2007 Hyundai Santa Fe 2.7 Serpentine Belt Diagram
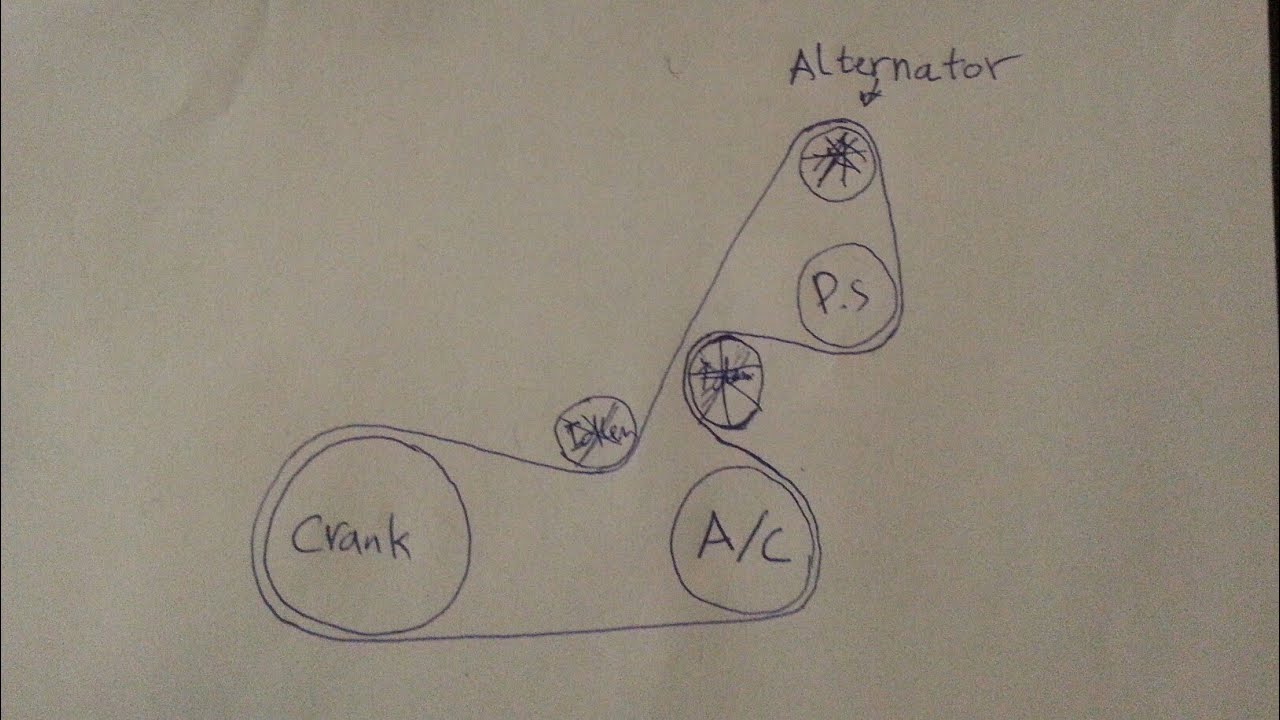
The serpentine belt in your 2007 Hyundai Santa Fe with the 2.7L engine is a critical component responsible for powering several essential accessories. Understanding its routing and proper maintenance is paramount for preventing breakdowns and ensuring the reliable operation of your vehicle. This article will provide a comprehensive guide to the serpentine belt diagram, its function, troubleshooting tips, and safety considerations.
Purpose of the Serpentine Belt Diagram
The serpentine belt diagram is an invaluable tool for several reasons:
- Repair and Replacement: If your serpentine belt breaks or needs replacement, the diagram shows the exact path the new belt must follow around all the pulleys. Incorrect routing can cause belt slippage, damage to components, and ultimately, vehicle failure.
- Troubleshooting: A squealing or slipping belt can indicate a problem with one of the driven accessories. The diagram helps you identify which accessory might be causing the issue, allowing for targeted diagnostics.
- Maintenance: Familiarizing yourself with the belt's routing allows for easier visual inspection for wear, cracks, or damage. Early detection of these issues can prevent a costly roadside breakdown.
- Learning: Understanding the serpentine belt system provides a deeper knowledge of how your engine operates and how various accessories are driven.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2007 Hyundai Santa Fe 2.7L engine uses a single serpentine belt to drive the following accessories:
- Crankshaft Pulley: The crankshaft pulley, driven directly by the engine, provides the rotational power to the serpentine belt.
- Alternator: The alternator generates electrical power to charge the battery and run the vehicle's electrical systems.
- Power Steering Pump: The power steering pump provides hydraulic pressure to assist with steering.
- Air Conditioning Compressor: The A/C compressor circulates refrigerant in the air conditioning system.
- Idler Pulley(s): Idler pulleys are smooth pulleys that guide the belt and maintain proper tension. They do not drive any accessories.
