifications. Remember to always double-check your work and consult a qualified mechanic if you encounter any difficulties.
To make things easier, we have a high-resolution, downloadable 2006 Dodge Ram 1500 fuse box diagram readily available. You can access it by following the download link below.
Disclaimer: Electrical systems can be complex. This guide provides general information only and should not be considered a substitute for professional advice. Always exercise caution and consult a qualified mechanic if you are unsure about any aspect of electrical repair or modification.
