2007 Nissan Titan Fuse Box Diagram
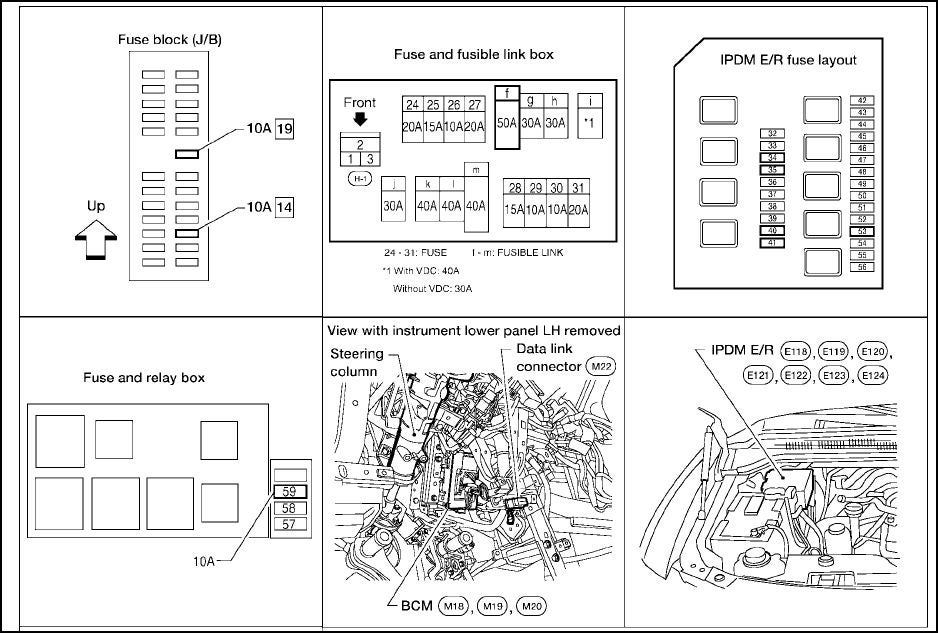
Alright, let's dive into the fuse box diagram for your 2007 Nissan Titan. This isn't just a piece of paper; it's a roadmap to your truck's electrical system. Whether you're troubleshooting a blown fuse, installing aftermarket accessories, or just trying to understand how your Titan ticks, knowing your way around the fuse boxes is crucial. We'll break down everything you need to know, from the basic layout to practical troubleshooting tips.
Purpose of the Fuse Box Diagram
Why bother with a fuse box diagram? Several reasons. Firstly, it's essential for diagnosing electrical problems. When a component like your radio, headlights, or power windows stops working, the fuse is often the first suspect. The diagram tells you exactly which fuse to check. Secondly, if you're adding aftermarket accessories like a new stereo or auxiliary lights, you need to identify suitable circuits to tap into. The diagram helps you do this safely and correctly. Finally, simply understanding the electrical architecture of your vehicle can empower you to perform basic maintenance and repairs yourself, saving you money and time.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2007 Nissan Titan actually has two primary fuse boxes: the Interior Fuse Box and the Engine Compartment Fuse Box. The Interior Fuse Box is typically located inside the cabin, usually under the dashboard on the driver's side. The Engine Compartment Fuse Box is, as the name suggests, under the hood, often near the battery or firewall.
- Interior Fuse Box: This box generally handles circuits related to interior components like the instrument panel, radio, power windows, power locks, and interior lighting.
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box: This box controls circuits related to engine management, headlights, brake lights, horn, windshield wipers, and other critical systems.
Each fuse box contains an array of fuses and relays. Fuses are designed to protect individual circuits from overcurrent, while relays act as electrically controlled switches, allowing a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit.
Common fuse ratings for the 2007 Titan range from 5 amps to 30 amps, and occasionally higher for specific circuits. Relays are typically identified by their function and amperage rating.
Understanding Fuse Box Symbols
Fuse box diagrams use a standardized set of symbols and notations. Let's break down the key elements:
- Lines: Solid lines represent direct electrical connections between components. Dotted lines may indicate ground connections or shielded wiring.
