2006 Ford F350 6.8 Serpentine Belt Routing Diagram
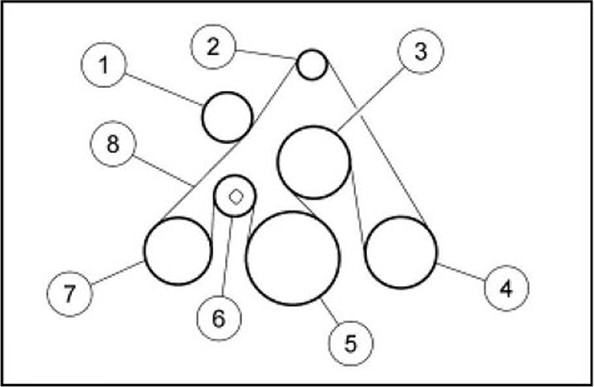
Alright, let's talk about the serpentine belt routing on your 2006 Ford F350 with the 6.8L V10 engine. This is a critical system to understand, whether you're tackling a simple belt replacement, diagnosing a squealing noise, or just trying to learn more about your truck. Having a clear understanding of the belt routing is essential for proper operation and preventing potential engine damage.
Why This Diagram Matters
The serpentine belt is responsible for powering several crucial engine components. A correctly routed belt ensures these components function as intended. Here's why understanding the routing diagram is so important:
- Repairs and Maintenance: Replacing the serpentine belt is a routine maintenance task. Knowing the correct routing ensures you install the new belt properly. Incorrect routing can lead to component failure and engine damage.
- Troubleshooting: Squealing belts, overheating, or power steering issues can often be traced back to a loose or incorrectly routed serpentine belt. The diagram helps you quickly identify if the belt is installed correctly.
- Understanding Your Engine: Knowing how the serpentine belt system works provides a deeper understanding of your engine's operation and the interconnectedness of its components.
- Preventing Damage: A misaligned or incorrectly routed belt can cause premature wear on the belt itself, as well as the pulleys it drives. This can lead to costly repairs down the line.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Before we dive into the diagram itself, let's cover some key specifications and components of the serpentine belt system on your 2006 F350 6.8L:
Key Specs:
- Engine: 6.8L Triton V10
- Belt Length: This varies depending on whether or not your truck has an A/C delete option, which is very rare. However, to be sure, it’s always best to verify by using a belt measuring tool or comparing the existing belt with the replacement before installation.
- Belt Type: Multi-ribbed serpentine belt. These belts are designed for efficient power transmission and are more resistant to slippage compared to older V-belts.
Main Parts:
- Crankshaft Pulley (Harmonic Balancer): The main pulley driven directly by the engine's crankshaft. It's the starting point for the serpentine belt's journey. The harmonic balancer is designed to dampen engine vibrations.
- Alternator Pulley: Drives the alternator, which generates electricity to power the vehicle's electrical system and charge the battery.
- Power Steering Pump Pulley: Drives the power steering pump, which provides hydraulic assistance for steering.
- Air Conditioning Compressor Pulley (if equipped): Drives the A/C compressor, responsible for cooling the cabin.
- Idler Pulley(s): Smooth pulleys that guide the belt along its path and maintain proper tension. They are not driven by any specific component.
- Tensioner Pulley: Spring-loaded pulley that automatically maintains the correct tension on the serpentine belt. This is crucial for preventing slippage and ensuring optimal performance. The tensioner pulley will have a nut or bolt that will allow it to be compressed, relieving the tension on the belt so that it can be installed or removed.
Symbols – Explaining the Diagram
Serpentine belt routing diagrams use specific symbols to represent different components and the path of the belt. Understanding these symbols is crucial for interpreting the diagram correctly.
- Solid Lines: These represent the path of the serpentine belt itself. Follow the line carefully to trace the belt's route around each pulley.
- Arrows: Arrows indicate the direction of belt travel. Pay close attention to these arrows to ensure you route the belt in the correct direction around each pulley.
- Pulley Symbols: Pulleys are typically represented by circles. The symbols may include labels (e.g., ALT for alternator, PS for power steering) to identify the component the pulley drives.
- Tensioner Symbol: The tensioner pulley is usually represented with an arrow or a spring symbol indicating its spring-loaded mechanism.
- Smooth Pulleys vs. Grooved Pulleys: Grooved pulleys drive components. Smooth Pulleys don't drive anything (these are usually the Idler Pulleys).
How It Works
The serpentine belt system is designed to efficiently transfer power from the engine's crankshaft to various accessories. Here's a simplified breakdown of how it works:
- The crankshaft pulley, driven by the engine, initiates the movement.
- The serpentine belt wraps around the crankshaft pulley and then travels to the other pulleys, such as the alternator, power steering pump, and A/C compressor (if equipped).
- The tensioner pulley maintains consistent tension on the belt, preventing slippage and ensuring optimal power transfer to all the driven components. The tensioner is spring-loaded and will automatically compensate for belt stretch over time.
- Idler pulleys guide the belt along its path, ensuring proper alignment and preventing interference with other engine components.
Real-World Use – Basic Troubleshooting
Here are some common issues related to the serpentine belt system and how the routing diagram can help you troubleshoot them:
- Squealing Belt: A squealing belt is often caused by slippage. Check the belt tension and condition. Use the diagram to ensure the belt is routed correctly around all pulleys. Look for signs of wear, such as cracks or glazing. A worn tensioner can also cause slippage.
- Overheating: A malfunctioning water pump (driven by the serpentine belt) can cause overheating. Verify that the belt is properly routed around the water pump pulley and that the belt tension is correct.
- Power Steering Issues: Difficulty steering can indicate a problem with the power steering pump. Check the belt routing and tension. Also, inspect the power steering pump pulley for damage.
- Alternator Problems: A dead battery or electrical issues can be caused by a malfunctioning alternator. Make sure the belt is properly routed around the alternator pulley and that the belt tension is correct.
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the serpentine belt for signs of wear, such as cracks, fraying, or missing ribs. Replace the belt if you notice any of these issues. Refer to the routing diagram to ensure you install the new belt correctly.
Safety – Risky Components
Working on the serpentine belt system involves certain risks. Here are some safety precautions to keep in mind:
- Engine Off: Always work on the serpentine belt system with the engine off and the key removed from the ignition. This prevents accidental starting of the engine.
- Hot Engine: Allow the engine to cool down completely before working on the serpentine belt. Components like the exhaust manifold can be extremely hot and cause burns.
- Rotating Parts: Keep your hands, hair, and clothing away from rotating parts, such as the pulleys and the belt itself, when the engine is running.
- Tools: Use the correct tools for the job. Using the wrong tools can damage components or cause injury. A serpentine belt tool kit is recommended for easy belt removal and installation.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris.
- Battery Disconnect (Optional): If you feel uncomfortable working near electrical components, disconnect the negative battery cable.
By understanding the serpentine belt routing diagram and following these safety precautions, you can confidently tackle repairs and maintenance on your 2006 Ford F350 6.8L. And remember to always consult your vehicle's repair manual for specific instructions and torque specifications.
We have the serpentine belt routing diagram readily available. Download it and keep it handy for any future maintenance or repairs you might need to perform.
