2006 Toyota Sequoia Fuse Box Diagram
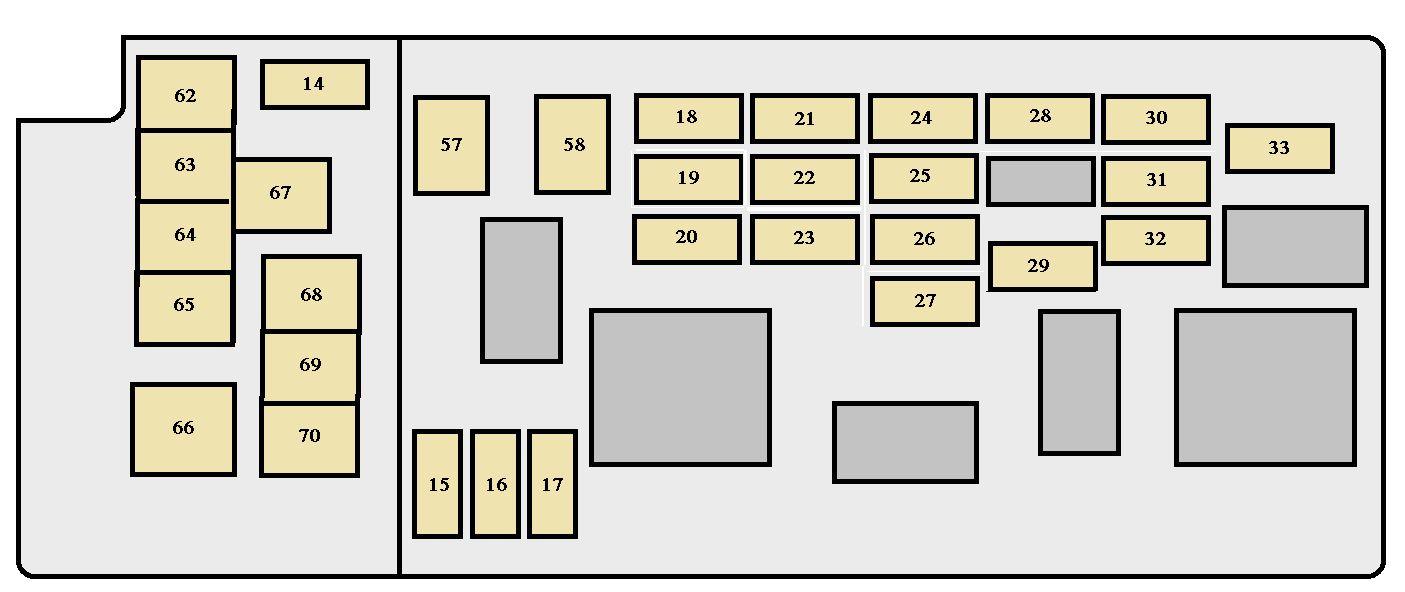
The 2006 Toyota Sequoia is a robust SUV, and understanding its electrical system is crucial for maintenance, repairs, and modifications. At the heart of that system lies the fuse box, and having its diagram at your fingertips can save you a significant amount of time and money. This article will dissect the 2006 Sequoia's fuse box diagram, giving you the knowledge to confidently troubleshoot electrical issues.
Purpose of the Fuse Box Diagram
Why bother with a fuse box diagram? Simple. It's your roadmap to the electrical system. The diagram serves several crucial purposes:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Problems: When a circuit fails, the fuse box is the first place to check. The diagram identifies which fuse protects which circuit, allowing you to quickly pinpoint the problem.
- Preventing Further Damage: Replacing a blown fuse with one of the correct amperage is essential. Using a fuse with a higher amperage than specified can overload the circuit and cause significant damage, potentially leading to a fire. The diagram specifies the correct amperage for each fuse.
- Performing Electrical Modifications: Adding aftermarket accessories like lights, amplifiers, or alarms requires tapping into the vehicle's electrical system. The diagram helps you identify safe and appropriate circuits to use, and to ensure you install additional fuses where needed to protect those circuits.
- General Electrical System Understanding: By studying the fuse box diagram, you gain a better understanding of how the various electrical components in your Sequoia are interconnected.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2006 Toyota Sequoia, depending on the trim and options package, typically has two or three fuse boxes:
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box: Located under the hood, usually near the battery. This box houses fuses and relays that protect critical engine components like the fuel pump, ignition system, and starter.
- Driver's Side Interior Fuse Box: Typically located on the driver's side, often behind a small access panel near the dashboard. This box covers interior electrical components such as the radio, power windows, and cigarette lighter (power outlet).