- Colors: While the diagram itself might not be in color, referencing the wiring harness diagrams in conjunction with the fuse box diagram will show the wire colors, which can be crucial for tracing circuits. Common colors include red (typically power), black (ground), and a variety of colors for signal and control wires.
- Icons: Each fuse and relay is usually labeled with a specific icon or abbreviation. These icons represent the component the fuse protects or the function the relay controls. For example:
- A headlight symbol indicates the headlight circuit fuse.
- A radio symbol represents the radio fuse.
- "IGN" often stands for ignition.
- "ECU" refers to the Engine Control Unit.
- Amperage Ratings: The amperage rating of each fuse is clearly marked on the diagram (e.g., 10A, 15A, 20A). Always replace a blown fuse with one of the same amperage rating. Using a fuse with a higher rating can bypass the circuit protection and potentially cause a fire.
How It Works: Circuit Protection
The fuse box is the heart of your Titan's electrical protection system. Each fuse is a sacrificial element designed to break the circuit if the current exceeds its rated amperage. This prevents damage to expensive components and reduces the risk of fire.
Here’s the process:
- Normal Operation: Current flows through the circuit, powering the intended component.
- Overcurrent: If a short circuit or overload occurs, the current in the circuit increases dramatically.
- Fuse Blows: The thin filament inside the fuse heats up rapidly and melts, breaking the circuit.
- Protection: The blown fuse prevents further current flow, protecting the wiring and the connected component.
Relays, on the other hand, act as remote-controlled switches. The relay coil is energized by a low-current signal, which closes the relay contacts and allows a high-current circuit to be completed. This is used to control high-power devices like headlights or starter motors without requiring a large switch on the dashboard.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting
Let's say your radio suddenly stops working. Here's how to use the fuse box diagram to troubleshoot the problem:
- Locate the Diagram: Find the fuse box diagram for your 2007 Nissan Titan. They are often located in the owner's manual, or you can find digital copies online.
- Identify the Radio Fuse: Consult the diagram and locate the fuse labeled for the radio (it might be labeled "RADIO," "AUDIO," or similar). Note its location and amperage rating.
- Inspect the Fuse: Open the fuse box and visually inspect the radio fuse. Look for a broken filament. If the filament is intact, the fuse is likely good.
- Test the Fuse: Even if the fuse looks good, it's best to test it with a multimeter. Set the multimeter to continuity mode (often indicated by a sound wave symbol). Touch the multimeter probes to the two terminals on the fuse. If the multimeter beeps or shows a low resistance reading, the fuse is good. If there's no beep or a high resistance reading, the fuse is blown.
- Replace the Fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the exact same amperage rating.
- Test the Circuit: Turn on the radio to see if it works. If the radio still doesn't work, or if the new fuse blows immediately, there's likely a short circuit or other problem in the radio circuit that needs further investigation.
Safety Considerations
Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous. Always observe the following safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the negative (-) terminal of the battery. This prevents accidental short circuits and potential shocks.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools to avoid short circuits and electrical shocks.
- Never Bypass a Fuse: Never use a wire or other conductive material to bypass a blown fuse. This can overload the circuit and cause a fire.
- Identify High-Current Components: Be especially cautious when working around high-current components like the starter motor, alternator, and battery. These components can deliver a significant electrical shock.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: If you're working on fuel-related electrical systems (e.g., fuel pump), work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling fumes.
Especially Risky Components: The ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) and airbag systems are sensitive and potentially dangerous. If you're not comfortable working on these systems, it's best to consult a qualified technician. Improper handling of airbag components can lead to accidental deployment, causing serious injury.
Remember, electrical problems can be complex. If you're not comfortable troubleshooting the issue yourself, it's always best to seek the help of a qualified mechanic. Messing with the electrical system without proper knowledge can lead to further damage or even safety hazards.
We have the complete fuse box diagram available for download. You can find it [link to downloadable file - insert hypothetical link here]. This detailed diagram will provide you with all the information you need to navigate the electrical system of your 2007 Nissan Titan.
