2006 Infiniti Qx56 Fuse Box Diagram
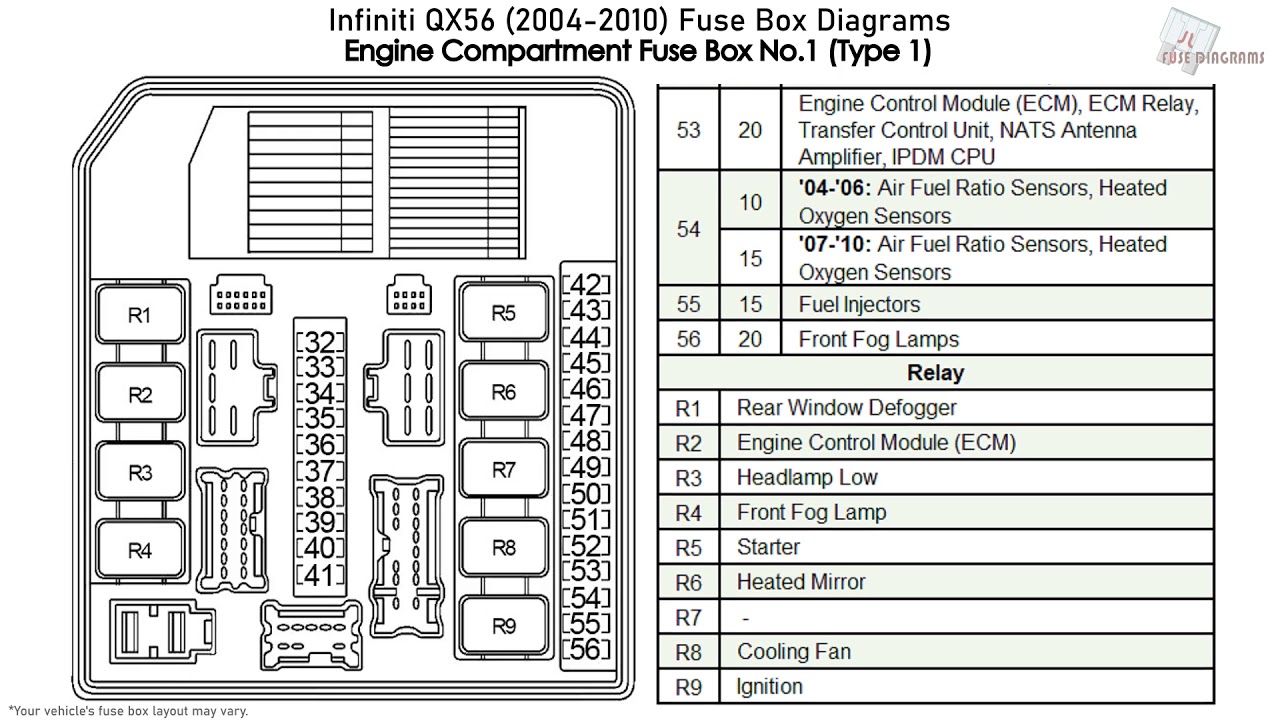
Alright folks, let's dive into the often-overlooked but absolutely critical world of the 2006 Infiniti QX56's fuse box. Understanding your vehicle's fuse box and its associated diagram is like having a roadmap to its electrical system. It's not just about replacing a blown fuse; it's about understanding how different circuits are protected, troubleshooting electrical issues effectively, and even customizing your ride with aftermarket accessories safely. This guide will provide you with a detailed look at the 2006 QX56 fuse box diagram, helping you diagnose problems and perform repairs with confidence.
Why Bother with the Fuse Box Diagram?
Why should you, an experienced DIYer, even care about a fuse box diagram? Here are a few key reasons:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Problems: When something electrical malfunctions in your QX56, the fuse box is one of the first places you should check. A blown fuse is often the culprit, and the diagram tells you exactly which fuse to inspect.
- Performing Repairs: Knowing which fuse protects which circuit is essential for repairing electrical components. If you're replacing a faulty sensor or motor, understanding the fuse layout allows you to disconnect the circuit and prevent further damage.
- Installing Aftermarket Accessories: Adding things like auxiliary lights, a new stereo, or a trailer brake controller requires tapping into the vehicle's electrical system. The fuse box diagram is invaluable for finding suitable circuits to tap into and ensuring proper fuse protection for your new accessories.
- General Vehicle Knowledge: Understanding your car's systems makes you a better car owner. Knowing the layout of the fuse box is a fundamental aspect of understanding your vehicle's electrical architecture.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the QX56 Fuse System
The 2006 Infiniti QX56 typically has two primary fuse box locations:
- Interior Fuse Box: Usually located under the dashboard on the driver's side. Access is generally gained by removing a panel or cover. This box primarily houses fuses for interior components like the audio system, power windows, interior lighting, and the climate control system.
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box: Located in the engine bay, typically near the battery. This box contains fuses and relays for critical engine components, headlights, anti-lock brakes (ABS), and other vital systems.
