2007 Hyundai Sonata Fuse Box Diagram
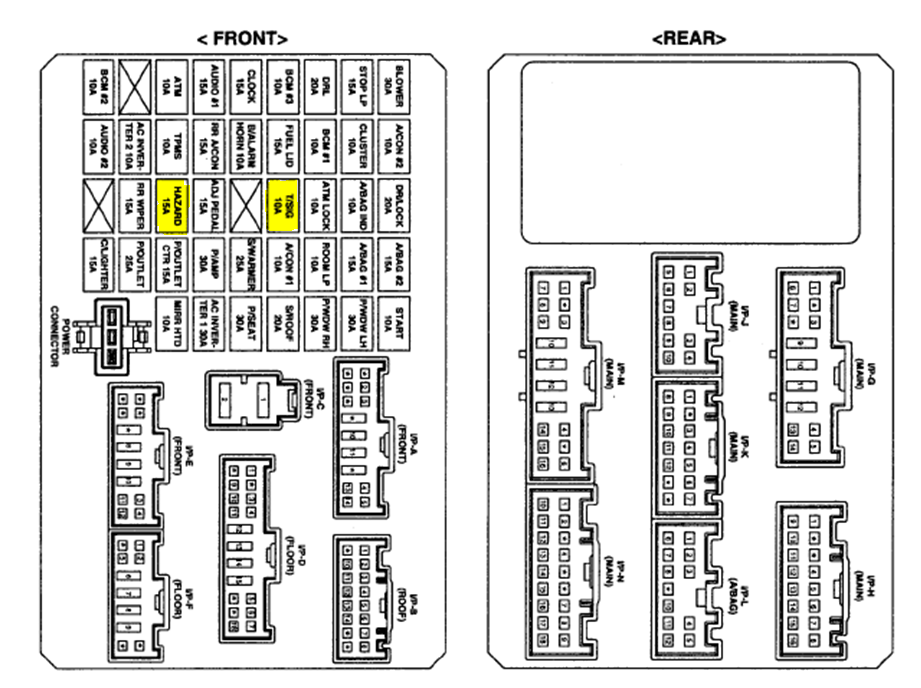
The 2007 Hyundai Sonata, a reliable and popular mid-size sedan, relies on a complex electrical system. At the heart of that system are the fuse boxes. Understanding the fuse box diagram is crucial for anyone performing DIY repairs, troubleshooting electrical issues, or even just wanting to understand how their car works. This article provides a detailed explanation of the 2007 Hyundai Sonata fuse box diagram, covering its purpose, key components, symbols, operation, and safety considerations.
Why Bother with a Fuse Box Diagram?
The fuse box diagram is your roadmap to your Sonata's electrical system. It's not just a pretty picture; it's an invaluable tool for:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Problems: When a circuit fails, the fuse box diagram helps you quickly identify the corresponding fuse.
- Performing Repairs: Knowing which fuse protects which component prevents accidental damage during repairs.
- Installing Aftermarket Accessories: If you're adding accessories like a new stereo or lights, the diagram helps you find a suitable power source and install a fuse to protect the new circuit.
- Understanding Your Car: Studying the diagram deepens your understanding of how your Sonata's electrical system is organized and protected.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2007 Sonata typically has two main fuse boxes:
- The Interior Fuse Box: Located inside the cabin, often under the dashboard on the driver's side. This box houses fuses for interior components like the radio, lights, power windows, and climate control.
- The Engine Compartment Fuse Box: Located in the engine bay, usually near the battery. This box contains fuses for engine-related components like the fuel pump, ignition system, and cooling fan. It may also contain relays.
Each fuse box contains a collection of fuses and sometimes relays. Fuses are sacrificial devices, designed to blow and break the circuit when excessive current flows through them, protecting more expensive components. Relays are electrically operated switches that allow a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit. This is common for components that draw a lot of power, like headlights or the starter motor.
Fuse Types: The 2007 Sonata typically uses blade-type fuses, also known as spade fuses. These fuses are small, color-coded, and easy to replace. Common fuse amperage ratings include 5A, 7.5A, 10A, 15A, 20A, 25A, 30A, and 40A. The color of the fuse corresponds to its amperage rating, making it easier to identify the correct replacement.