- Tensioner Pulley: The tensioner pulley applies the necessary tension to the serpentine belt. It's typically spring-loaded or hydraulic and is crucial for preventing slippage. Understanding the operation of the tensioner is essential for proper belt installation.
The specific belt length and dimensions are crucial for proper operation. Refer to your owner's manual or a reputable parts supplier for the correct belt specification for your 2007 Santa Fe 2.7L.
Symbols and Conventions of the Diagram
Serpentine belt diagrams generally use standardized symbols and conventions to convey information clearly. Here's a breakdown:
- Solid Lines: Represent the path of the serpentine belt itself. The thickness of the line may sometimes indicate the relative width of the belt.
- Circles: Represent pulleys. Larger circles generally indicate larger diameter pulleys, while smaller circles represent smaller pulleys or idlers.
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of rotation of each pulley. Pay close attention to the arrow directions, as incorrect belt routing will reverse the direction of certain accessories, potentially causing damage.
- Labels: Each pulley is typically labeled with an abbreviation indicating the accessory it drives (e.g., ALT for Alternator, P/S for Power Steering, A/C for Air Conditioning).
- Tensioner Symbol: The tensioner pulley is often represented with a special symbol indicating its spring-loaded or hydraulic nature. This symbol might include a spring or a small arrow indicating the direction of tension.
- Colors: While not always present, some diagrams may use different colors to highlight specific sections of the belt path or to differentiate between smooth and grooved pulley surfaces. Grooved pulleys are the driving pulleys that the belt needs to grip to turn.
Typical Diagram Example: The diagram will depict the crankshaft pulley at the "bottom" as it's the primary drive, with the belt weaving up and around the other accessories. The tensioner will be strategically placed to provide optimal belt tension.
How It Works
The serpentine belt system operates on the principle of transmitting rotational force from the engine's crankshaft to various accessories. The crankshaft pulley, connected directly to the engine's rotating assembly, drives the serpentine belt. As the crankshaft pulley rotates, it pulls the belt around the other pulleys connected to the alternator, power steering pump, A/C compressor, and idler pulleys. The tensioner pulley maintains the proper tension on the belt, ensuring sufficient grip and preventing slippage. The direction of rotation of each accessory is determined by the routing of the belt around its respective pulley. If the belt isn't tight enough it will slip, if it is too tight it can damage the bearings in the driven accessories.
Real-World Use – Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some common issues and troubleshooting tips related to the serpentine belt:
- Squealing Noise: A squealing noise, especially when the engine is first started or under load, often indicates a loose or worn serpentine belt. Check the belt tension and inspect the belt for cracks, glazing, or missing ribs.
- Slipping: Slipping can cause a loss of power to the accessories. This can manifest as dim headlights, a hard-to-turn steering wheel, or poor A/C performance. Look for signs of oil or coolant contamination on the belt, which can reduce its grip.
- Belt Cracks: Cracks are a sign of aging and impending failure. Replace the belt immediately if you see significant cracking.
- Belt Fraying: Fraying along the edges of the belt can indicate misalignment of the pulleys or damage to the belt's edges. Check the pulley alignment and replace the belt.
- Accessory Failure: If an accessory like the alternator or power steering pump seizes, it can cause the serpentine belt to break. Diagnose and repair the failed accessory before replacing the belt.
- Tensioner Problems: A faulty tensioner can cause belt slippage or excessive wear. Check the tensioner for smooth operation and proper tension. If the tensioner is bouncing excessively, or is making noises it should be replaced.
Troubleshooting Tip: Use a belt dressing *sparingly* as a temporary fix for a squealing belt. However, excessive use of belt dressing can attract dirt and debris, accelerating belt wear. The best solution is to address the underlying cause of the squealing.
Safety Considerations
Working on the serpentine belt system involves several safety risks:
- Moving Parts: The engine must be off and the key removed before working on the serpentine belt. Never attempt to work on the belt while the engine is running.
- Hot Surfaces: The engine and exhaust components can be very hot. Allow the engine to cool down completely before working on the belt.
- Battery Disconnection: While not always necessary, disconnecting the negative battery terminal can prevent accidental starting of the engine while you are working on the belt.
- Spring-Loaded Tensioner: The tensioner pulley is often spring-loaded and can snap back forcefully if not handled carefully. Use the correct tools and techniques to relieve the tension safely. Incorrectly releasing the tensioner can lead to injury.
- Tools: Use appropriate tools for the job. Avoid using makeshift tools, as they can damage components or cause injury. Use the correct size wrench or socket to avoid rounding off bolts.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris.
The serpentine belt system, while seemingly simple, is a critical component for the functionality of your 2007 Hyundai Santa Fe 2.7L engine. By understanding the diagram, its components, and potential problems, you can ensure the reliable operation of your vehicle and prevent costly breakdowns.
We have the serpentine belt diagram available for download. This diagram will provide you with a visual representation of the belt routing for your specific vehicle. Feel free to access and download this resource for your convenience.