Key components within these fuse boxes include:
- Fuses: These are the sacrificial links in the electrical circuits. They are designed to blow (interrupt the circuit) when the current exceeds a safe level, protecting the wiring and components from damage. Fuses are rated in amperes (amps), indicating the maximum current they can handle.
- Relays: Relays are electrically operated switches that control high-current circuits using a low-current signal. They're used for components like headlights, fuel pump, and starter motor. A relay consists of a coil that creates a magnetic field when energized, which in turn closes a set of contacts, completing the circuit.
- Circuit Breakers: Some circuits may be protected by circuit breakers instead of fuses. Circuit breakers are resettable and automatically interrupt the circuit when an overload occurs. Once the overload is removed, the circuit breaker can be reset manually or automatically.
Understanding the Symbols in the Fuse Box Diagram
Fuse box diagrams aren't just a jumble of lines and numbers. They use a standardized set of symbols to represent different components and their functions. Here's a breakdown of common symbols:
- Lines: Lines represent the electrical wiring connecting the various components. Thicker lines may indicate higher current carrying capacity.
- Boxes: Boxes typically represent fuses, relays, or circuit breakers. The diagram will usually have a legend indicating which shape represents which component type.
- Numbers: Each fuse and relay is assigned a number, which corresponds to a specific location within the fuse box. This number is critical for identifying the correct fuse or relay on the diagram and in the actual fuse box.
- Amperage Rating: Next to each fuse, you'll find its amperage rating (e.g., 10A, 20A, 30A). This indicates the maximum current the fuse can handle before blowing. Always replace a blown fuse with one of the same amperage rating. Using a higher-rated fuse can damage the circuit it's protecting.
- Component Labels: The diagram will label each fuse and relay with the component or system it protects (e.g., "Headlights," "Fuel Pump," "Power Windows").
- Colors: While the diagrams are generally printed in black and white, some manufacturers use color-coding to identify different circuits or voltage levels. Refer to the diagram's legend for color-coding information.
- Icons: Standard icons represent different components, such as a lightbulb for lighting circuits, a fan for the cooling system, or a steering wheel for the power steering system.
How It Works: The Electrical Circuit Protection System
The fuse box acts as the central distribution and protection point for the vehicle's electrical system. Each electrical circuit is wired to a fuse or circuit breaker. When the current flow in a circuit exceeds the fuse's amperage rating (usually due to a short circuit or overload), the fuse's internal filament melts, breaking the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity. This prevents damage to the wiring and components connected to that circuit. This whole process is designed to prevent electrical fires.
Relays, on the other hand, are used to control high-current circuits with a low-current signal. For example, the headlight switch in the cabin only handles a small amount of current, but it activates a relay in the engine compartment that then allows a large amount of current to flow to the headlights. This design protects the headlight switch from overheating and failing.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's how you can use the fuse box diagram to troubleshoot common electrical problems:
- Identify the Symptom: What's not working? Is it a light, a power window, or something else?
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse box diagram (remember we have a downloadable one for you!). Find the fuse or relay associated with the malfunctioning component.
- Inspect the Fuse: Pull the suspected fuse from the fuse box. Visually inspect it. If the thin wire inside the fuse is broken, the fuse is blown.
- Test the Fuse (Optional): Use a multimeter to test the fuse for continuity. Set the multimeter to the continuity setting (usually indicated by a diode symbol or a sound). Place the probes on either end of the fuse. If the multimeter shows continuity (usually a beep or a reading of 0 ohms), the fuse is good. If there's no continuity, the fuse is blown.
- Replace the Fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage rating.
- Test the Component: Turn on the component that was malfunctioning. If it now works, the problem was a blown fuse. If the fuse blows again immediately, there is likely a short circuit in the wiring or the component itself. This requires further investigation.
Safety First! Highlighting Risky Components
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Keep these safety precautions in mind:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the negative (-) terminal of the battery. This prevents accidental shorts and electrical shocks.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools designed for electrical work.
- Never Bypass a Fuse: Never replace a fuse with a wire or any other conductive material. This bypasses the circuit protection and can lead to a fire.
- Handle Relays Carefully: Relays can get hot during operation. Allow them to cool before handling them.
- Be Careful Around the Airbag System: The airbag system is electrically triggered and can be dangerous if mishandled. If you're working near the airbag system, consult a qualified technician.
- High Current Components: Be extremely careful when working on the main power feeds and circuits connected to the alternator and starter. These circuits carry high current, and short circuits can cause severe burns and damage to the vehicle.
Remember, if you're uncomfortable working on the electrical system, it's always best to consult a qualified mechanic. Electrical issues can be complex and dangerous if not handled correctly.
You've now got a solid foundation for understanding the 2006 Infiniti QX56's fuse box diagram. This knowledge will be invaluable for troubleshooting electrical problems and performing repairs on your own.
We have the complete 2006 Infiniti QX56 fuse box diagram available for download. This detailed diagram will provide you with all the information you need to confidently tackle electrical repairs and modifications. Just [link to download the diagram]. Happy wrenching!