Decoding the Symbols
The fuse box diagram uses various symbols to represent different components and circuits. Understanding these symbols is crucial for interpreting the diagram correctly.
- Lines: Lines represent electrical wires or conductors. A solid line typically indicates a direct connection, while a dashed line may indicate a less common connection or a connection through a switch.
- Colors: Wire colors are often indicated next to the lines. Knowing the wire color can help you trace a circuit physically in the car. Common colors include red (power), black (ground), and various other colors for different signals.
- Icons: Icons represent specific components, such as:
- Fuse Symbol: A small, squiggly line inside a rectangle.
- Relay Symbol: A coil with a switch symbol next to it.
- Lamp Symbol: A circle with an "X" inside.
- Motor Symbol: A circle with an "M" inside.
The diagram will also have labels that describe what each fuse protects. These labels may be abbreviated (e.g., "RAD" for radio, "HTR" for heater). Consult your owner's manual for a complete list of abbreviations.
How It Works: A Simplified View
Think of the electrical system as a network of pathways. Power flows from the battery, through wires, to various components. Each pathway is protected by a fuse. If too much current tries to flow through a pathway (due to a short circuit or an overloaded circuit), the fuse blows, breaking the circuit and preventing damage to the components. The relay acts like a gatekeeper in some of these pathways. The relay allows the flow of current to high-draw items when a signal is sent from a control unit or switch.
For example, if your radio stops working, the first step is to check the fuse labeled "Radio" (or its abbreviation) in the interior fuse box. If the fuse is blown (the thin wire inside is broken), replacing it with a fuse of the same amperage rating should restore power to the radio. If the fuse blows again immediately, it indicates a problem in the radio circuit, such as a short circuit.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting
Here's a basic troubleshooting scenario using the fuse box diagram:
- Problem: Your headlights are not working.
- Step 1: Consult the fuse box diagram (both interior and engine compartment). Locate the fuses labeled "Headlights" or "Headlamp." There might be separate fuses for the left and right headlights, and potentially separate fuses for high and low beams.
- Step 2: Visually inspect the fuses. A blown fuse will have a broken filament inside. You can also use a multimeter to check continuity (a good fuse will have continuity, a blown fuse will not).
- Step 3: If a fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the exact same amperage rating. Never use a fuse with a higher amperage rating, as this can damage the wiring and components.
- Step 4: If the headlights still don't work after replacing the fuse, or if the new fuse blows immediately, the problem is likely not the fuse itself. There may be a problem with the headlight switch, the wiring, or the headlights themselves. Further diagnosis is needed.
Important Note: Before replacing any fuses, turn off the ignition and all electrical accessories. This will prevent accidental short circuits during the fuse replacement process.
Safety First: Respect the Electrical System
Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous if you're not careful. Here are some safety precautions to keep in mind:
- Disconnect the Battery: Whenever working on the electrical system, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent accidental short circuits.
- Use the Right Tools: Use insulated tools designed for automotive electrical work.
- Never Use a Higher Amp Fuse: Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating than specified can overload the circuit and cause a fire.
- Be Careful Around High-Current Components: Be especially careful around components that handle high currents, such as the starter motor, alternator, and main power feeds. These components can deliver a powerful electrical shock. These are considered very risky.
- Don't Work in Wet Conditions: Avoid working on the electrical system in wet or damp conditions. Water conducts electricity and increases the risk of electric shock.
Warning: The SRS (Supplemental Restraint System, or airbags) is a highly sensitive and potentially dangerous system. Never attempt to diagnose or repair the SRS system yourself unless you have the proper training and equipment. Accidental deployment of an airbag can cause serious injury.
Conclusion
Understanding the 2007 Hyundai Sonata fuse box diagram is a valuable skill for any car owner. It allows you to troubleshoot electrical problems, perform repairs, and gain a deeper understanding of your car's electrical system. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult a qualified mechanic if you're unsure about any procedure.
We have the 2007 Hyundai Sonata Fuse Box Diagram available for download. This will provide you with a high-resolution version that you can print out or view on your computer for easier reference during your troubleshooting and repair projects.
