2007 Nissan Altima Fuse Box Diagram
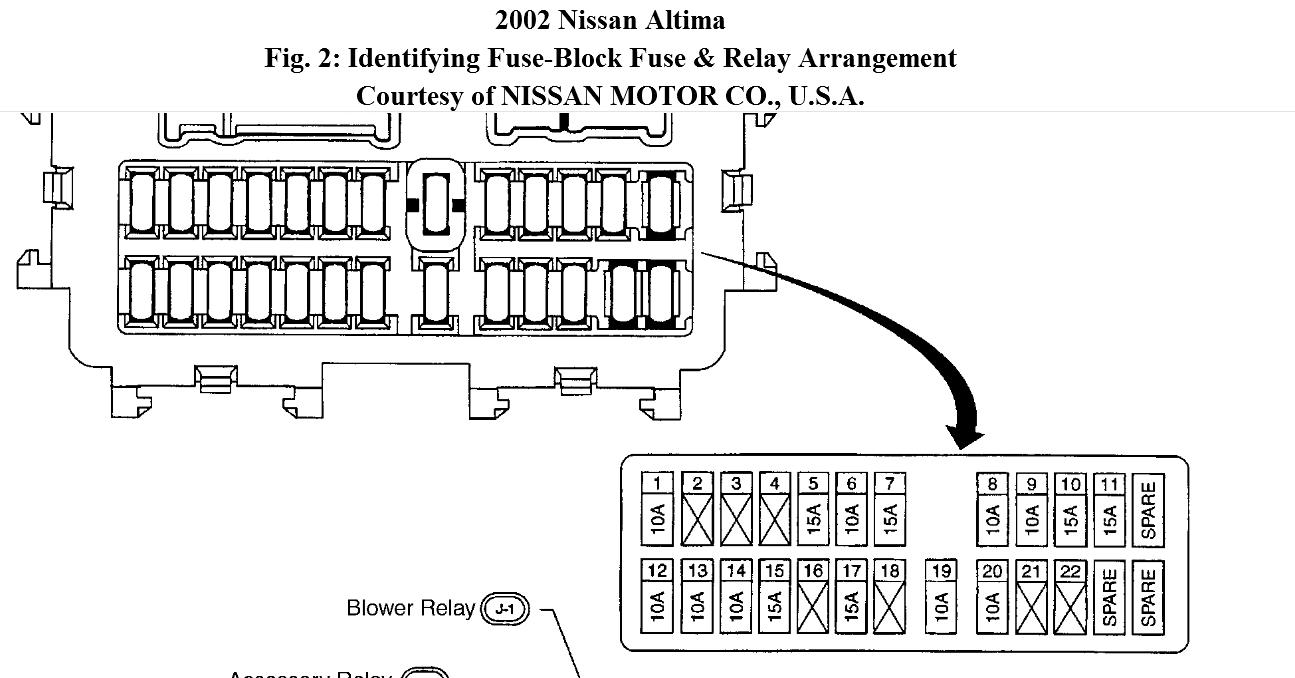
Alright, let's dive into the 2007 Nissan Altima fuse box diagram. Understanding this diagram is crucial for anyone who wants to perform even basic electrical troubleshooting or modifications on their Altima. It's your roadmap to the car's electrical system, and with a little knowledge, you can diagnose problems, replace faulty fuses, and even tap into circuits for aftermarket accessories.
Purpose of the Fuse Box Diagram
Why bother with a fuse box diagram? Several reasons:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Problems: When something electrical stops working – headlights, radio, power windows – the first thing you should check is the fuses. The diagram tells you which fuse protects which circuit.
- Replacing Blown Fuses: Identifying the correct replacement fuse is vital. Using the wrong amperage can damage components or even cause a fire.
- Adding Aftermarket Accessories: Want to install a new stereo, alarm system, or auxiliary lights? You'll need to identify a suitable power source. The diagram helps you find the correct fuse to tap into.
- Understanding Your Car's Electrical System: Even if you don't plan on doing any work yourself, understanding the basics of the fuse system gives you a better grasp of how your car functions.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2007 Nissan Altima actually has multiple fuse boxes, but we'll focus on the two most common ones:
- Interior Fuse Box: Located, generally, under the dashboard on the driver's side. This box primarily controls interior components like the radio, lights, power windows, and other comfort features. This is likely the one you'll interact with the most.
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box: Found under the hood, usually near the battery. This box protects critical engine components, such as the fuel pump, ignition system, cooling fan, and the ECU (Engine Control Unit) itself.