- (Optional) Rear Cargo Area Fuse Box: Some Sequoia models may have a fuse box in the rear cargo area to manage circuits for rear power outlets, towing equipment, and other rear-specific electrical functions.
The fuse box itself consists of several key components:
- Housing: The physical enclosure that holds the fuses and relays.
- Fuses: Overcurrent protection devices. These contain a thin wire that melts and breaks the circuit when the current exceeds a specified level, preventing damage to the protected component. Different types of fuses exist, including blade fuses (most common), cartridge fuses, and fusible links (for high-current applications).
- Relays: Electrically operated switches that allow a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit. They are commonly used to control components like headlights, horns, and air conditioning compressors.
- Terminals: Metal connectors that provide electrical contact between the fuses/relays and the vehicle's wiring harness.
- Cover: A protective cover that usually has the fuse box diagram printed on its inside.
Symbols and Interpretation
Understanding the symbols used on the fuse box diagram is paramount. Here’s a breakdown of common elements:
- Lines: Solid lines indicate direct electrical connections between components. Dashed lines might represent a ground connection or a control signal.
- Colors: Wire colors are often indicated on the diagram using abbreviations (e.g., "WHT" for white, "BLU" for blue, "RED" for red). These colors help you trace wires within the harness.
- Icons: These represent the components protected by each fuse. Common icons include:
- Light Bulb: Headlights, taillights, interior lights
- Steering Wheel: Power steering
- Engine: Engine control unit (ECU)
- Radio: Audio system
- Window: Power windows
- Fan: Cooling fan, blower motor
- Cigarette Lighter/Power Outlet: Accessory power
- Amperage Rating: This is typically indicated by a number followed by "A" (e.g., "15A" for 15 amps). The amperage rating indicates the maximum current the fuse can handle before blowing.
Important Note: Toyota may have made minor changes to the fuse box configuration during the 2006 model year. Always refer to the specific diagram found on the inside of your vehicle's fuse box cover for the most accurate information. Discrepancies can exist, and using the wrong diagram could lead to misdiagnosis and potential damage.
How It Works
The fuse box serves as a central distribution point for electrical power throughout the vehicle. The battery provides the main power source, and the wiring harness carries this power to the fuse box. Each circuit is protected by a fuse or relay. When a component draws excessive current (due to a short circuit or malfunction), the fuse blows, interrupting the flow of electricity and preventing damage to the component and the wiring harness.
Relays act as remotely controlled switches. The ECU (Engine Control Unit) or other control modules can send a low-current signal to a relay, which then closes a high-current circuit to power a specific component. This is useful for controlling high-power devices like headlights or starters, where a smaller, more easily controlled signal is desirable.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's how you can use the fuse box diagram for troubleshooting:
- Identify the Problem: Determine which electrical component is not working.
- Locate the Correct Fuse Box: Depending on the component, determine whether it’s protected by a fuse in the engine compartment fuse box, the interior fuse box, or the rear cargo area fuse box (if equipped).
- Consult the Diagram: Find the icon or description on the fuse box diagram that corresponds to the non-working component.
- Check the Fuse: Remove the fuse using a fuse puller (often located inside the fuse box cover). Inspect the fuse. If the small wire inside the fuse is broken or blackened, the fuse is blown.
- Replace the Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the exact same amperage rating. Never use a fuse with a higher amperage rating, as this can damage the circuit.
- Test the Component: After replacing the fuse, test the component to see if it now works. If the fuse blows again immediately, there is likely a short circuit in the wiring or the component itself. Further diagnosis is needed.
Safety Precautions
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Here are some safety precautions to keep in mind:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical component, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent accidental short circuits.
- Use the Correct Tools: Use insulated tools to prevent electric shock.
- Never Replace a Fuse with a Higher Amperage Fuse: Doing so can overload the circuit and cause a fire.
- Avoid Working in Wet Conditions: Water can conduct electricity and create a shock hazard.
- High-Current Components: Be particularly cautious when working with high-current components like the starter motor, alternator, and battery. These components can deliver a large amount of current, which can cause serious burns or even death.
- Seek Professional Help: If you are not comfortable working with electrical systems, seek the assistance of a qualified mechanic.
We have a downloadable PDF file containing the 2006 Toyota Sequoia fuse box diagram. This comprehensive document includes detailed diagrams for all three fuse box locations, along with fuse descriptions, amperage ratings, and component locations. Having this resource readily available will greatly simplify your troubleshooting and repair efforts.