Key Specs to Consider:
- Fuse Ampere Rating (Amps): This is the *maximum* current a fuse can handle before blowing. It's crucial to use the correct amperage replacement. Fuses are commonly available in ratings like 5A, 7.5A, 10A, 15A, 20A, 25A, and 30A.
- Fuse Type: The 2007 Altima generally uses standard blade-type fuses, also known as ATO or APR fuses. Mini-blade fuses might also be present in some circuits.
- Circuit Number/Name: Each fuse is assigned a number and a name (e.g., "Room Lamp," "Fuel Pump Relay"). The diagram uses these identifiers.
Symbols – Decoding the Diagram
Fuse box diagrams aren't always the most intuitive things to read, but understanding the basic symbols will make things much easier. The important symbols are as follows:
- Fuse Representation: A fuse is generally represented by a rectangular box with a number inside (the amperage rating). Sometimes it might be depicted as a wavy line inside a box.
- Relays: Relays are represented by a square or rectangular shape with internal symbols (often a coil). Relays are *electromagnetic switches* that allow a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit. For example, the headlight relay allows the headlight switch to control the high current needed for the headlights without damaging the switch.
- Wiring Lines: Solid lines represent the electrical wires connecting the fuses to the components. Dashed lines might indicate ground connections or shielding.
- Ground Symbol: The ground symbol looks like an upside-down Christmas tree, indicating the circuit's connection to the vehicle's chassis (ground).
- Component Names/Abbreviations: The diagram will use abbreviations for various components, like "ECU" (Engine Control Unit), "ABS" (Anti-lock Braking System), "A/C" (Air Conditioning), etc.
- Color Coding: Some diagrams *might* use color coding for different circuits, but this isn't always standard. If present, a legend will explain the color scheme.
How It Works: A Simplified Electrical Circuit
To understand the fuse box, you need to grasp the basic concept of an electrical circuit. Electricity flows from the battery (positive terminal) through a wire to the component (e.g., a light bulb). From the component, the electricity flows back to the battery (negative terminal or ground), completing the circuit. The fuse is placed *in line* with this circuit. If the current exceeds the fuse's amperage rating (due to a short circuit or overload), the fuse's internal filament melts, breaking the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity. This protects the component and wiring from damage.
Think of it like this: the fuse is a weak link in the chain. If the chain experiences too much stress, the weak link breaks, preventing the entire chain from snapping.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's how you can use the fuse box diagram for troubleshooting:
- Identify the Problem: Determine which electrical component isn't working (e.g., the cigarette lighter).
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse box diagram (often found in the owner's manual or online). Find the fuse that corresponds to the problematic component (e.g., "Cigar Lighter").
- Inspect the Fuse: Remove the fuse using a fuse puller (a small plastic tool designed for this purpose). Visually inspect the fuse. If the thin wire inside the fuse is broken or melted, the fuse is blown.
- Test the Fuse: Even if the fuse looks OK, it's always a good idea to test it with a multimeter set to continuity mode. If the multimeter shows no continuity (no beep or reading), the fuse is bad.
- Replace the Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the *exact* same amperage rating. Do not use a fuse with a higher amperage rating, as this can cause damage or a fire.
- Test the Component: After replacing the fuse, test the component to see if it's working again.
- If the Fuse Blows Again: If the new fuse blows immediately, there's a short circuit in the wiring or the component itself. This requires further diagnosis, possibly by a professional.
Safety Considerations
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous, so take the following precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery. This will prevent accidental short circuits.
- Use the Correct Fuse: Always use a fuse with the correct amperage rating. Using a higher amperage fuse can overload the circuit and cause a fire.
- Avoid Wet Conditions: Never work on electrical systems in wet conditions.
- High-Current Circuits: Be especially careful around high-current circuits, such as the starter motor and alternator. These circuits can deliver a powerful shock.
- ECU and Airbag Circuits: The ECU (Engine Control Unit) and airbag circuits are sensitive and complex. If you're not comfortable working on these systems, it's best to leave them to a professional. *Accidental activation of the airbag can cause serious injury.*
Risk Areas: The fuel pump circuit, ignition coil circuits, and anything related to the ECU can be particularly sensitive and potentially dangerous to tamper with if you're not careful and knowledgeable.
We have the complete 2007 Nissan Altima fuse box diagram available for download. This detailed diagram will provide you with the precise location and function of each fuse in both the interior and engine compartment fuse boxes. Having this diagram handy will save you time and frustration when troubleshooting electrical issues or adding aftermarket accessories to your Altima. Contact us for the download link!
